
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy.

Sir Peter Mansfield was a British physicist who was awarded the 2003 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, shared with Paul Lauterbur, for discoveries concerning Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Mansfield was a professor at the University of Nottingham.

Mass General Brigham is a not-for-profit, integrated health care system that engages in medical research, teaching, and patient care. It is the largest hospital-based research enterprise in the United States, with annual funding of more than $2 billion. The system's annual revenue was nearly $18 billion in 2022. It is also an educational institution, founded by Brigham and Women's Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital. The system provides clinical care through two academic hospitals, three specialty hospitals, seven community hospitals, home care services, a health insurance plan, and a robust network of specialty practices, urgent care facilities, and outpatient clinics/surgical centers. It is the largest private employer in Massachusetts. In 2023, the system reported that from 2017–2021 its overall economic impact was $53.4 billion – more than the annual state budget.
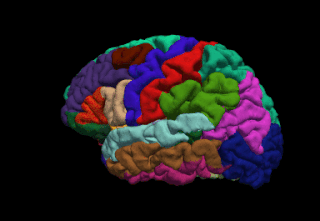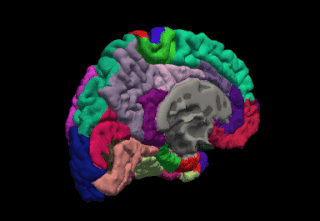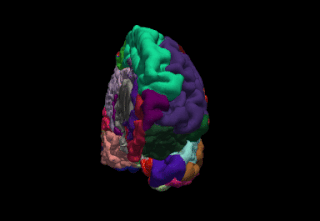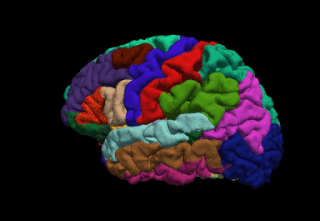
FreeSurfer is brain imaging software originally developed by Bruce Fischl, Anders Dale, Martin Sereno, and Doug Greve. Development and maintenance of FreeSurfer is now the primary responsibility of the Laboratory for Computational Neuroimaging at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. FreeSurfer contains a set of programs with a common focus of analyzing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of brain tissue. It is an important tool in functional brain mapping and contains tools to conduct both volume based and surface based analysis. FreeSurfer includes tools for the reconstruction of topologically correct and geometrically accurate models of both the gray/white and pial surfaces, for measuring cortical thickness, surface area and folding, and for computing inter-subject registration based on the pattern of cortical folds.

Jonathan Marc Rothberg is an American scientist and entrepreneur. He is best known for his contributions to next-generation DNA sequencing. He resides in Miami, Florida.
Kenneth Kin Man Kwong is a Hong Kong-born American nuclear physicist. He is a pioneer in human brain imaging. He received his bachelor's degree in Political Science in 1972 from the University of California, Berkeley. He went on to receive his Ph.D. in physics from the University of California, Riverside studying photon-photon collision interactions.

Sir Paul Terence Callaghan was a New Zealand physicist who, as the founding director of the MacDiarmid Institute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology at Victoria University of Wellington, held the position of Alan MacDiarmid Professor of Physical Sciences and was President of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance.
The Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, usually referred to as just the "Martinos Center," is a major hub of biomedical imaging technology development and translational research. The Center is part of the Department of Radiology at Massachusetts General Hospital and is affiliated with both Harvard University and MIT. Bruce Rosen is the Director of the Center and Monica Langone is the Administrative Director.
The Human Connectome Project (HCP) is a five-year project sponsored by sixteen components of the National Institutes of Health, split between two consortia of research institutions. The project was launched in July 2009 as the first of three Grand Challenges of the NIH's Blueprint for Neuroscience Research. On September 15, 2010, the NIH announced that it would award two grants: $30 million over five years to a consortium led by Washington University in St. Louis and the University of Minnesota, with strong contributions from University of Oxford (FMRIB) and $8.5 million over three years to a consortium led by Harvard University, Massachusetts General Hospital and the University of California Los Angeles.
Bruce Rosen is an American physicist and radiologist and a leading expert in the area of functional neuroimaging. His research for the past 30 years has focused on the development and application of physiological and functional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques, as well as new approaches to combine functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data with information from other modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and noninvasive optical imaging. The techniques his group has developed to measure physiological and metabolic changes associated with brain activation and cerebrovascular insult are used by research centers and hospitals throughout the world.

