Mechanical may refer to:
Mechanical may refer to:

Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering.

Mechanical engineering is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches.

A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage to multiply force. Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines that were defined by Renaissance scientists:

Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology.
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from two Latin words: pro, meaning before or forward; and pellere, meaning to drive. A propulsion system consists of a source of mechanical power, and a propulsor.

A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems.

Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of biophysics.
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
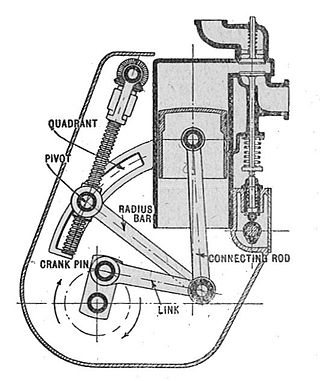
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected to manage forces and movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing ideal movement, pure rotation or sliding for example, and are called joints. A linkage modeled as a network of rigid links and ideal joints is called a kinematic chain.
Applied mechanics is the branch of science concerned with the motion of any substance that can be experienced or perceived by humans without the help of instruments. In short, when mechanics concepts surpass being theoretical and are applied and executed, general mechanics becomes applied mechanics. It is this stark difference that makes applied mechanics an essential understanding for practical everyday life. It has numerous applications in a wide variety of fields and disciplines, including but not limited to structural engineering, astronomy, oceanography, meteorology, hydraulics, mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, nanotechnology, structural design, earthquake engineering, fluid dynamics, planetary sciences, and other life sciences. Connecting research between numerous disciplines, applied mechanics plays an important role in both science and engineering.
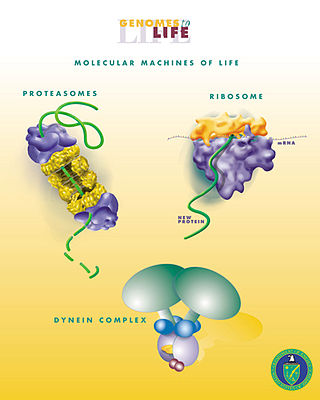
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies.

Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering. Manufacturing engineering requires the ability to plan the practices of manufacturing; to research and to develop tools, processes, machines and equipment; and to integrate the facilities and systems for producing quality products with the optimum expenditure of capital.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics:
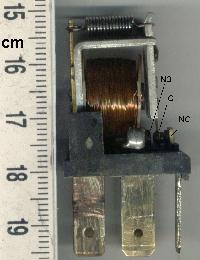
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process (generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering.
This glossary of engineering terms is a list of definitions about the major concepts of engineering. Please see the bottom of the page for glossaries of specific fields of engineering.
Industrial and production engineering (IPE) is an interdisciplinary engineering discipline that includes manufacturing technology, engineering sciences, management science, and optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations. It is concerned with the understanding and application of engineering procedures in manufacturing processes and production methods. Industrial engineering dates back all the way to the industrial revolution, initiated in 1700s by Sir Adam Smith, Henry Ford, Eli Whitney, Frank Gilbreth and Lilian Gilbreth, Henry Gantt, F.W. Taylor, etc. After the 1970s, industrial and production engineering developed worldwide and started to widely use automation and robotics. Industrial and production engineering includes three areas: Mechanical engineering, industrial engineering, and management science.
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.
This glossary of civil engineering terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts pertaining specifically to civil engineering, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For a more general overview of concepts within engineering as a whole, see Glossary of engineering.
In mechanical engineering, kinematic synthesis determines the size and configuration of mechanisms that shape the flow of power through a mechanical system, or machine, to achieve a desired performance. The word synthesis refers to combining parts to form a whole. Hartenberg and Denavit describe kinematic synthesis as
...it is design, the creation of something new. Kinematically, it is the conversion of a motion idea into hardware.
This glossary of engineering terms is a list of definitions about the major concepts of engineering. Please see the bottom of the page for glossaries of specific fields of engineering.