
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them (phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a functional change of the target protein (substrate) by changing enzyme activity, cellular location, or association with other proteins. The human genome contains about 500 protein kinase genes and they constitute about 2% of all human genes. There are two main types of protein kinase. The great majority are serine/threonine kinases, which phosphorylate the hydroxyl groups of serines and threonines in their targets. Most of the others are tyrosine kinases, although additional types exist. Protein kinases are also found in bacteria and plants. Up to 30% of all human proteins may be modified by kinase activity, and kinases are known to regulate the majority of cellular pathways, especially those involved in signal transduction.

Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC.

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.

A polyhistidine-tag, best known by the trademarked name His-tag, is an amino acid motif in proteins that typically consists of at least six histidine (His) residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as a hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, or His6 tag. The tag was invented by Roche, although the use of histidines and its vectors are distributed by Qiagen. Various purification kits for histidine-tagged proteins are commercially available from multiple companies.
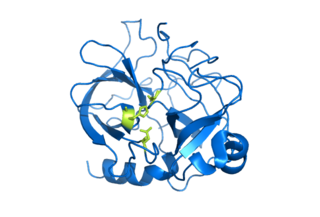
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like.
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis.

Malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP+).
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a biomolecule from a mixture, based on a highly specific macromolecular binding interaction between the biomolecule and another substance. The specific type of binding interaction depends on the biomolecule of interest; antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptor and ligand, or protein and nucleic acid binding interactions are frequently exploited for isolation of various biomolecules. Affinity chromatography is useful for its high selectivity and resolution of separation, compared to other chromatographic methods.

An ATP-binding motif is a 250-residue sequence within an ATP-binding protein’s primary structure. The binding motif is associated with a protein’s structure and/or function. ATP is a molecule of energy, and can be a coenzyme, involved in a number of biological reactions. ATP is proficient at interacting with other molecules through a binding site. The ATP binding site is the environment in which ATP catalytically actives the enzyme and, as a result, is hydrolyzed to ADP. The binding of ATP causes a conformational change to the enzyme it is interacting with.
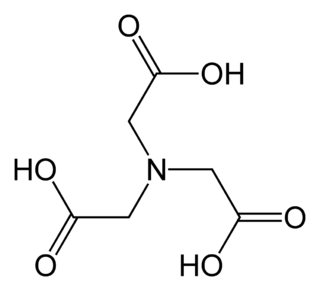
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is the aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula N(CH2CO2H)3. It is a colourless solid that is used as a chelating agent, which forms coordination compounds with metal ions (chelates) such as Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.

The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or motif found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
In molecular biology the FYVE zinc finger domain is named after the four cysteine-rich proteins: Fab 1, YOTB, Vac 1, and EEA1, in which it has been found. FYVE domains bind phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, in a way dependent on its metal ion coordination and basic amino acids. The FYVE domain inserts into cell membranes in a pH-dependent manner. The FYVE domain has been connected to vacuolar protein sorting and endosome function.

ADP-ribosylation is the addition of one or more ADP-ribose moieties to a protein. It is a reversible post-translational modification that is involved in many cellular processes, including cell signaling, DNA repair, gene regulation and apoptosis. Improper ADP-ribosylation has been implicated in some forms of cancer. It is also the basis for the toxicity of bacterial compounds such as cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, and others.

Histidine kinases (HK) are multifunctional, and in non-animal kingdoms, typically transmembrane, proteins of the transferase class of enzymes that play a role in signal transduction across the cellular membrane. The vast majority of HKs are homodimers that exhibit autokinase, phosphotransfer, and phosphatase activity. HKs can act as cellular receptors for signaling molecules in a way analogous to tyrosine kinase receptors (RTK). Multifunctional receptor molecules such as HKs and RTKs typically have portions on the outside of the cell that bind to hormone- or growth factor-like molecules, portions that span the cell membrane, and portions within the cell that contain the enzymatic activity. In addition to kinase activity, the intracellular domains typically have regions that bind to a secondary effector molecule or complex of molecules that further propagate signal transduction within the cell. Distinct from other classes of protein kinases, HKs are usually parts of a two-component signal transduction mechanisms in which HK transfers a phosphate group from ATP to a histidine residue within the kinase, and then to an aspartate residue on the receiver domain of a response regulator protein. More recently, the widespread existence of protein histidine phosphorylation distinct from that of two-component histidine kinases has been recognised in human cells. In marked contrast to Ser, Thr and Tyr phosphorylation, the analysis of phosphorylated Histidine using standard biochemical and mass spectrometric approaches is much more challenging, and special procedures and separation techniques are required for their preservation alongside classical Ser, Thr and Tyr phosphorylation on proteins isolated from human cells.

Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) is a glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the HRG gene. The HRG protein is produced in the liver, and it could also be synthesized by monocytes, macrophages, and megakaryocytes. It possesses a multi-domain structure, which makes it capable of binding to numerous ligands and modulating various biological processes including immunity, vascularization and coagulation.
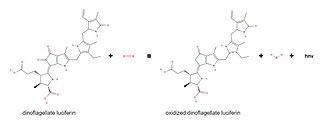
Dinoflagellate luciferase (EC 1.13.12.18, Gonyaulax luciferase) is a specific luciferase, an enzyme with systematic name dinoflagellate-luciferin:oxygen 132-oxidoreductase.
Low complexity regions (LCRs) in protein sequences, also defined in some contexts as compositionally biased regions (CBRs), are regions in protein sequences that differ from the composition and complexity of most proteins that is normally associated with globular structure. LCRs have different properties from normal regions regarding structure, function and evolution.
Transition metal amino acid complexes are a large family of coordination complexes containing the conjugate bases of the amino acids, the 2-aminocarboxylates. Amino acids are prevalent in nature, and all of them function as ligands toward the transition metals. Not included in this article are complexes of the amides and ester derivatives of amino acids. Also excluded are the polyamino acids including the chelating agents EDTA and NTA.
Protoxin-I, also known as ProTx-I, or Beta/omega-theraphotoxin-Tp1a, is a 35-amino-acid peptide neurotoxin extracted from the venom of the tarantula Thrixopelma pruriens. Protoxin-I belongs to the inhibitory cystine knot (ICK) family of peptide toxins, which have been known to potently inhibit voltage-gated ion channels. Protoxin-I selectively blocks low voltage threshold T-type calcium channels, voltage gated sodium channels and the nociceptor cation channel TRPA1. Due to its unique ability to bind to TRPA1, Protoxin-I has been implicated as a valuable pharmacological reagent with potential applications in clinical contexts with regards to pain and inflammation
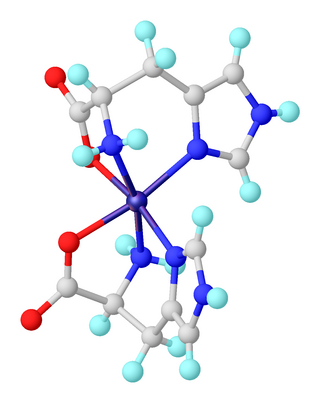
A transition metal imidazole complex is a coordination complex that has one or more imidazole ligands. Complexes of imidazole itself are of little practical importance. In contrast, imidazole derivatives, especially histidine, are pervasive ligands in biology where they bind metal cofactors.
















