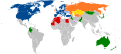
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber. The organization's strategic concepts include deterrence.

The Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC) is a post–Cold War, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) institution. The EAPC is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and Central Asia. States meet to cooperate and discuss political and security issues. It was formed on 29 May 1997 at a Ministers’ meeting held in Sintra, Portugal, as the successor to the North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC), which was created in 1991.

The Partnership for Peace is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust and cooperation between the member states of NATO and other states mostly in Europe, including post-Soviet states; 18 states are members. The program contains 6 areas of cooperation, which aims to build relationships with partners through military-to-military cooperation on training, exercises, disaster planning and response, science and environmental issues, professionalization, policy planning, and relations with civilian government. During policy negotiations in the 1990s, a primary controversy regarding PfP was its ability to be interpreted as a program that is a stepping stone for joining NATO with full Article 5 guarantees.

The NATO Parliamentary Assembly serves as the consultative interparliamentary organisation for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It consists of delegates from the parliaments of the 32 NATO member countries as well as from associate and partner countries. Its current President is Michał Szczerba from Poland, elected in 2023. Its current Secretary General is Ruxandra Popa, who has been in this position since January 2020.

The Conference on Interaction and Confidence-Building Measures in Asia (CICA) is an inter-governmental forum for enhancing cooperation towards promoting peace, security and stability in Asia. It is a forum based on the recognition that there is a close link between peace, security and stability in Asia and in the rest of the world. The key idea of the Conference is based on the priority of the indivisibility of security, joint initiative and mutually beneficial interaction of small and large states.

The inaugural session of the Black Sea Forum for Partnership and Dialogue (BSF) was held on June 4–6, 2006 in Bucharest. The Forum is a Romanian initiative, initially meant to hold annual presidential-level summits and thematic or sectoral-cooperation meeting during those annual intervals. The Forum is not meant to create new regional institutions, but rather to turn into a regular consultative process among countries of the extended Black Sea region and between this group of countries and international organizations such as the European Union. After the inaugural summit, no other summits were planned.
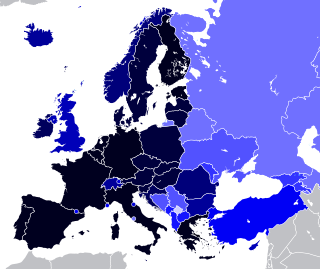
Turkey is a founding member of the United Nations, the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, has been in the Council of Europe since 1949, and in NATO since 1952. Since 2005, Turkey is in accession negotiations with the European Union, having been an associate member since 1963 and is also in European Customs Union. Turkey is also a member of the G20 industrial nations which brings together the 20 largest economies of the world.

The 2006 Riga summit or the 20th NATO Summit was a NATO summit held in the Olympic Sports Centre, Riga, Latvia from 28 to 29 November 2006. The most important topics discussed were the War in Afghanistan and the future role and borders of the alliance. Further, the summit focused on the alliance's continued transformation, taking stock of what has been accomplished since the 2002 Prague Summit. NATO also committed itself to extending further membership invitations in the upcoming 2008 Bucharest Summit. This summit was the first NATO summit held on the territory of the Baltic states.

The 2004 Istanbul summit was held in Istanbul, Turkey from 28 to 29 June 2004. It was the 18th NATO summit in which NATO's Heads of State and Governments met to make formal decisions about security topics. In general, the summit is seen as a continuation of the transformation process that began in the 2002 Prague summit, which hoped to create a shift from a Cold War alliance against Soviet aggression to a 21st-century coalition against new and out-of-area security threats. The summit consisted of four meetings.

The Istanbul Cooperation Initiative (ICI) is a NATO initiative that was launched during the organisation's 2004 Istanbul summit.

The 1999 Washington summit was the 16th NATO summit, a three-day meeting held in Washington, D.C., on April 23–25, 1999.

The 2007 Arab League Summit, also called the 2007 Riyadh Summit, refers to a convention of leaders from 21 members of the Arab League who gathered in Riyadh for the 19th Arab summit in March 2007. The summit convened on the 28 March 2007 and was preceded by a set of preparatory meetings starting on 24 March 2007. United Nations Secretary General Ban Ki-moon and the European Union's foreign policy chief Javier Solana also attended the summit. The main goal of the conference was to re-launch the Arab Peace Initiative.
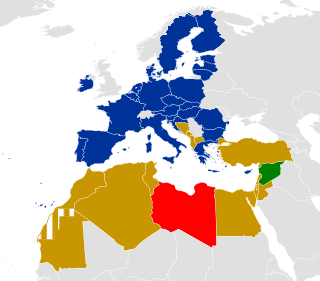
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 16 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
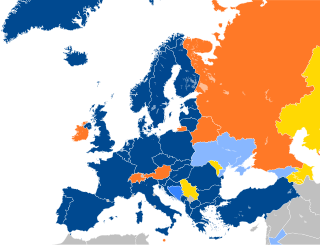
NATO maintains foreign relations with many non-member countries across the globe. NATO runs a number of programs which provide a framework for the partnerships between itself and these non-member nations, typically based on that country's location. These include the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council and the Partnership for Peace.

Bernardino León Gross is a Spanish diplomat and politician and former United Nations Special Representative and Head of the United Nations Support Mission in Libya. Prior to this appointment by United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, he served as the European Union Special Representative (EUSR) for the Southern Mediterranean. León is a former Secretary General at the office of the Spanish Prime Minister, Sherpa for the G20 and Spanish Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs. His diplomatic career has mainly been devoted to the Arab world.

Middle East economic integration refers to the process of improving economic cooperation, coordination, and connectivity among countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. This process aims to create a unified economic space that allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor across national borders within the region. The objectives behind such integration include enhancing regional trade, stimulating economic growth, achieving economies of scale, and fostering stability and peace through economic interdependence.
Serbia is a member state of several international organizations :

The relationship between Azerbaijan and NATO started in 1992 when Azerbaijan joined the newly created North Atlantic Cooperation Council. Considerable partnership between NATO and Azerbaijan dates back to 1994, when the latter joined Partnership for Peace program. Azerbaijan established a diplomatic Mission to NATO in 1997 by the Presidential Decree on 21 November.
The China–Arab States Cooperation Forum is a formal dialogue initiative between China and the Arab League established in 2004. It serves as the primary multilateral coordination mechanism between China and the Arab states.
Operation Sea Guardian was launched as a maritime security operation by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) during the Warsaw Summit in July 2016, aiming to expand NATO's role within the Mediterranean Sea.

 Egypt (joined in February 1995)
Egypt (joined in February 1995) Israel (joined in February 1995)
Israel (joined in February 1995) Mauritania (joined in February 1995)
Mauritania (joined in February 1995) Morocco (joined in February 1995)
Morocco (joined in February 1995) Tunisia (joined in February 1995)
Tunisia (joined in February 1995)