Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable at home. However, in recent years it may equally refer to those from developed countries who travel to developing countries for lower-priced medical treatments. The motivation may be also for medical services unavailable or non-licensed in the home country: There are differences between the medical agencies world-wide, whether a drug is approved in their country or not. Even within Europe, although therapy protocols might be approved by the European Medical Agency (EMA), several countries have their own review organizations in order to evaluate whether the same therapy protocol would be "cost-effective", so that patients face differences in the therapy protocols, particularly in the access of these drugs, which might be partially explained by the financial strength of the particular Health System.
The term managed care or managed healthcare is used in the United States to describe a group of activities intended to reduce the cost of providing health care and providing American health insurance while improving the quality of that care. It has become the essentially exclusive system of delivering and receiving American health care since its implementation in the early 1980s, and has been largely unaffected by the Affordable Care Act of 2010.
...intended to reduce unnecessary health care costs through a variety of mechanisms, including: economic incentives for physicians and patients to select less costly forms of care; programs for reviewing the medical necessity of specific services; increased beneficiary cost sharing; controls on inpatient admissions and lengths of stay; the establishment of cost-sharing incentives for outpatient surgery; selective contracting with health care providers; and the intensive management of high-cost health care cases. The programs may be provided in a variety of settings, such as Health Maintenance Organizations and Preferred Provider Organizations.

Geisinger Health System (GHS) is a regional health care provider to central, south-central and northeastern Pennsylvania. Headquartered in Danville, Pennsylvania, Geisinger services over 3 million patients in 45 counties.
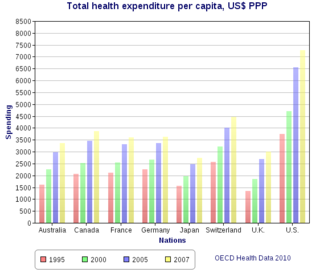
The health care system in Japan provides healthcare services, including screening examinations, prenatal care and infectious disease control, with the patient accepting responsibility for 30% of these costs while the government pays the remaining 70%. Payment for personal medical services is offered by a universal health care insurance system that provides relative equality of access, with fees set by a government committee. All residents of Japan are required by the law to have health insurance coverage. People without insurance from employers can participate in a national health insurance programme, administered by local governments. Patients are free to select physicians or facilities of their choice and cannot be denied coverage. Hospitals, by law, must be run as non-profit and be managed by physicians.

Mercy Medical Center is a Catholic hospital in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. The smaller of two metro hospitals, Mercy frequently ranks as either the best in Iowa or one of the top three. Mercy is a non-profit, acute-care medical center with a level III trauma center. Mercy Cedar Rapids is independent and not directly associated with other Mercy hospitals across the state and country. In addition to the non-profit hospital and clinics, Mercy operates outpatient and urgent-care clinics in a for-profit partnership with MercyCare Community Physicians.
Health information exchange (HIE) is the mobilization of health care information electronically across organizations within a region, community or hospital system. Participants in data exchange are called in the aggregate Health Information Networks (HIN). In practice the term HIE may also refer to the health information organization (HIO) that facilitates the exchange.

Universal Health Services, Inc. (UHS) is an American Fortune 500 company that provides hospital and healthcare services, based in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania. In 2020, its annual revenues were $11.6 billion.
Health care in Saudi Arabia is a national health care system in which the government provides free health care services through a number of government agencies. There is also a growing role and increased participation from the private sector in the provision of health care services. Saudi Arabia has been ranked among the 26 best countries in providing high quality healthcare.
Patient safety is a discipline that emphasizes safety in health care through the prevention, reduction, reporting, and analysis of error and other types of unnecessary harm that often lead to adverse patient events. The frequency and magnitude of avoidable adverse events, often known as patient safety incidents, experienced by patients was not well known until the 1990s, when multiple countries reported significant numbers of patients harmed and killed by medical errors. Recognizing that healthcare errors impact 1 in every 10 patients around the world, the World Health Organization calls patient safety an endemic concern. Indeed, patient safety has emerged as a distinct healthcare discipline supported by an immature yet developing scientific framework. There is a significant transdisciplinary body of theoretical and research literature that informs the science of patient safety.

