Related Research Articles

A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.

The striatum, or corpus striatum, is a nucleus in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.

The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Dopamine is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones. These pathways and cell groups form a dopamine system which is neuromodulatory.

The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and some primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the forebrain. The ventral striatum includes the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle.

Dopaminergic pathways in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons.

The nigrostriatal pathway is a bilateral dopaminergic pathway in the brain that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) in the midbrain with the dorsal striatum in the forebrain. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is critical in the production of movement as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop. Dopaminergic neurons of this pathway release dopamine from axon terminals that synapse onto GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), located in the striatum.

The ventral tegmental area (VTA), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and other dopamine pathways; it is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. The VTA plays an important role in a number of processes, including reward cognition and orgasm, among others, as well as several psychiatric disorders. Neurons in the VTA project to numerous areas of the brain, ranging from the prefrontal cortex to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between.

The midbrain is anatomically delineated into the tectum (roof) and the tegmentum (floor). The midbrain tegmentum extends from the substantia nigra to the cerebral aqueduct in a horizontal section of the midbrain. It forms the floor of the midbrain that surrounds below the cerebral aqueduct as well as the floor of the fourth ventricle while the midbrain tectum forms the roof of the fourth ventricle. The tegmentum contains a collection of tracts and nuclei with movement-related, species-specific, and pain-perception functions. The general structures of midbrain tegmentum include red nucleus and the periaqueductal grey matter.
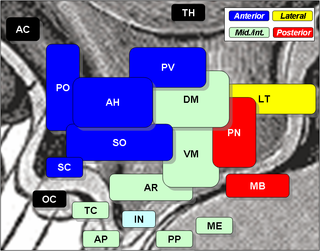
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts.

The habenula is a small bilateral neuronal structure in the brain of vertebrates, that has also been called a microstructure since it is no bigger than a pea. The naming as little rein describes its elongated shape in the epithalamus, where it borders the third ventricle, and lies alongside the pineal gland.
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a second messenger signaling cascade that induces a broad, long-lasting signal. This modulation can last for hundreds of milliseconds to several minutes. Some of the effects of neuromodulators include: altering intrinsic firing activity, increasing or decreasing voltage-dependent currents, altering synaptic efficacy, increasing bursting activity and reconfigurating synaptic connectivity.
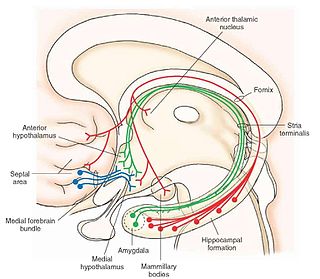
The medial forebrain bundle (MFB) is a neural pathway containing fibers from the basal olfactory regions, the periamygdaloid region and the septal nuclei, as well as fibers from brainstem regions, including the ventral tegmental area and nigrostriatal pathway.

The reward system is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience, associative learning, and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component. Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding.
The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. This region was discovered by the researchers, M. Barrot, J.Kaufling and T. Jhou. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and possesses robust functional and structural links to the dopamine pathways. Notably, both acute and chronic exposure to psychostimulants have been shown to induce FosB and ΔFosB expression in the RMTg; no other drug type has been shown to induce these proteins in the RMTg.
The mesencephalic locomotor region (MLR) is a functionally defined area of the midbrain that is associated with the initiation and control of locomotor movements in vertebrate species.
Ilana B. Witten is an American neuroscientist and professor of psychology and neuroscience at Princeton University. Witten studies the mesolimbic pathway, with a focus on the striatal neural circuit mechanisms driving reward learning and decision making.
References
- ↑ Molochnikov, Ilana; Cohen, Dana (1 January 2014). "Hemispheric differences in the mesostriatal dopaminergic system". Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience. 8: 110. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00110 . PMC 4052732 . PMID 24966817.
- ↑ Roseberry, Aaron G.; Stuhrman, Katherine; Dunigan, Anna I. (1 September 2015). "Regulation of the mesocorticolimbic and mesostriatal dopamine systems by α-melanocyte stimulating hormone and agouti-related protein". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 56: 15–25. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.06.020. ISSN 1873-7528. PMID 26116876. S2CID 43619316.
- ↑ Zhou, Fu-Ming; Wilson, Charles; Dani, John A. (1 February 2003). "Muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms in the mesostriatal dopamine systems". The Neuroscientist. 9 (1): 23–36. doi:10.1177/1073858402239588. ISSN 1073-8584. PMID 12580337. S2CID 8266496.
- ↑ Chase, Henry W.; Kumar, Poornima; Eickhoff, Simon B.; Dombrovski, Alexandre Y. (9 January 2017). "Reinforcement Learning Models and Their Neural Correlates: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis". Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. 15 (2): 435–459. doi:10.3758/s13415-015-0338-7. ISSN 1530-7026. PMC 4437864 . PMID 25665667.
- ↑ Cools, A. R. (1 March 1990). "Role of neostriatal and mesostriatal or mesolimbic dopaminergic fibres in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia: prospects, concepts and facts". Yakubutsu, Seishin, Kodo = Japanese Journal of Psychopharmacology. 10 (1): 15–34. ISSN 0285-5313. PMID 2220127.