Related Research Articles

Gettysburg National Cemetery is a United States national cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, created for Union casualties from the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. The Battle of Gettysburg, which was fought between July 1 to 3, 1863, resulted in the largest number of casualties of any Civil War battle but also was considered the war's turning point, leading ultimately to the Union victory.

The Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.

The Peach Orchard is a Gettysburg Battlefield site at the southeast corner of the north-south Emmitsburg Road intersection with the Wheatfield Road. The orchard is demarcated on the east and south by Birney Avenue, which provides access to various memorials regarding the "momentous attacks and counterattacks in…the orchard on the afternoon of July 2, 1863."

Devil's Den is a boulder-strewn hill on the south end of Houck's Ridge at Gettysburg Battlefield, used by artillery and sharpshooters on the second day of the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War. A tourist attraction since the memorial association era, several boulders are worn from foot traffic and the site includes numerous cannons, memorials, and walkways, including a bridge spanning two boulders.

Seminary Ridge is a dendritic ridge that served as an area of military engagements during the Battle of Gettysburg, the bloodiest battle of the American Civil War, which was fought between July 1 and July 3, 1863 in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Seminary Ridge also served as a military installation during World War II.

J.W. Wells State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Michigan. The 678-acre (2.74 km2) park is located in Menominee County on the shore of Lake Michigan's Green Bay, just south of Cedar River. It is on M-35, roughly midway between Menominee and Escanaba. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.

Rock Creek is an 18.9-mile-long (30.4 km) tributary of the Monocacy River in south-central Pennsylvania and serves as the border between Cumberland and Mount Joy townships. Rock Creek was used by the Underground Railroad and flows near several Gettysburg Battlefield sites, including Culp's Hill, the Benner Hill artillery location, and Barlow Knoll.

Pennsylvania Route 134 (PA 134), also called Taneytown Road, is a north–south, two-lane state highway in Adams County, Pennsylvania. It runs from the Maryland border at the Mason–Dixon line in Mount Joy Township north to U.S. Route 15 Business in Gettysburg. PA 134 runs through farmland between the Maryland border and an interchange with the US 15 freeway. North of here, the route passes through Round Top and serves Gettysburg National Military Park before reaching its northern terminus. Taneytown Road was created in 1800 to connect Gettysburg with Taneytown, Maryland. The road was used during the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg for the procession to the cemetery consecration at which the Gettysburg Address was delivered. PA 134 was designated to its current alignment in 1928, with the section north of Round Top paved. The southern portion of the route was paved in the 1930s.

Dolliver Memorial State Park is a state park in Webster County, Iowa, United States, featuring high bluffs and deep ravines on the Des Moines River. The park is located 10 miles (16 km) south of Fort Dodge and 3 miles (4.8 km) northwest of Lehigh. The park contains two listings on the National Register of Historic Places: Dolliver Memorial State Park, Entrance Area and Dolliver Memorial State Park, Picnic, Hiking & Maintenance Area .
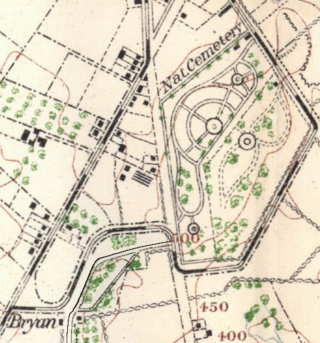
The Brian Farm is an American Civil War area of the Gettysburg Battlefield used during the Pickett's Charge. On January 23, 2004, the farm's buildings, Boundary Stone Wall, and ID tablet were designated historic district contributing structures after the tract was used for the 1918 Camp Colt and other postwar camps.
Plum Run is a Pennsylvania stream flowing southward from the Gettysburg Battlefield between the Gettys-Black Divide on the east and on the west, the drainage divide for Pitzer Run, Biesecker Run, Willoughby Run, and Marsh Creek.
The World War II Prisoner of War camp on the Gettysburg Battlefield was established on a former military engagement site of the American Civil War in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania in the United States.

