
Cabernet Sauvignon is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Lebanon's Beqaa Valley. Cabernet Sauvignon became internationally recognized through its prominence in Bordeaux wines, where it is often blended with Merlot and Cabernet Franc. From France and Spain, the grape spread across Europe and to the New World where it found new homes in places like California's Napa Valley, New Zealand's Hawke's Bay, South Africa's Stellenbosch region, Australia's Margaret River, McLaren Vale and Coonawarra regions, and Chile's Maipo Valley and Colchagua. For most of the 20th century, it was the world's most widely planted premium red wine grape until it was surpassed by Merlot in the 1990s. However, by 2015, Cabernet Sauvignon had once again become the most widely planted wine grape, with a total of 341,000 hectares (3,410 km2) under vine worldwide.

Sauvignon blanc is a green-skinned grape variety that originates from the city of Bordeaux in France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French words sauvage ("wild") and blanc ("white") due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in South West France. It is possibly a descendant of Savagnin. Sauvignon blanc is planted in many of the world's wine regions, producing a crisp, dry, and refreshing white varietal wine. The grape is also a component of the famous dessert wines from Sauternes and Barsac. Sauvignon blanc is widely cultivated in France, Chile, Romania, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Bulgaria, the states of Oregon, Washington, and California in the US. Some New World Sauvignon blancs, particularly from California, may also be called "Fumé Blanc", a marketing term coined by Robert Mondavi in reference to Pouilly-Fumé.

Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone, as in the Loire's Chinon. In addition to being used in blends and produced as a varietal in Canada and the United States, it is sometimes made into ice wine in those regions.

Chile has a long history in the production of wine, with roots dating back to the 16th century when the Spanish conquistadors introduced Vitis vinifera vines to the region. In the mid-19th century, French wine varieties such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Carmenère, and Franc were introduced. During the early 1980s, the Chilean wine industry underwent a renaissance with the introduction of stainless steel fermentation tanks and the use of oak barrels for aging. This led to a rapid growth in exports as quality wine production increased. The number of wineries in Chile rose from 12 in 1995 to over 70 in 2005.

Chenin blanc is a white wine grape variety from the Loire Valley of France. Its high acidity means it can be used to make varieties from sparkling wines to well-balanced dessert wines, although it can produce very bland, neutral wines if the vine's natural vigor is not controlled. Outside the Loire, it is found in most of the New World wine regions; it is the most widely planted variety in South Africa, where it was historically also known as Steen. The grape may have been one of the first to be grown in South Africa by Jan van Riebeeck in 1655, or it may have come to that country with Huguenots fleeing France after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. Chenin blanc was often misidentified in Australia, as well, so tracing its early history in the country is not easy. It may have been introduced in James Busby's collection of 1832, but C. Waterhouse was growing Steen at Highercombe in Houghton, South Australia, by 1862.

White wine is a wine that is fermented without skin contact. The colour can be straw-yellow, yellow-green, or yellow-gold. It is produced by the alcoholic fermentation of the non-coloured pulp of grapes, which may have a skin of any colour. White wine has existed for at least 4,000 years.

Sémillon is a golden-skinned grape used to make dry and sweet white wines, mostly in France and Australia. Its thin skin and susceptibility to botrytis make it dominate the sweet wine region Sauternes AOC and Barsac AOC.

Sancerre is a French wine Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) for wine produced in the area of Sancerre in the eastern part of the Loire valley, southeast of Orléans. Almost all of the appellation lies on the left bank of the Loire, opposite Pouilly-Fumé. It is well regarded for and primarily associated with Sauvignon blanc. Some Pinot noir is also grown, accounting for around 20% of the region's production, making mostly light red wines under the designation of Sancerre Rouge. A rosé style from Pinot noir is also produced in a style similar to Beaujolais, which is produced from the Gamay grape.
A wine fault is a sensory-associated (organoleptic) characteristic of a wine that is unpleasant, and may include elements of taste, smell, or appearance, elements that may arise from a "chemical or a microbial origin", where particular sensory experiences might arise from more than one wine fault. Wine faults may result from poor winemaking practices or storage conditions that lead to wine spoilage.
South African wine has a history dating back to 1659 with the first bottle being produced in Cape Town by its founder and governor Jan van Riebeeck. Access to international markets led to new investment in the South African wine market. Production is concentrated around Cape Town and almost exclusively located within the Western Cape province, with major vineyard and production centres at Constantia, Paarl, Stellenbosch and Worcester.

3-Mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol, also known as MMB, is a common odorant found in food and cat urine. The aromas ascribed to MMB include catty, roasty, broth-like, meaty, and savory, or similar to cooked leeks.

Victorian wine is wine made in the Australian state of Victoria. With over 600 wineries, Victoria has more wine producers than any other Australian wine-producing state but ranks third in overall wine production due to the lack of a mass bulk wine-producing area like South Australia's Riverland and New South Wales's Riverina. Viticulture has existed in Victoria since the 19th century and experienced a high point in the 1890s when the region produced more than half of all wine produced in Australia. The phylloxera epidemic that soon followed took a hard toll on the Victoria wine industry which did not fully recover till the 1950s.

