The Hephthalites, sometimes called the White Huns, were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, part of the larger group of Eastern Iranian Huns. They formed an empire, the Imperial Hephthalites, and were militarily important from 450 CE, when they defeated the Kidarites, to 560 CE, when combined forces from the First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanian Empire defeated them. After 560 CE, they established "principalities" in the area of Tokharistan, under the suzerainty of the Western Turks and of the Sasanian Empire, before the Tokhara Yabghus took over in 625.

Xionites, Chionites, or Chionitae were a nomadic people in the Central Asian regions of Transoxiana and Bactria.
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Europe as the Chionites, and may even be considered as identical to the Chionites. The 5th century Byzantine historian Priscus called them Kidarite Huns, or "Huns who are Kidarites". The Huna/Xionite tribes are often linked, albeit controversially, to the Huns who invaded Eastern Europe during a similar period. They are entirely different from the Hephthalites, who replaced them about a century later.
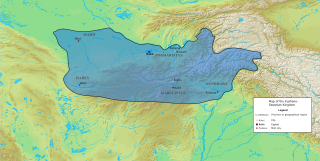
The Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom was a polity established by the Sasanian Empire in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries. The Sasanian Empire captured the provinces of Sogdia, Bactria and Gandhara from the declining Kushan Empire following a series of wars in 225 CE. The local Sasanian governors then went on to take the title of Kushanshah or "King of the Kushans", and to mint coins. They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire.

Khingila I was the founding king of the Hunnic Alkhan dynasty. He was a contemporary of Khushnavaz.

Kipunada, also Kipanadha, was probably the last ruler of the Kushan Empire around 335-350 CE. He is known for his gold coinage. He succeeded Shaka I. Kipunada was probably only a local ruler in the area of Taxila, in western Punjab, and he may have been a subject of Gupta Emperor Samudragupta.

Peroz I Kushanshah was Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 245 to 275. He was the successor of Ardashir I Kushanshah. He was an energetic ruler, who minted coins in Balkh, Herat, and Gandhara. Under him, the Kushano-Sasanians further expanded their domains into the west, pushing the weakened Kushan Empire to Mathura in North India.

The Alchon Huns, also known as the Alkhan, Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alakhana, and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and Central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India.

Ardashir I Kushanshah was the first Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 233 to 245. He was succeeded by Peroz I Kushanshah.

The Talagan copper scroll, also known as Schøyen Copper Scroll, was discovered and published in 2006 by Gudrun Melzer and Lore Sander. The scroll, dated to 492/3, mentions the four Alchon Huns kings Khingila, Toramana, Javukha, and Mehama as donors to a Buddhist reliquary stupa.

The term Iranian Huns is sometimes used for a group of different tribes that lived in Central Asia, in the historical regions of Transoxiana, Bactria, Tokharistan, Kabul Valley, and Gandhara, overlapping with the modern-day Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Eastern Iran, Pakistan, and Northwest India, between the fourth and seventh centuries. They also threatened the Northeast borders of Sasanian Iran and forced the Shahs to lead many ill-documented campaigns against them.

Peroz II Kushanshah was the penultimate Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 303 to 330. He was the successor of Hormizd II Kushanshah.

Peroz, was according to modern scholarship an early Kidarite ruler in Gandhara, right after the end of Kushano-Sasanians.

Kirada, is considered by modern scholarship as the first known ruler of the Kidarite Huns in the area of Gandhara in northwestern India, possibly at the same time as another Kidarite ruler named Yosada.

Javukha was the third known king of the Alchon Huns, in the 5th century CE. He is described as such in the Talagan copper scroll inscription, where he is also said to be Maharaja, and the "son of Sadavikha". In the scroll he also appears to be rather contemporary with Toramana.
The Kingdom of Rob was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script have been found from the archives of the Kingdom of Rob.
Hind was the name of a southeastern Sasanian province lying near the Indus River in modern-day southern Pakistan. The boundaries of the province are obscure. The Austrian historian and numismatist Nikolaus Schindel has suggested that the province may have corresponded to the Sindh region, where the Sasanians notably minted unique gold coins of themselves. According to the modern historian C. J. Brunner, the province possibly included—whenever jurisdiction was established—the areas of the Indus River, including the southern part of Punjab.

Tobazini, Gobazini or Goboziko was a ruler of southern Central Asia. He is only known from his coinage, found in Bactria and Northern Afghanistan. The legends on his coins are in Bactrian, but they are often difficult to read: a typical legend reads t/gobazini/o šauo "King Tobazini". Tobazini is often considered one of the last rulers of the Kidarites, circa 450 CE.

The Chilek silver bowl is a silver bowl found in the area of Samarkand, and considered as the "best known specimen of Hephthalite art". More specifically, the bowl seems to belong to the Alchon Huns, south of the Hindu-Kush, during the last third of the 5th century CE. The Alchons have long been considered as a part or a sub-division of the Hephthalites, or as their eastern branch, but now tend to be considered as a separate entity.
The Sasanian-Kidarite Wars were a series of military confrontations between the Sassanid Empire and the Kidarites.

![]()
![]()
![]() Me-ha-ma), ruled c.461-493, was a king of Alchon Huns dynasty. He is little known, but the Talagan copper scroll mentions him as an active ruler making a donation to a Buddhist stupa in 492/93. [1] [2] At that time, it is considered that the Alchon Huns were firmly in charge of the Buddhist region around Taxila, but had not yet started to conquer much else in the India sub-continent.
Me-ha-ma), ruled c.461-493, was a king of Alchon Huns dynasty. He is little known, but the Talagan copper scroll mentions him as an active ruler making a donation to a Buddhist stupa in 492/93. [1] [2] At that time, it is considered that the Alchon Huns were firmly in charge of the Buddhist region around Taxila, but had not yet started to conquer much else in the India sub-continent.


















