
The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally described by Verill in 1881, it was later lowered by Chun (1920) to a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of the Chiroteuthidae. However, Roper et al. (1969) raised it back to the family level, and this has not been changed since. The taxonomy of this family is extremely unstable, and there have been at times one genus, two genera and four subgenera(Salcedo-Vargas & Okutani, 1994), two genera and several 'groups', five genera and one species with an uncertain placement, or six genera.

The water deer is a small deer superficially more similar to a musk deer than a true deer. Native to China and Korea, there are two subspecies: the Chinese water deer and the Korean water deer. Despite certain anatomical peculiarities, including a pair of prominent tusks, and its lack of antlers, it is classified as a cervid. Yet, its unique anatomical characteristics have caused it to be classified in its own genus (Hydropotes) as well as its own subfamily (Hydropotinae). However, studies of mitochondrial control region and cytochrome b DNA sequences placed it near Capreolus within an Old World section of the subfamily Capreolinae. Its prominent tusks, similar to those of musk deer, have led to both subspecies being colloquially named vampire deer in English-speaking areas to which they have been imported. The species is listed as vulnerable by the IUCN. It was first described to the Western world by Robert Swinhoe in 1870.

Andira inermis is a nitrogen-fixing tree native to the area from southern Mexico through Central America to northern South America ; it has been introduced to the Caribbean, the Antilles, Florida, and Africa. The tree has many names due to its wide distribution and multiple uses: it is also known as the cabbage bark, almendro macho, almendro de río or river almond (Honduras), bastard cabbage tree, cabbage angelin, cabbage bark, cabbage tree, carne asada, guacamayo (Honduras), Jamaica cabbage tree, harino (Panama), moca, partridge wood, worm bark, or yellow cabbage tree.

Nepenthes dubia is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sumatra, where it grows at an altitude of 1600–2700 m above sea level. The specific epithet dubia is the Latin word for "doubtful".

Nepenthes inermis is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sumatra. The specific epithet inermis is Latin for "unarmed" and refers to the upper pitchers of this species, which are unique in that they completely lack a peristome.

Stomatosuchus is an extinct stomatosuchid neosuchian from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Egypt that grew up to 10 metres (33 ft) long when it was alive. Unlike most other crocodyliforms, it is difficult to determine exactly what S. inermis ate. Its flattened skull had a long, flat, lid-like snout, which was lined with small, conical teeth. The mandible may have been toothless and may have supported a pelican-like throat pouch. The type, and only, specimen of S. inermis consists of a partial skull and two caudal vertebrae.
Mastigoteuthis is a genus of whip-lash squid containing at least seven valid species. Some teuthologists consider Idioteuthis synonymous with this taxon.

Mastigoteuthis agassizii is a species of whip-lash squid. It is the type species of the genus.
Mastigoteuthis iselini is a species of whip-lash squid. Some authors treat it as a junior synonym of Mastigoteuthis atlantica.
Mastigoteuthis dentata is a species of whip-lash squid.

Mastigoteuthis glaukopis is a species of whip-lash squid.

Mastigoteuthis grimaldii is a species of whip-lash squid.
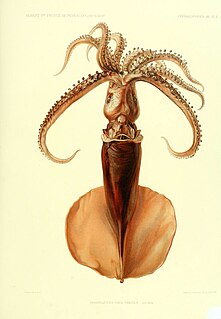
Mastigoteuthis magna is a species of whip-lash squid, characterised by a lack of photophores. The skin is heavily pigmented a deep red by a numerous chromatophores.
Mastigoteuthis psychrophila is a species of whip-lash squid. It was first described by Kir Nazimovich Nesis in 1977, based on four individuals found in Antarctic waters. The largest was 143 mm long. The squid's tentacles are 15 mm in diameter, with 0.15 mm diameter club suckers. Integumental photophores are present upon the head, arms and fins. Although uncertain, it is believed to have more than two series of photophores on the arms, differing from other species in the M. agassizii group. However, this species, like the rest of the family, is badly in need of revision.

The Solomon's naked-backed fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the Solomon Islands.

The marbled grouper, donkey fish, mutton hamlet, rockhind and sicklefish grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is a predatory reef fish which is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.

Lambertia inermis, Noongar chittick, is a shrub which is endemic to south-west Western Australia. It grows to 6 metres high and flowers from spring to winter. A more complete description is given in Florabase and Australian Flora online.

The highlands punaré, Thrichomys inermis, is a caviomorph rodent of South America from the spiny rat family. It is endemic to gallery forest, savanna and rocky outcrop habitats in Bahia State within the Caatinga ecoregion of eastern Brazil at elevations from 260 m to 1030 m. It sometimes nests and often takes refuge in crevices in rock formations, as means of both predator avoidance and moderating temperature extremes. The species tolerates a degree of habitat disturbance. Although hunted, it is considered common throughout its range. Its karyotype has 2n = 26 and FN = 48.

Bromus inermis is a species of the true grass family (Poaceae). This rhizomatous grass is native to Europe.

Sepiella inermis is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae. It is found primarily in the Indo-Pacific region. In this region, Sepiella inermis is an economically important species, and is sold and eaten.















