Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.

In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. Neoclassical economics, currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, usually models the firm as maximizing profit.

Inventory or stock refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation.

Manufacturingresource planning is defined as a method for the effective planning of all resources of a manufacturing company. Ideally, it addresses operational planning in units, financial planning, and has a simulation capability to answer "what-if" questions and is an extension of closed-loop MRP.
Business Planning and Control System (BPCS) is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software product.

Operations management is an area of management concerned with designing and controlling the process of production and redesigning business operations in the production of goods or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as few resources as needed and effective in meeting customer requirements.
Safety stock is a term used by logisticians to describe a level of extra stock that is maintained to mitigate risk of stockouts caused by uncertainties in supply and demand. Adequate safety stock levels permit business operations to proceed according to their plans. Safety stock is held when uncertainty exists in demand, supply, or manufacturing yield, and serves as an insurance against stockouts.
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. In the context of capacity planning, design capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period. Effective capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period due to constraints such as quality problems, delays, material handling, etc.

The business terms push and pull originated in logistics and supply chain management, but are also widely used in marketing and in the hotel distribution business.
The demand chain is that part of the value chain which drives demand.
Supply-chain optimization (SCO) aims to ensure the optimal operation of a manufacturing and distribution supply chain. This includes the optimal placement of inventory within the supply chain, minimizing operating costs including manufacturing costs, transportation costs, and distribution costs. Optimization often involves the application of mathematical modelling techniques using computer software. It is often considered to be part of supply chain engineering, although the latter is mainly focused on mathematical modelling approaches, whereas supply chain optimization can also be undertaken using qualitative, management based approaches.
Order fulfillment is in the most general sense the complete process from point of sales inquiry to delivery of a product to the customer. Sometimes it describes the more narrow act of distribution or the logistics function. In the broader sense it refers to the way firms respond to customer orders.
Production leveling, also known as production smoothing or – by its Japanese original term – heijunka (平準化), is a technique for reducing the mura (unevenness) which in turn reduces muda (waste). It was vital to the development of production efficiency in the Toyota Production System and lean manufacturing. The goal is to produce intermediate goods at a constant rate so that further processing may also be carried out at a constant and predictable rate.
Backflush accounting is a subset of management accounting focused on types of "postproduction issuing;" It is a product costing approach, used in a Just-In-Time (JIT) operating environment, in which costing is delayed until goods are finished. Backflush accounting delays the recording of costs until after the events have taken place, then standard costs are used to work backwards to 'flush' out the manufacturing costs. The result is that detailed tracking of costs is eliminated. Journal entries to inventory accounts may be delayed until the time of product completion or even the time of sale, and standard costs are used to assign costs to units when journal entries are made. Backflushing transaction has two steps: one step of the transaction reports the produced part which serves to increase the quantity on-hand of the produced part and a second step which relieves the inventory of all the component parts. Component part numbers and quantities-per are taken from the standard bill of material (BOM). This represents a huge saving over the traditional method of a) issuing component parts one at a time, usually to a discrete work order, b) receiving the finished parts into inventory, and c) returning any unused components, one at a time, back into inventory.
Demand forecasting is known as the process of making future estimations in relation to customer demand over a specific period. Generally, demand forecasting will consider historical data and other analytical information to produce the most accurate predictions. More specifically, the methods of demand forecasting entails using predictive analytics of historical data to understand and predict customer demand in order to understand key economic conditions and assist in making crucial supply decisions to optimise business profitability. Demand forecasting methods are divided into two major categories, qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative methods are based on expert opinion and information gathered from the field. It is mostly used in situations when there is minimal data available to analyse. For example, when a business or product is newly being introduced to the market. Quantitative methods however, use data, and analytical tools in order to create predictions. Demand forecasting may be used in production planning, inventory management, and at times in assessing future capacity requirements, or in making decisions on whether to enter a new market.
Demand Flow Technology (DFT) is a strategy for defining and deploying business processes in a flow, driven in response to customer demand. DFT is based on a set of applied mathematical tools that are used to connect processes in a flow and link it to daily changes in demand. DFT represents a scientific approach to flow manufacturing for discrete production. It is built on principles of demand pull where customer demand is the central signal to guide factory and office activity in the daily operation. DFT is intended to provide an alternative to schedule-push manufacturing which primarily uses a sales plan and forecast to determine a production schedule.
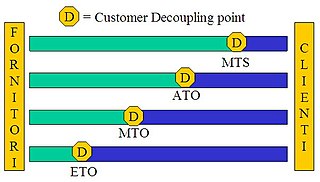
Final Assembly Schedule, often abbreviated as FAS and sometimes referred to as finishing schedule, is a schedule of end items to finish the product for specific customer orders in a make to order (MTO) or assemble-to-order (ATO) environment.
Inventory management software is a software system for tracking inventory levels, orders, sales and deliveries. It can also be used in the manufacturing industry to create a work order, bill of materials and other production-related documents. Companies use inventory management software to avoid product overstock and outages. It is a tool for organizing inventory data that before was generally stored in hard-copy form or in spreadsheets.

Production planning is the planning of production and manufacturing modules in a company or industry. It utilizes the resource allocation of activities of employees, materials and production capacity, in order to serve different customers.
Operations management for services has the functional responsibility for producing the services of an organization and providing them directly to its customers. It specifically deals with decisions required by operations managers for simultaneous production and consumption of an intangible product. These decisions concern the process, people, information and the system that produces and delivers the service. It differs from operations management in general, since the processes of service organizations differ from those of manufacturing organizations.