
Automotive safety is the study and practice of automotive design, construction, equipment and regulation to minimize the occurrence and consequences of traffic collisions involving motor vehicles. Road traffic safety more broadly includes roadway design.
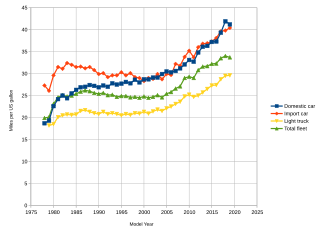
Corporate average fuel economy (CAFE) standards are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the United States Congress in 1975, after the 1973–74 Arab Oil Embargo, to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks produced for sale in the United States. More recently, efficiency standards were developed and implemented for heavy-duty pickup trucks and commercial medium-duty and heavy-duty vehicles.

Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are technologies that assist drivers with the safe operation of a vehicle. Through a human-machine interface, ADAS increase car and road safety. ADAS use automated technology, such as sensors and cameras, to detect nearby obstacles or driver errors, and respond accordingly. ADAS can enable various levels of autonomous driving.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation, focused on transportation safety in the United States.

The National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act was enacted in the United States in 1966 to empower the federal government to set and administer new safety standards for motor vehicles and road traffic safety. The Act was the first mandatory federal safety standards for motor vehicles. The Act created the National Highway Safety Bureau. The Act was one of a number of initiatives by the government in response to increasing number of cars and associated fatalities and injuries on the road following a period when the number of people killed on the road had increased 6-fold and the number of vehicles was up 11-fold since 1925. The reduction of the rate of death attributable to motor-vehicle crashes in the United States represents the successful public health response to a great technologic advance of the 20th century—the motorization of the United States.

A side collision is a vehicle crash where the side of one or more vehicles is impacted. These crashes typically occur at intersections, in parking lots, and when two vehicles pass on a multi-lane roadway.

Marion Clifton Blakey is an American businesswoman and former government official who served as president and CEO of Rolls-Royce North America. Prior to joining Rolls-Royce, she served as the eighth full-time chief executive of the Aerospace Industries Association, an American defense industry trade association from 2007 to 2015. Before this, she served a five-year term as the 15th Administrator of the Federal Aviation Administration. Blakey was the second woman to hold the position, serving as a successor to Jane Garvey, the first woman to hold the Administrator title. She was the second Administrator who was not a licensed pilot. She was awarded the Wright Brothers Memorial Trophy in 2013.

Transportation safety in the United States encompasses safety of transportation in the United States, including automobile crashes, airplane crashes, rail crashes, and other mass transit incidents, although the most fatalities are generated by road incidents annually killing 32,479 people in 2011 to over 42,000 people in 2022. The number of deaths per passenger-mile on commercial airlines in the United States between 2000 and 2010 was about 0.2 deaths per 10 billion passenger-miles. For driving, the rate was 150 per 10 billion vehicle-miles: 750 times higher per mile than for flying in a commercial airplane. For a person who drives a million miles in a lifetime this amounts to a 1.5% chance of death.
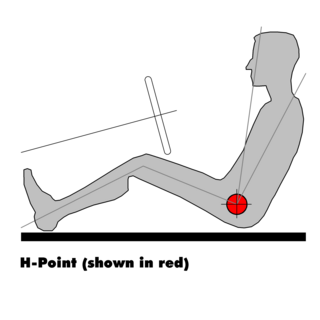
The H-point is the theoretical, relative location of an occupant's hip: specifically the pivot point between the torso and upper leg portions of the body—as used in vehicle design, automotive design and vehicle regulation as well as other disciplines including chair and furniture design.
A connected car is a car that can communicate bidirectionally with other systems outside of the car. This connectivity can be used to provide services to passengers or to support or enhance self-driving functionality. For safety-critical applications, it is anticipated that cars will also be connected using dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) or cellular radios, operating in the FCC-granted 5.9 GHz band with very low latency.

On September 16, 2011, The Galloping Ghost, a highly modified North American P-51D Mustang racing aircraft, crashed into spectators while competing at the Reno Air Races in Reno, Nevada, killing the pilot, Jimmy Leeward, and ten people on the ground. Sixty-nine more people on the ground were injured. It was the third-deadliest airshow disaster in U.S. history, following accidents in 1972 and 1951.

The Alliance for Automotive Innovation (AAI) is a Washington, D.C.-based trade association and lobby group whose members include international car and light duty truck manufacturers that build and sell products in the United States.

The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations define AEBS. UN ECE regulation 131 requires a system which can automatically detect a potential forward collision and activate the vehicle braking system to decelerate a vehicle with the purpose of avoiding or mitigating a collision. UN ECE regulation 152 says deceleration has to be at least 5 metres per second squared.
The Midland train crash was a rail crossing accident that occurred on November 15, 2012 in Midland, Texas. A freight train struck a flatbed trailer being used as a parade float carrying 26 passengers, killing four and injuring 16. The parade was en route to a veterans' benefit sponsored by the local charity Show of Support/Hunt for Heroes.

A New Car Assessment Program is a government car safety program tasked with evaluating new automobile designs for performance against various safety threats.

People who are driving as part of their work duties are an important road user category. First, workers themselves are at risk of road traffic injury. Contributing factors include fatigue and long work hours, delivery pressures, distractions from mobile phones and other devices, lack of training to operate the assigned vehicle, vehicle defects, use of prescription and non-prescription medications, medical conditions, and poor journey planning. Death, disability, or injury of a family wage earner due to road traffic injury, in addition to causing emotional pain and suffering, creates economic hardship for the injured worker and family members that may persist well beyond the event itself.

Christopher A. Hart is an American lawyer, government official, and pilot. He served as the 13th chairman of the National Transportation Safety Board. He served as Acting NTSB Chairman beginning April 26, 2014, and in June 2014 was nominated by President Barack Obama to serve as Chairman of the NTSB. He was confirmed to serve as chairman on February 5, 2015. Robert Sumwalt succeeded him as chairman in August 2017.

Tesla Autopilot is an advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) developed by Tesla that amounts to partial vehicle automation. Tesla provides "Base Autopilot" on all vehicles, which includes lane centering and traffic-aware cruise control. Owners may purchase or subscribe to Full Self-Driving (FSD) which adds semi-autonomous navigation that responds to traffic lights and stop signs, lane change assistance, self-parking, and the ability to summon the car from a garage or parking spot.

Heidi R. King served as acting Administrator of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
















