
When a fluid flows around an object, the fluid exerts a force on the object. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direction. Lift conventionally acts in an upward direction in order to counter the force of gravity, but it is defined to act perpendicular to the flow and therefore can act in any direction.

Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges,vacuum gauges or compound gauges. The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge.
In electrochemistry, the electrochemical potential (ECP), μ, is a thermodynamic measure of chemical potential that does not omit the energy contribution of electrostatics. Electrochemical potential is expressed in the unit of J/mol.
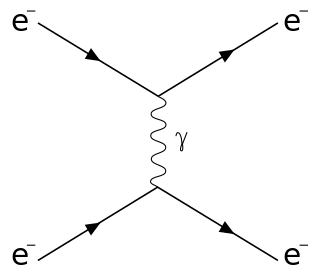
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called diffuse reflections and unscattered reflections are called specular (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering. As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering research, noted the connection between light scattering and acoustic scattering in the 1870s. Near the end of the 19th century, the scattering of cathode rays and X-rays was observed and discussed. With the discovery of subatomic particles and the development of quantum theory in the 20th century, the sense of the term became broader as it was recognized that the same mathematical frameworks used in light scattering could be applied to many other phenomena.

In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to tensile stress and may undergo elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to compressive stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has dimension of force per area, with SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa).
Stress–strain analysis is an engineering discipline that uses many methods to determine the stresses and strains in materials and structures subjected to forces. In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material.
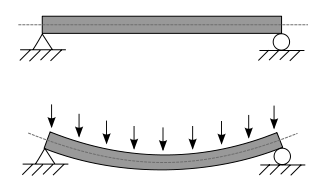
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam's axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam's support points. The total effect of all the forces acting on the beam is to produce shear forces and bending moments within the beams, that in turn induce internal stresses, strains and deflections of the beam. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile, equilibrium conditions, length, and their material.

In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape (deformation) of a structural component under load, such as the bowing of a column under compression or the wrinkling of a plate under shear. If a structure is subjected to a gradually increasing load, when the load reaches a critical level, a member may suddenly change shape and the structure and component is said to have buckled. Euler's critical load and Johnson's parabolic formula are used to determine the buckling stress of a column.
In mechanics, a cylinder stress is a stress distribution with rotational symmetry; that is, which remains unchanged if the stressed object is rotated about some fixed axis.

Electronic-hydraulic analogies are the representation of electronic circuits by hydraulic circuits. Since electric current is invisible and the processes in play in electronics are often difficult to demonstrate, the various electronic components are represented by hydraulic equivalents. Electricity was originally understood to be a kind of fluid, and the names of certain electric quantities are derived from hydraulic equivalents.

Drawing is a manufacturing process that uses tensile forces to elongate metal, glass, or plastic. As the material is drawn (pulled), it stretches and becomes thinner, achieving a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at higher temperatures to hot work large wires, rods, or hollow tubes in order to reduce forces.

In the field of solid mechanics, torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. Torsion is expressed in either the pascal (Pa), an SI unit for newtons per square metre, or in pounds per square inch (psi) while torque is expressed in newton metres (N·m) or foot-pound force (ft·lbf). In sections perpendicular to the torque axis, the resultant shear stress in this section is perpendicular to the radius.
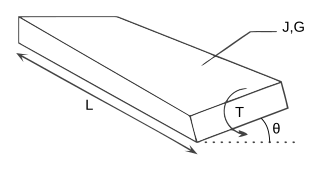
The torsion constant or torsion coefficient is a geometrical property of a bar's cross-section. It is involved in the relationship between angle of twist and applied torque along the axis of the bar, for a homogeneous linear elastic bar. The torsion constant, together with material properties and length, describes a bar's torsional stiffness. The SI unit for torsion constant is m4.

Classical cable theory uses mathematical models to calculate the electric current along passive neurites, particularly the dendrites that receive synaptic inputs at different sites and times. Estimates are made by modeling dendrites and axons as cylinders composed of segments with capacitances and resistances combined in parallel. The capacitance of a neuronal fiber comes about because electrostatic forces are acting through the very thin lipid bilayer. The resistance in series along the fiber is due to the axoplasm's significant resistance to movement of electric charge.
A cell membrane defines a boundary between a cell and its environment. The primary constituent of a membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that forms in a water-based environment due to the hydrophilic nature of the lipid head and the hydrophobic nature of the two tails. In addition there are other lipids and proteins in the membrane, the latter typically in the form of isolated rafts.
Gas diffusion electrodes (GDE) are electrodes with a conjunction of a solid, liquid and gaseous interface, and an electrical conducting catalyst supporting an electrochemical reaction between the liquid and the gaseous phase.
The gaseous detection device (GDD) is a method and apparatus for the detection of signals in the gaseous environment of an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM) and all scanned beam type of instruments that allow a minimum gas pressure for the detector to operate.
In engineering, physics, and chemistry, the study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems. While it draws from fields as diverse as continuum mechanics and thermodynamics, it places a heavy emphasis on the commonalities between the topics covered. Mass, momentum, and heat transport all share a very similar mathematical framework, and the parallels between them are exploited in the study of transport phenomena to draw deep mathematical connections that often provide very useful tools in the analysis of one field that are directly derived from the others.
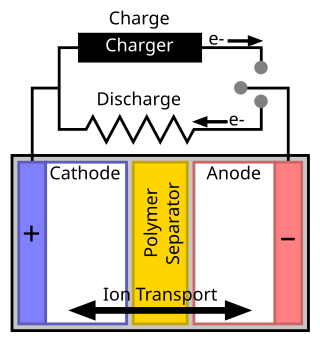
A separator is a permeable membrane placed between a battery's anode and cathode. The main function of a separator is to keep the two electrodes apart to prevent electrical short circuits while also allowing the transport of ionic charge carriers that are needed to close the circuit during the passage of current in an electrochemical cell.
Teledeltos paper is an electrically conductive paper. It is formed by a coating of carbon on one side of a sheet of paper, giving one black and one white side. Western Union developed Teledeltos paper in the late 1940s for use in spark printer based fax machines and chart recorders.












