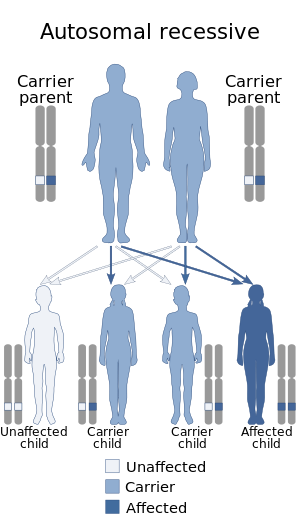
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms.

Castlemandisease (CD) describes a group of rare lymphoproliferative disorders that involve enlarged lymph nodes, and a broad range of inflammatory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Whether Castleman disease should be considered an autoimmune disease, cancer, or infectious disease is currently unknown.
Pemberton's sign was named after Hugh Pemberton, who characterized it in 1946.

Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

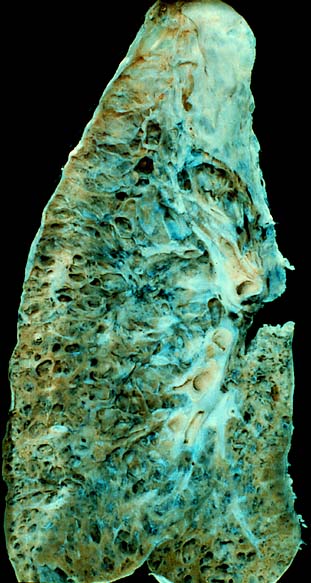
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.

Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies:
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present with lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, deep vein thrombosis, and other obstructive symptoms. It is named after John Kelso Ormond, who rediscovered the condition in 1948.
Mediastinal germ cell tumors are tumors that derive from germ cell rest remnants in the mediastinum. Germ cell tumors most commonly occur in the gonad but occasionally elsewhere.
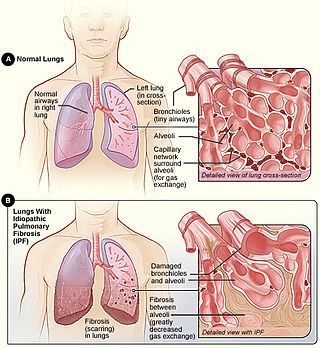
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic scarring lung disease characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.

Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.

Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways. There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.

Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. Megakaryoblasts are the most immature precursor cells in a platelet-forming lineage; they mature to promegakaryocytes and, ultimately, megakaryocytes which cells shed membrane-enclosed particles, i.e. platelets, into the circulation. Platelets are critical for the normal clotting of blood. While malignant megakaryoblasts usually are the predominant proliferating and tissue-damaging cells, their similarly malignant descendants, promegakaryocytes and megakaryocytes, are variable contributors to the malignancy.
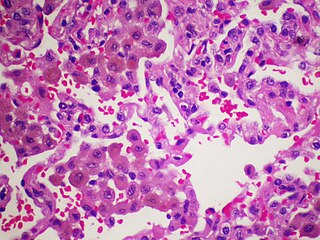
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia featuring elevated numbers of macrophages within the alveoli of the lung. The alveolar macrophages have a characteristic light brown pigmentation and accumulate in the alveolar lumen and septa regions of the lower lobes of the lungs. The typical effects of the macrophage accumulation are inflammation and later fibrosis of the lung tissue.
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.

Multifocal fibrosclerosis and idiopathic fibrosclerosis are disorders of unknown aetiology, characterised by fibrous lesions (co-)occurring at a variety of sites. Known manifestations include retroperitoneal fibrosis, mediastinal fibrosis and Riedel's thyroiditis.
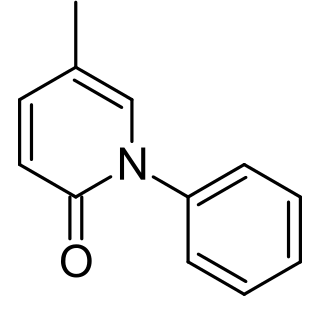
Pirfenidone, sold under the brand name Pirespa among others, is a medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It works by reducing lung fibrosis through downregulation of the production of growth factors and procollagens I and II.

Idiopathic sclerosing mesenteritis (ISM) is a rare disease of the small intestine, characterized by chronic inflammation and eventual fibrosis of the mesentery. It has also been called mesenteric lipodystrophy, or retractile mesenteritis.
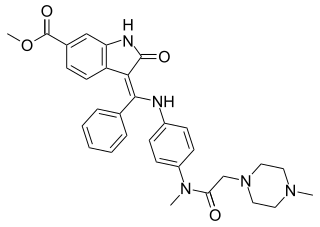
Nintedanib, sold under the brand names Ofev and Vargatef, is an oral medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and along with other medications for some types of non-small-cell lung cancer.