
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity, and luster, but may have properties that differ from those of the pure metals, such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength.

Smelting is a process of applying heat to an ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical- reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures as the chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide is lower than the bonds in the ore.

Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable for use as solder should have a lower melting point than the pieces to be joined. The solder should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time. Solder used in making electrical connections also needs to have favorable electrical characteristics.

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.

Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and recycled metals. Slag is mainly a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous, ferroalloy or non-ferrous/base metals. Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions.

In metallurgy, a flux is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper ores consists of a series of physical, chemical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.
Converting is a type of metallurgical smelting that includes several processes; the most commercially important form is the treatment of molten metal sulfides to produce crude metal and slag, as in the case of copper and nickel converting. A now-uncommon form is batch treatment of pig iron to produce steel by the Bessemer process. The vessel used was called the Bessemer converter. Modern steel mills use basic oxygen process converters.

Arsenical bronze is an alloy in which arsenic, as opposed to or in addition to tin or other constituent metals, is combined with copper to make bronze. The use of arsenic with copper, either as the secondary constituent or with another component such as tin, results in a stronger final product and better casting behavior.
In metallurgy, refining consists of purifying an impure metal. It is to be distinguished from other processes such as smelting and calcining in that those two involve a chemical change to the raw material, whereas in refining, the final material is usually identical chemically to the original one, only it is purer. The processes used are of many types, including pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical techniques.
Speisses are alloys of heavy metals like iron, cobalt, nickel and copper with arsenic, antimony and, occasionally, tin. The latter elements lower the melting point to around 1000 °C. Speisses commonly occur in lead smelting operations and copper smelting operations.
Copper slag is a by-product of copper extraction by smelting. During smelting, impurities become slag which floats on the molten metal. Slag that is quenched in water produces angular granules which are disposed of as waste or utilized as discussed below.
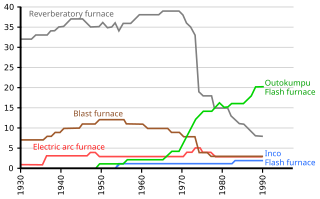
Flash smelting is a smelting process for sulfur-containing ores including chalcopyrite. The process was developed by Outokumpu in Finland and first applied at the Harjavalta plant in 1949 for smelting copper ore. It has also been adapted for nickel and lead production.
Archaeometallurgical slag is slag discovered and studied in the context of archaeology. Slag, the byproduct of iron-working processes such as smelting or smithing, is left at the iron-working site rather than being moved away with the product. As it weathers well, it is readily available for study. The size, shape, chemical composition and microstructure of slag are determined by features of the iron-working processes used at the time of its formation.

Cobalt extraction refers to the techniques used to extract cobalt from its ores and other compound ores. Several methods exist for the separation of cobalt from copper and nickel. They depend on the concentration of cobalt and the exact composition of the ore used.

Plants for the production of lead are generally referred to as lead smelters. Primary lead production begins with sintering. Concentrated lead ore is fed into a sintering machine with iron, silica, limestone fluxes, coke, soda ash, pyrite, zinc, caustics or pollution control particulates. Smelting uses suitable reducing substances that will combine with those oxidizing elements to free the metal. Reduction is the final, high-temperature step in smelting. It is here that the oxide becomes the elemental metal. A reducing environment pulls the final oxygen atoms from the raw metal.

The ISASMELT process is an energy-efficient smelting process that was jointly developed from the 1970s to the 1990s by Mount Isa Mines and the Government of Australia’s CSIRO. It has relatively low capital and operating costs for a smelting process.

The Bottom-blown Oxygen Converter or BBOC is a smelting furnace developed by the staff at Britannia Refined Metals Limited (“BRM”), a British subsidiary of MIM Holdings Limited. The furnace is currently marketed by Glencore Technology. It is a sealed, flat-bottomed furnace mounted on a tilting frame that is used in the recovery of precious metals. A key feature is the use of a shrouded lance to inject oxygen through the bottom of the furnace, directly into the precious metals contained in the furnace, to oxidize base metals or other impurities as part of their removal as slag.
William H. Peirce was an American civil engineer and metallurgist, who pioneered copper production in the early 20th century. Among his achievements was the Peirce-Smith converter, invented with Elias Anton Cappelen Smith.

The Manhès–David process is a refining process of the copper mattes, invented in 1880 by the French industrialist Pierre Manhès and his engineer Paul David. Inspired by the Bessemer process, it consists of the use of a converter to oxidise with air the undesirable chemical elements contained in the matte, to transform it into copper.













