The Massey Foundation was incorporated in 1918. It is responsible for the construction of many Toronto landmarks. It was the first trust of its kind in Canada.
In 1896, Hart Massey, an industrialist who built the Massey-Harris farm equipment company, died. In his will he decreed that the majority of his estate be disposed of by 1916 for the benefit of various public institutions and causes. The trustees decided to establish the Massey Foundation. The trustees were family members, including Hart's son Chester and Chester's son, Vincent. In 1918, the foundation was incorporated.
The Massey Foundation was designed to create new projects. One of the first projects supported was the Massey Memorial Organ (completed in 1907 with Massey estate funds and named for Hart Massey) which is located in Chautauqua Institution and the completion of Hart House, which was started in 1911 with Massey estate funds and also named after Hart Massey. It also funded the construction of the Hart House Theatre. In 1933, the foundation undertook the renovation of Massey Hall. In 1962, it built and endowed Massey College at the University of Toronto.
In 1950, the Massey Foundation (in collaboration with the Royal Architectural Institute of Canada) began the Massey Medals for Architecture program which ran until 1970. In 1982, the Governor General's Medals in Architecture program began in order to continue the tradition of this awards program.
In 1959, the Massey Foundation also established the Massey Medal "to recognize outstanding personal achievement in the exploration, development or description of the geography of Canada." The Medal is awarded by the Royal Canadian Geographical Society.
Raymond Hart Massey was a Canadian actor, known for his commanding, stage-trained voice. For his lead role in Abe Lincoln in Illinois (1940), Massey was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor. He reprised his role as Lincoln on television and in How the West Was Won (1962). Among his other well-known roles were Dr. Gillespie in the NBC television series Dr. Kildare (1961–1966), John Brown in Santa Fe Trail (1940) and Seven Angry Men (1955), Abraham Farlan in A Matter of Life and Death (1946), and Jonathan Brewster in Arsenic and Old Lace (1944).
Arthur Charles Erickson was a Canadian architect and urban planner. He studied at the University of British Columbia and, in 1950, received his B.Arch. (Honours) from McGill University. He is known as Canada's most influential architect and was the only Canadian architect to win the American Institute of Architects AIA Gold Medal. When told of Erickson's award, Philip Johnson said, "Arthur Erickson is by far the greatest architect in Canada, and he may be the greatest on this continent."

Charles Vincent Massey was a Canadian diplomat and statesman who served as the 18th governor general of Canada from 1952 to 1959. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada.
Denton Massey was a Canadian engineer, Anglican priest and politician.

Massey College is a postgraduate college of the University of Toronto. The college was established, built and partially endowed in 1962 by the Massey Foundation and officially opened in 1963, though women were not admitted until 1974. It was modeled around the traditional Cambridge and Oxford collegiate system and features a central court and porters lodge.

Massey Hall is a performing arts theatre in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1894, it is known for its outstanding acoustics and was the long-time hall of the Toronto Symphony Orchestra. An intimate theatre, it was originally designed to seat 3,500 patrons, but after extensive renovations in the 1940s, it now seats only up to 2,765. It has an extensive history of concerts by artists of many musical genres which continues today.

Thom Mayne is an American architect. He is based in Los Angeles. In 1972, Mayne helped found the Southern California Institute of Architecture (SCI-Arc), where he is a trustee and the coordinator of the Design of Cities postgraduate program. Since then he has held teaching positions at SCI-Arc, the California State Polytechnic University, Pomona and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). He is principal of Morphosis Architects, an architectural firm based in Culver City, California and New York City, New York. Mayne received the Pritzker Architecture Prize in March 2005.

Raymond Junichi Moriyama was a Canadian architect.

Hart House is a student activity centre at the University of Toronto. Established in 1919, it is one of the earliest North American student centres, being the location of student debates and conferences since its construction. Hart House was initiated and financed by Vincent Massey, an alumnus and benefactor of the university, and was named in honour of his grandfather, Hart Massey. The Collegiate Gothic-revival complex was the work of architect Henry Sproatt, who worked alongside decorator Alexander Scott Carter, and engineer Ernest Rolph, and subsequently designed the campanile at its southwestern corner, Soldiers' Tower. In 1957, the house hosted U.S. President John F. Kennedy.

The Massey family is a Canadian family with Methodist roots that has been prominent since the mid-19th century, known for manufacturing farm equipment and for being patrons of the arts in Canada. The family's manufacturing company, later known as Massey Ferguson, provided the Masseys with their significant fortune. Subsequent generations of Masseys have risen to prominence in the arts, philanthropy and governance. The Massey name remains visible through institutions such as Massey Hall, Massey College and the Massey Lectures.
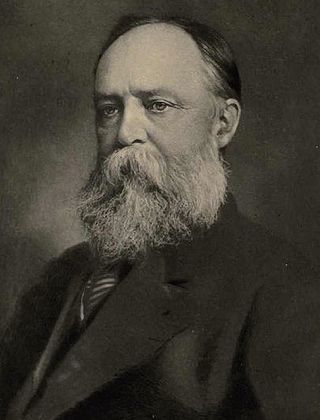
Sir Byron Edmund Walker, CVO was a Canadian banker. He was the president of the Canadian Bank of Commerce from 1907 to 1924, and a generous patron of the arts, helping to found and nurture many of Canada's cultural and educational institutions, including the University of Toronto, National Gallery of Canada, the Champlain Society, Appleby College, Art Gallery of Ontario and Royal Ontario Museum.