The healthcare delivery system of Pakistan is complex because it includes healthcare subsystems by federal governments and provincial governments competing with formal and informal private sector healthcare systems. Healthcare is delivered mainly through vertically managed disease-specific mechanisms. The different institutions that are responsible for this include: provincial and district health departments, parastatal organizations, social security institutions, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and private sector. The country's health sector is also marked by urban-rural disparities in healthcare delivery and an imbalance in the health workforce, with insufficient health managers, nurses, paramedics and skilled birth attendants in the peripheral areas. Pakistan's gross national income per capita in 2013 was $5,041 and the total expenditure on health per capita in 2014 was $129, constituting 2.6% of the country's GDP.
The healthcare reform in China refers to the previous and ongoing healthcare system transition in modern China. China's government, specifically the National Health and Family Planning Commission, plays a leading role in these reforms. Reforms focus on establishing public medical insurance systems and enhancing public healthcare providers, the main component in China's healthcare system. In urban and rural areas, three government medical insurance systems—Urban Residents Basic Medical Insurance, Urban Employee Basic Medical Insurance, and the New Rural Co-operative Medical Scheme—cover almost everyone. Various public healthcare facilities, including county or city hospitals, community health centers, and township health centers, were founded to serve diverse needs. Current and future reforms are outlined in Healthy China 2030.
MedStar Health is a not-for-profit healthcare organization. It operates more than 120 entities, including ten hospitals in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area of the United States. In 2011 it was ranked as the employer with the largest number of local employees in the region.
Sutter Health is a not-for-profit integrated health delivery system headquartered in Sacramento, California. It operates 24 acute care hospitals and over 200 clinics in Northern California.
St. Luke's is a 532-bed hospital in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. It was founded in 1884 as Cedar Rapids’ first hospital and is now one of two hospitals in Cedar Rapids, the other being Mercy Medical Center. St. Luke's emergency department treats over 55,000 patients each year and the most cases of trauma in Iowa. This has led to a partnership with the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics for training future ER doctors. It is the area's only Level III Regional Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. St. Luke's provides a Level III trauma center.

Healthcare in Denmark is largely provided by the local governments of the five regions, with coordination and regulation by central government, while nursing homes, home care, and school health services are the responsibility of the 98 municipalities. Some specialised hospital services are managed centrally.

The Helen DeVos Children's Hospital (HDCH) is a nationally ranked, freestanding, 241-bed, pediatric acute care children's hospital located in downtown Grand Rapids, Michigan. It is affiliated with the Michigan State University College of Human Medicine and is a member of the Spectrum health system, the only children's hospital in the system. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout Grand Rapids region and features an ACS verified level I pediatric trauma center. Its regional pediatric intensive-care unit and neonatal intensive care units serve the region. It is named for Helen DeVos, wife of Amway founder Richard DeVos, a major donor.
Health care in Panama is provided through the government and private sector businesses. The public sector is funded through the Ministry of Health (MINSA), and the Social Security Fund (CSS), which operate separate facilities. The CSS is both a health care provider and a pension fund administrator. It is funded by contributions from employers and employees. About 3.47 million people of the population of roughly 3.9 million were covered by its provisions in 2013, this included both the contributors and their dependents. MINSA provides low cost facilities for those not covered. In 2014 it operated 830 health facilities.

Vivian S. Lee is an American radiologist and health care executive. The president of Verily Health Platforms. Lee is the author of the book, The Long Fix: Solving America's health Care Crisis with Strategies That Work for Everyone. A senior lecturer at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, Lee is also a senior fellow at the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 2019, she was named #11 in Modern Healthcare's 100 Most Influential People in Healthcare.

Healthcare in Belize is provided through both public and private healthcare systems. The Ministry of Health (MoH) is the government agency responsible for overseeing the entire health sector and is also the largest provider of public health services in Belize. The MoH offers affordable care to a majority of Belizeans with a strong focus on providing quality healthcare through a range of public programs and institutions.
A safety net hospital is a type of medical center in the United States that by legal obligation or mission provides healthcare for individuals regardless of their insurance status or ability to pay. This legal mandate forces safety net hospitals (SNHs) to serve all populations. Such hospitals typically serve a proportionately higher number of uninsured, Medicaid, Medicare, Children's Health Insurance Program (CHiP), low-income, and other vulnerable individuals than their "non-safety net hospital" counterpart. Safety net hospitals are not defined by their ownership terms; they can be either publicly or privately owned. The missions of safety net hospitals are rather, to focus and emphasize their devotion to providing the best possible care for those who are barred from health care due to the various possible adverse circumstances. These circumstances mostly revolve around problems with financial payments, insurance plans, or health conditions. As per America's Health Care Safety Net: Intact but Endangered, safety net hospitals are known for maintaining an open-door policy for their services.