
The Prussian Class P 8 of the Prussian state railways was a 4-6-0 steam locomotive built from 1906 to 1923 by the Berliner Maschinenbau and twelve other German factories. The design was created by Robert Garbe. It was intended as a successor to the Prussian P 6, which was regarded as unsatisfactory.

The Prussian G 8.1 was a heavier, stronger development of the G 8 and was initially referred to as a 'strengthened standard class'.

The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway was the state railway company in Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz. After its second nationalisation in 1890 up to the merger of the Länderbahnen into the Deutsche Reichsbahn in 1920 it was under the direction of the Grand Duchy's Executive Railway Board in Schwerin.
The Mecklenburg T 3 was a German, goods train, tank locomotive built for the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway from 1884. Originally designated as the Class XVII it had an 0-6-0T wheel arrangement and was based on the Prussian T 3.
The Oldenburg G 4.2 steam locomotives were goods train engines built for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways between 1895 and 1909 in several series.

The Oldenburg G 7 steam locomotive was a German 0-8-0 locomotive produced for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways. It was an eight-coupled engine, intended for heavy goods train duties, and was based on the Prussian G 7. It had a 1,660 mm diameter boiler located 2,820 mm above the top of the rails in the plate frame, and was equipped with a single Walschaerts valve gear as well as a Lentz valve gear. Thirteen were taken over by the Deutsche Reichsbahn, grouped into DRG Class 55.62 and given numbers 55 6201–55 6213.

The Mecklenburg T 4 was a German steam locomotive built for the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway as a goods train 2-6-0T with a leading axle and three coupled axles. In 1925 it was incorporated in the renumbering plan of the Deutsche Reichsbahn as DRG Class 91.19.
The Prussian G 5.4 was a German goods train locomotive with a compound engine. Due to its top speed of 65 km/h it was also used on passenger services. The G 5.4, like the G 5.3, differed from the G 5.1 and G 5.2 in having a shorter wheelbase and higher boiler pitch. In addition, the Krauss-Helmholtz bogies enabled its riding qualities to be improved, especially at higher speeds. Between 1901 and 1910 a total of about 760 vehicles of the Class G 5.4 were built for the Prussian state railways. The last 25 locomotives were fitted once again with an Adams axle.

In 1905 the Prussian state railways grouped six-coupled, medium-powered, goods train, tank locomotives into its Class G 3. In addition to standard locomotives, there were also 285 G 3s that were not built to German state railway norms, because they had been built, in most cases, before the foundation of the Prussian state railways.

The steam locomotives of DRG Class 34.73, formerly the Mecklenburg Class P 3.1 were passenger train locomotives operated by the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway and were based on the Prussian P 3.1. They were sometimes used in express train services to begin with. Of the 41 examples belonging to this administration, which were built between 1888 and 1908, two originally came from the Lloyd Railway (Neustrelitz-Warnemünde). One improvement over the Mecklenburg P 2 was the braked coupled axle.
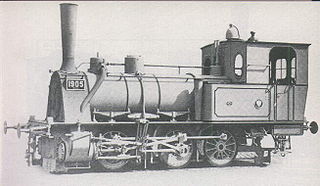
The Prussian Class T 3 steam locomotives procured for the Prussian state railways were 0-6-0 tank locomotives. Together with the Prussian T 2 they were the first locomotives that were built to railway norms. The first units were delivered by Henschel in 1882.

The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway grouped the various 2-2-2 steam locomotives procured between 1848 and 1863 into its Mecklenburg Class I.

The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway grouped early, 2-4-0, passenger train locomotives from the Friedrich-Franz Railway into its Class III.
The Mecklenburg Class G 2, formerly Class VIII, were goods train locomotives with the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway. They were built for the route between Güstrow and Neubrandenburg with its steep inclines.
The Mecklenburg Class G 3 was an early German steam locomotive operated by the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway. Formerly the Class IX it was a copy of the Prussian G 3.
The Prussian Class P 2 consisted of various types of early, passenger train, steam locomotive operated by the Prussian state railways. There were 294 2-4-0 locomotives, 24 0-4-2 locomotives and two engines with a 4-4-0 wheel arrangement. Of the 2-4-0 type, 88 came from railway companies that were the predecessors to the Prussian state railways and did not comply with Prussian norms, 24 were of the Ruhr-Sieg type and 182 were standard P 2s. The 0-4-2 locomotives were identical with the Prussian G 2.

The Prussian G 7.3 was a class of 2-8-0 locomotives of the Prussian state railways. The third class of the G 7 series, they were intended to power heavy goods trains on steep inclines, on which the permissible axle load was not yet that high. This affected for example, the Paderborn–Holzminden and Betzdorf–Siegen routes.

The Prussian G 7.2 was a class of 0-8-0 tender compound locomotives of the Prussian state railways. In the 1925 Deutschen Reichsbahn renumbering plan, the former Prussian locomotives produced from 1895 to 1911 were given the class designation 55.7–13; while the former Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg Friedrich-Franz Railway locomotives were classified as 55.57.
The Prussian G 4.2 was a class of compound 0-6-0 goods locomotive of the Prussian State Railways. It was a compound version of the G 3 and G 4.1 types by Henschel.