Friuli-Venezia Giulia wine is wine made in the northeastern Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. There are 11 denominazione di origine controllata (DOC) and 3 denominazione di origine controllata e garantita (DOCG) in the Friuli-Venezia Giulia area. The region has 3 indicazione geografica tipica (IGT) designations Alto Livenza, delle Venezie and Venezia Giulia. Nearly 62% of the wine produced in the region falls under a DOC designation. The area is known predominantly for its white wines, which are considered some of the best examples of Italian wine in that style. Along with the Veneto and Trentino-Alto Adige, the Friuli-Venezia Giulia forms the Tre Venezie wine region, which ranks with Tuscany and Piedmont as Italy's world class wine regions.

The aromas of wine are more diverse than its flavours. The human tongue is limited to the primary tastes perceived by taste receptors on the tongue – sourness, bitterness, saltiness, sweetness and savouriness. The wide array of fruit, earthy, leathery, floral, herbal, mineral, and woodsy flavour present in wine are derived from aroma notes sensed by the olfactory bulb. In wine tasting, wine is sometimes smelled before taking a sip in order to identify some components of the wine that may be present. Different terms are used to describe what is being smelled. The most basic term is aroma which generally refers to a "pleasant" smell as opposed to odour which refers to an unpleasant smell or possible wine fault. The term aroma may be further distinguished from bouquet which generally refers to the smells that arise from the chemical reactions of fermentation and aging of the wine.

Touraine is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) in the Loire Valley wine region in France that produce dry, white wines and red wines rich in tannins. The AOC status was awarded by a decree of December 24, 1939. The wine-growing area extends over 5,300 hectares departments of Indre-et-Loire, Indre and Loir-et-Cher and comprises a total of 70 communes and it is thus a "subregional" appellation covering the same area as a number of local AOCs.

Incrocio Manzoni or Manzoni grapes is a family of grape varieties named after Professor Luigi Manzoni (1888-1968) of Italy's oldest school of oenology located in Conegliano, in the Veneto region. Manzoni created the new grape varieties by selecting, crossing and grafting vines from various vineyards during the 1920s and 1930s. The family includes both white and red grape varieties. Although most Manzonis are grown in northeastern Italy, they are mainly grown in the Piave area of Province of Treviso and are only now starting to be sold commercially in Europe and the United States.
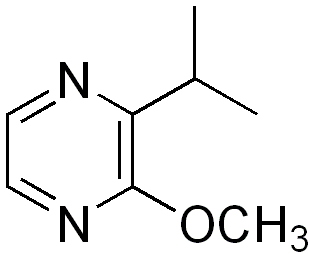
Isopropyl methoxypyrazine (IPMP) is a methoxypyrazine, a class of chemical compounds that produce odors. The odor is rather undesirable and is produced by the Asian lady beetle or by the actinomycete Streptomyces sp. It can be detected by human taste at concentrations of as low as 2 nanograms per litre.
Cabernet blanc is a white German and Swiss wine grape variety that is a crossing of the French wine grape Cabernet Sauvignon and Regent. The grape was bred by Swiss grape breeder Valentin Blattner in 1991. Cabernet blanc has strong resistance to most grape disease including botrytis bunch rot, downy and powdery mildew and tends to produce loose clusters of small, thick-skinned grape berries which can hang on the vine late into the harvest season to produce dessert wines. Today the grape is found primarily in the Palatinate wine region of Germany with some experimental plantings in Spain and the Netherlands. In France, in the Languedoc, Domaine La Colombette is heavily investing in PIWI grapes. Amongst others the Cabernet Blanc in their cuvée "Au Creux du Nid", is gaining wide acclaim.
Cygne blanc is a white Australian wine grape variety that is a seedling of Cabernet Sauvignon that was discovered in 1989 in Western Australia. Unlike Cabernet blanc, which was a crossing of Cabernet Sauvignon and Resistenzpartner, and Shalistin which is a white-berried color mutation of Cabernet Sauvignon, Cygne blanc is a selfling that sprang from a seed of a Cabernet Sauvignon berry that fell on the ground and took root.
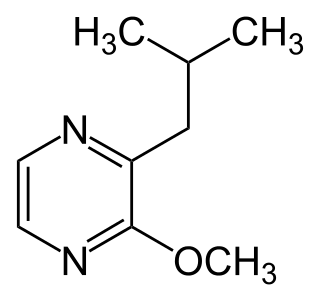
3-Isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine is a methoxypyrazine that is very similar to isopropyl methoxy pyrazine except that the alkyl side-group contains an isobutyl group attached to the carbon alpha to the methoxy sidegroup instead of an isopropyl side-group at that same carbon position.
