Hart Almerrin Massey was a Canadian businessman and philanthropist who was a member of the prominent Massey family. He was an industrialist who built the agricultural equipment firm that became Massey Ferguson, now part of AGCO.

The Royal Architectural Institute of Canada (RAIC) is a not-for-profit, national organization that has represented architects and architecture for over 100 years, in existence since 1907. The RAIC is the leading voice for excellence in the built environment in Canada, demonstrating how design enhances the quality of life, while addressing important issues of society through responsible architecture. The RAIC’s mission is to promote excellence in the built environment and to advocate for responsible architecture. The organization national office is based in Ottawa with a growing federated chapter model. Current chapters and networks are based in British Columbia, Alberta and Nova Scotia.

The University of Toronto is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada. Originally controlled by the Church of England, the university assumed its present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. As a collegiate university, it comprises 11 colleges each with substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs and significant differences in character and history. The university maintains three campuses, the oldest of which is St. George, located in downtown Toronto. The other two satellite campuses are located in Scarborough and Mississauga.

Shore Tilbe Perkins+Will, formerly Shore Tilbe Irwin & Partners (STIP), is a Canadian architecture firm based in Toronto, Ontario. Since its founding as Shore and Moffat in 1945, and later as Shore Tilbe Irwin & Partners, the firm has completed numerous buildings, complexes and master plans across Canada, as well as at locations in the United States and Bermuda. From early educational and residential projects, the firm rose to prominence in the early 1950s, winning Governor General's Medals in Architecture and commissions from the government of Ontario for departmental buildings, and it went on to design prominent landmarks such as Purdy's Wharf in Halifax, Nova Scotia, and the redesign of Nathan Phillips Square in Toronto. The firm's scope today mostly encompasses community centres, libraries, pharmaceutical laboratories, offices and university teaching buildings, although the firm has also completed religious spaces, corporate interiors and public plazas.
Barton Myers is an American architect and president of Barton Myers Associates Inc. in Santa Barbara, California. With a career spanning more than 40 years, Myers is a fellow of the American Institute of Architects and was a member of the Ontario Association of Architects while working in Canada earlier in his career.

The McCall MacBain Arts Building is a landmark building located at 853 Sherbrooke Street West in Montreal, Quebec, in the centre of McGill University's downtown campus. The Arts Building is the oldest existing building on campus, and it was designed in the Classical Revival style by John Ostell. Construction began in 1839, and the building's central block and east wing were completed in 1843. The west and north wings were finished in 1861 and 1925, respectively, after involving multiple architects, including Alexander Francis Dunlop and Harold Lea Fetherstonhaugh. Today, the Arts Building is made up of a central block and three distinct wings – Dawson Hall (east), Molson Hall (west) and Moyse Hall (north). The building currently houses the Department of French Language and Literature, the Department of English, and the Department of Art History and Communication Studies. It also hosts lectures for several other departments from the Faculty of Arts.
Marianne McKenna, OC, FRAIC, OAA, OAQ, AIA, RIBA is a Canadian architect and a founding partner of KPMB Architects, a Toronto-based practice established in 1987. She is an invested Officer of The Order of Canada "for her contributions as an architect, designing structures that enrich the public realm". Her projects include the renovation and expansion of The Royal Conservatory TELUS Centre for Performance and Learning and Koerner Hall. McKenna and KPMB were selected by The Brearley School, an independent all-girls school located in New York City, to lead the renovation of its building located on the Upper East Side. Her current projects also include for Banff Centre for Arts and Creativity in Banff, Alberta and an expansion and renovation of historic Massey Hall in Toronto In 2010 she was named one of Canada’s Top 100 Most Powerful Women and in 2014 she was named one of Toronto’s top 50 Powerful People by MacLean’s Magazine.
John Massey is a Canadian artist from Toronto, Canada. Since the 1980s, Massey's installations, sculptures, and films have established him as one of Canada's prominent contemporary artists. Massey combines conventional photography with computer manipulation. In his photograph and video projects he uses minimal effects to create works that inhabit a middle ground between the depicted and the created. His works are widely exhibited and are in many private and public collections, including the Art Gallery of Ontario, the Stedelijk Museum in Amsterdam, the Fonds National dâ Art Contemporain, Paris, and the Ydessa Hendeles Art Foundation. In 2006, Massey's work was included in the exhibition "Beyond Cinema: The Art of Projection" at the Hamburger Bahnhof in Berlin. In 2014, his works were included in the Montreal Biennale. He was awarded the Gershon Iskowitz Award for lifetime achievement in 2001.

Henry Sears was a Canadian modernist architect, and an urban and gallery planner. He was a founding partner of both Klein & Sears Architects and Sears & Russell Architects Ltd. His work centred around social housing development on a neighbourhood scale. It spanned Canada, the United States and Europe.