Related Research Articles
The Salt River Project (SRP) encompasses two separate entities: the Salt River Project Agricultural Improvement and Power District, an agency of the state of Arizona that serves as an electrical utility for the Phoenix metropolitan area, and the Salt River Valley Water Users' Association, a utility cooperative that serves as the primary water provider for much of central Arizona. It is one of the primary public utility companies in Arizona.

Parker Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam that crosses the Colorado River 155 miles (249 km) downstream of Hoover Dam. Built between 1934 and 1938 by the Bureau of Reclamation, it is 320 feet (98 m) high, 235 feet (72 m) of which are below the riverbed (the deep excavation was necessary in order to reach the bedrock on which the foundation of the dam was built), making it the deepest dam in the world. The portion of the dam above the foundation stands 85 feet (25.9 m) tall, making it the only dam in the world that stands more underground than above ground. The dam's primary functions are to create a reservoir, and to generate hydroelectric power. The reservoir behind the dam is called Lake Havasu and can store 647,000 acre⋅ft (798,000,000 m3; 2.11×1011 US gal; 1.76×1011 imp gal). The dam straddles the Arizona-California state border at the narrows the river passes through between the Whipple Mountains in San Bernardino County, California and the Buckskin Mountains in La Paz County, Arizona.

Elephant Butte Dam or Elephant Butte Dike, originally Engle Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on the Rio Grande near Truth or Consequences, New Mexico. The dam impounds Elephant Butte Reservoir, which is used mainly for agriculture but also provides for recreation, hydroelectricity, and flood and sediment control. The construction of the dam has reduced the flow of the Rio Grande to a small stream for most of the year, with water being released only during the summer irrigation season or during times of exceptionally heavy snow melt.

The Colorado–Big Thompson Project is a federal water diversion project in Colorado designed to collect West Slope mountain water from the headwaters of the Colorado River and divert it to Colorado's Front Range and plains. In Colorado, approximately 80% of the state's precipitation falls on the West Slope, in the Rocky Mountains, while around 80% of the state's growing population lives along the eastern slope, between the cities of Fort Collins and Pueblo.

The Klamath Project is a water-management project developed by the United States Bureau of Reclamation to supply farmers with irrigation water and farmland in the Klamath Basin. The project also supplies water to the Tule Lake National Wildlife Refuge, and the Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge. The project was one of the first to be developed by the Reclamation Service, which later became the Bureau of Reclamation.
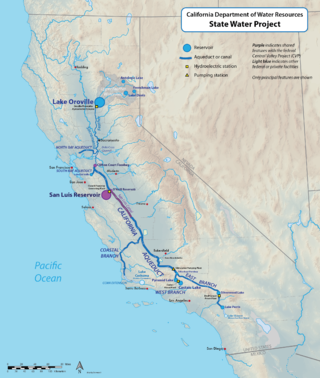
The California State Water Project, commonly known as the SWP, is a state water management project in the U.S. state of California under the supervision of the California Department of Water Resources. The SWP is one of the largest public water and power utilities in the world, providing drinking water for more than 27 million people and generating an average of 6,500 GWh of hydroelectricity annually. However, as it is the largest single consumer of power in the state itself, it has a net usage of 5,100 GWh.

Monticello Dam is a 304-foot (93 m) high concrete arch dam in Napa County, California, United States, constructed between 1953 and 1957. The dam impounded Putah Creek to create Lake Berryessa in the Vaca Mountains.

Kachess Lake is a lake and reservoir along the course of the Kachess River in Washington state, US. The upper part of the lake, north of a narrows, is called Little Kachess Lake. The Kachess River flows into the lake from the north, and out from the south. Kachess Lake is the middle of the three large lakes which straddle Interstate 90 north of the Yakima River in the Cascade Range. The other two are Cle Elum Lake, the easternmost which is also north of I-90 and Keechelus Lake, the westernmost, which is south of I-90.
The Central Utah Project is a US federal water project that was authorized for construction under the Colorado River Storage Project Act of April 11, 1956, as a participating project. In general, the Central Utah Project develops a portion of Utah's share of the yield of the Colorado River, as set out in the Colorado River Compact of 1922.

McKay Reservoir is a reservoir in Umatilla County of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is an impoundment of McKay Creek, a tributary of the Umatilla River. The reservoir is located 6 miles (9.7 km) south of Pendleton on U.S. Route 395. The reservoir has a capacity of 65,534 acre-feet (80,835,000 m3) of water. The reservoir and land that immediately surrounds it are designated as the McKay Creek National Wildlife Refuge. The reservoir and creek that it impounds are named for Dr. William C. McKay. McKay was an early settler in the Pendleton, Oregon area. He settled near the mouth of McKay Creek about 1851. The place was originally called Houtama. He died in Pendleton in 1893.

Whiskeytown Dam is an earthfill dam on Clear Creek, a tributary of the Sacramento River of northern California in the United States.

Waconda Lake, also known as Glen Elder Reservoir, is a reservoir in Mitchell County and Osborne County, Kansas, United States. Built and managed by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation for flood control and irrigation, it is also used for recreation. Glen Elder State Park is located on its north shore.

The Minidoka Project is a series of public works by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to control the flow of the Snake River in Wyoming and Idaho, supplying irrigation water to farmlands in Idaho. One of the oldest Bureau of Reclamation projects in the United States, the project involves a series of dams and canals intended to store, regulate and distribute the waters of the Snake, with electric power generation as a byproduct. The water irrigates more than a million acres (4,000 km²) of otherwise arid land, producing much of Idaho's potato crop. Other crops include alfalfa, fruit and sugar beets. The primary irrigation district lies between Ashton in eastern Idaho and Bliss in the southwestern corner of the state. Five main reservoirs collect water, distributing it through 1,600 miles (2,600 km) of canals and 4,000 miles (6,400 km) of lateral distribution ditches.

Gerber Dam is a concrete arch dam located 14 miles east of Bonanza, Oregon, and about 12 miles north of the California border, in Klamath County, Oregon.

Pactola Dam is an embankment dam on Rapid Creek in Pennington County, South Dakota, about 10 miles (16 km) west of Rapid City. The dam was completed in 1956 by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to provide flood control, water supply and recreation. Along with the nearby Deerfield Dam, it is part of the Rapid Valley Unit of the Pick-Sloan Missouri Basin Program. U.S. Route 385 runs along the crest of the dam. The dam forms Pactola Lake, which at over 1,200 acres (490 ha) is the largest and deepest body of water in the Black Hills.

Ochoco Dam is a dam in Central Oregon, 6 miles (9.7 km) east of Prineville in Crook County, Oregon, in the United States.

Agency Valley Dam is a dam in Oregon, United States, built on the North Fork Malheur River in the eastern part of the state, immediately north of the small town of Beulah in Malheur County. The dam impounds the river to create Beulah Reservoir.

Cheney Reservoir is a reservoir on the North Fork Ninnescah River in Reno, Kingman, and Sedgwick counties of Kansas in the United States. Built and managed by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation for local water supply, it is also used for flood control and recreation. Cheney State Park is located on its shore.
Deer Flat Upper Embankment is a dam in the western United States in southwestern Idaho. Located in the Treasure Valley in Canyon County, it is directly southwest of Nampa.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to infrastructure of the U.S. state of Washington.
References
- ↑ "Dam details - Mason Dam - Bureau of Reclamation". Archived from the original on 2012-09-26. Retrieved 2012-07-13.
- ↑ "Phillips Lake, Oregon".
- ↑ Harber, Terri. "Mason Dam plan moves ahead". Baker City Herald. Retrieved May 14, 2015.