The Angle is a Gettysburg Battlefield area which includes the 1863 Copse of Trees used as the target landmark for Pickett's Charge, the 1892 monument that marks the high-water mark of the Confederacy, a rock wall, and several other Battle of Gettysburg monuments.
United States v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. Co., 160 U.S. 668 (1896), was a case to prevent trolley operations on the Gettysburg Battlefield. The dispute began in August 1891 when the Gettysburg Battlefield Memorial Association's board approved attorney Samuel Swope's motion to deny trolley right-of-way along GBMA roads. Despite the 1896 US Supreme Court ruling that the railway could be seized for historic preservation, as well as earlier legislative efforts to appropriate federal acquisition funds, create a War Department commission, and form the Gettysburg National Military Park; the trolley continued operations until obsolete in 1916.
Emmor Cope (1834-1927) was an American Civil War officer of the Union Army noted for the "Map of the Battlefield of Gettysburg from the original survey made August to October, 1863", which he researched by horseback as a sergeant after being ordered back to Gettysburg by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. Cope is also noted for commemorative era battlefield administration and designs, including the layout of the 1913 Gettysburg reunion. Cope had enlisted as a Private of Company A,, temporarily detached to Battery C, 5th U.S. Artillery, and mustered out as a V Corps aide-de-camp of Maj Gen Gouverneur K. Warren.
Spangler Woods is a Gettysburg Battlefield location used during the Battle of Gettysburg and is near the Virginia Monument. On July 2, 1863, Garnett's Brigade bivouacked on the border of the woods.

The Wheatfield Road is a Gettysburg Battlefield crossroad from the Peach Orchard east-southeastward along the north side of The Wheatfield, north of the Valley of Death, and over the north foot of Little Round Top. In addition to modern tourist use, the road is notable for Battle of Gettysburg use and postbellum trolley use associated with the 1892-1896 US v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. case of the US Supreme Court.
The McMillan Woods CCC camp was Civilian Conservation Corps camp NP-2 on the Gettysburg Battlefield planned in September 1933 near CCC Camp Renaissance in Pitzer Woods. Captain Francis J. Moran moved from Camp Renaissance to become the new camp NP-2 commander in October 1933 The camp opened a new recreation hall in 1934 and provided manpower for building the veterans camp for the 1938 Gettysburg reunion, and about 50 enrollees of CCC Company #1355-C served as aides for unaccompanied veterans. During the reunion, Company F of the 34th Infantry used the CCC camp and had a headquarters office under Major C. Gilchrist and Capt. E. E. Wright. Captain Frederick L. Slade was the CCC commander on April 1, 1939.

Rose Woods is a Gettysburg Battlefield forested area that is an American Civil War site of the battle's Hood's Assault, McLaws' Assault, and McCandless' Advance. "Scene of the first line of Union defenses" on the Battle of Gettysburg, Second Day; the 1st Texas Infantry and 3rd Arkansas Infantry Regiments attacked Ward's 2nd Brigade line in the woods. The last combat on the Battle of Gettysburg, Third Day, was "in the early evening. Colonel William McCandless's brigade of Pennsylvania Reserves advanced across the Wheatfield into Rose's Woods where they managed to inflict heavy losses on the 15th Georgia" which had failed to retreat to Warfield Ridge after Longstreet's Assault. Two days later Timothy H. O'Sullivan photographed corpses moved for burial to the edge of Rose Woods and which were subsequently reinterred in cemeteries.

The Oak Ridge Seminary was an antebellum school for "young ladies" west of the borough of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. One of 2 girls schools used as an American Civil War hospital for Battle of Gettysburg casualties, the female seminary had also been used as a prison, and General Lee's "Headquarters and tents [were] pitched in the space adjoining Oak Ridge Seminary"
References
- ↑ Cope, Emmor, "McMillan Woods Rifle Pits (Structure number MD15, LCS ID 006988) & Earthworks (Structure number MD16)", NPS.gov, archived from the original on December 13, 2012
- ↑ "List of Classified Structures". United States Department of War. p. 36.
6 shallow dish-shaped depressions in ground. 2' deep, 7'11" diameter. Overgrown & filled w/ decomposed leaves. Located ca 20' form E edge of McMillan Woods, 60' from West Confederate Ave.
[ dead link ] - ↑ Cope, Emmor (1920), "Pitzer Woods - Cast Iron Site ID Tablet (ID52)", NPS.gov, United States Department of War, archived from the original on September 15, 2012, retrieved June 6, 2011,
1 of 35 Site ID Tablets by War Dept's … Designer … Cope, E. B. … Painted raised letter and border inscription tablet, 2'1"x1'8". Mounted on fluted post, 3' high.
- ↑ "An Imaginary Battle Fought at Gettysburg" (Google News Archive). Reading Eagle . July 25, 1906. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ↑ "Camp Information for NP-2-PA". Pennsylvania CCC Archive. Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. Archived from the original on December 25, 2012. Retrieved February 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Out of the Past: 50 Years Ago". June 29, 1995. Retrieved February 1, 2010.