Ferenc Andras Jolesz was a Hungarian-American physician and scientist best known for his research on image guided therapy, the process by which information derived from diagnostic imaging is used to improve the localization and targeting of diseased tissue to monitor and control treatment during surgical and interventional procedures. He pioneered the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-guided interventions and introduced of a variety of new medical procedures based on novel combinations of imaging and therapy delivery.
Guillermo J. Tearney is an American pathologist recognized as one of the inventors of Intracoronary optical coherence tomography. His research focuses on translational medicine, developing and moving to clinical use optical imaging methods for disease diagnosis.

The Gordon Center for Medical Imaging is an American multidisciplinary research center at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School that develops biomedical imaging technologies.
The history of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) includes the work of many researchers who contributed to the discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and described the underlying physics of magnetic resonance imaging, starting early in the twentieth century. One researcher was American physicist Isidor Isaac Rabi who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1944 for his discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance, which is used in magnetic resonance imaging. MR imaging was invented by Paul C. Lauterbur who developed a mechanism to encode spatial information into an NMR signal using magnetic field gradients in September 1971; he published the theory behind it in March 1973.

Lucio Frydman is an Israeli chemist whose research focuses on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and solid-state NMR. He was awarded the 2000 Günther Laukien Prize, the 2013 Russell Varian Prize and the 2021 Ernst Prize. He is Professor and Head of the Department of Chemical and Biological Physics at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel and Chief Scientist in Chemistry and Biology at the US National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in Tallahassee, Florida. He is a fellow of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance and of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. He was the Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Magnetic Resonance (2011-2021).

The history of X-ray computed tomography dates back to at least 1917 with the mathematical theory of the Radon transform In the early 1900s an Italian radiologist named Alessandro Vallebona invented tomography which used radiographic film to see a single slice of the body. It was not widely used until the 1930s, when Dr Bernard George Ziedses des Plantes developed a practical method for implementing the technique.
Marco Loggia is a US-based Italian neuroscientist who specializes in brain imaging. He is an associate professor at Harvard Medical School, and directs the Pain and Neuroinflammation Imaging Laboratory, located at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). He is also the co-director of the Center of Integrative Pain NeuroImaging (CiPNI) at MGH. He is known for his work on brain mechanisms of pain, especially using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). He has been a pioneer in the use of Arterial Spin Labeling and second-generation TSPO PET ligands for the study of chronic pain. He is a Section Editor for the journal PAIN, and also serves on the editorial board for the Journal of Pain and Pain Medicine. His work has been highlighted by many media outlets, including Popular Science, New Scientist, Scientific American, ABC News, la Repubblica, Sky TG24, the Harvard Gazette and others.

Portable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is referred to the imaging provided by an MRI scanner that has mobility and portability. It provides MR imaging to the patient in-time and on-site, for example, in intensive care unit (ICU) where there is danger associated with moving the patient, in an ambulance, after a disaster rescue, or in a field hospital/medical tent.

Matthew D. Sacchet is a neuroscientist, Associate Professor of Psychiatry, and Director of the Meditation Research Program at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital. His research focuses on advancing the science of meditation and includes studies of brain structure and function using multimodal neuroimaging, in addition to clinical trials, neuromodulation, and computational approaches. He is notable for his work at the intersection of meditation, neuroscience, and mental illness. His work has been cited over 6,000 times and covered by major media outlets including CBS, NBC, NPR, Time, Vox, and The Wall Street Journal. In 2017 Forbes Magazine selected Sacchet for the “30 Under 30”.
Ronald Walsworth is an American physicist, engineer, and professor at the University of Maryland.











