
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a member of a group of genetic disorders called inherited retinal dystrophy (IRD) that cause loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision. As peripheral vision worsens, people may experience "tunnel vision". Complete blindness is uncommon. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual and often begins in childhood.

Amblyopia, also called lazy eye, is a disorder of sight in which the brain fails to fully process input from one eye and over time favors the other eye. It results in decreased vision in an eye that typically appears normal in other aspects. Amblyopia is the most common cause of decreased vision in a single eye among children and younger adults.
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and of the interpretative faculty of the brain.

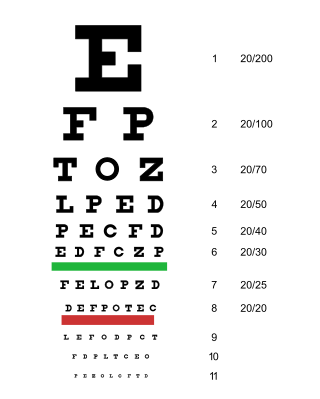
An eye chart is a chart used to measure visual acuity comprising lines of optotypes in ranges of sizes. Optotypes are the letters or symbols shown on an eye chart. Eye charts are often used by health care professionals, such as optometrists, physicians and nurses, to screen persons for vision impairment. Ophthalmologists, physicians who specialize in the eye, also use eye charts to monitor the visual acuity of their patients in response to various therapies such as medications or surgery.

The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and keeping balance.

Electroretinography measures the electrical responses of various cell types in the retina, including the photoreceptors, inner retinal cells, and the ganglion cells. Electrodes are placed on the surface of the cornea or on the skin beneath the eye to measure retinal responses. Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) responses are measured with an EOG test with skin-contact electrodes placed near the canthi. During a recording, the patient's eyes are exposed to standardized stimuli and the resulting signal is displayed showing the time course of the signal's amplitude (voltage). Signals are very small, and typically are measured in microvolts or nanovolts. The ERG is composed of electrical potentials contributed by different cell types within the retina, and the stimulus conditions can elicit stronger response from certain components.

Central serous chorioretinopathy, also known as central serous retinopathy (CSR), is an eye disease that causes visual impairment, often temporary, usually in one eye. When the disorder is active it is characterized by leakage of fluid under the retina that has a propensity to accumulate under the central macula. This results in blurred or distorted vision (metamorphopsia). A blurred or gray spot in the central visual field is common when the retina is detached. Reduced visual acuity may persist after the fluid has disappeared.
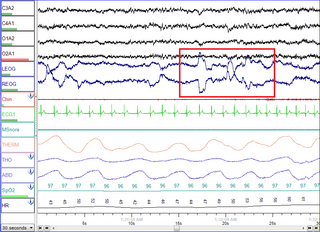
Electrooculography (EOG) is a technique for measuring the corneo-retinal standing potential that exists between the front and the back of the human eye. The resulting signal is called the electrooculogram. Primary applications are in ophthalmological diagnosis and in recording eye movements. Unlike the electroretinogram, the EOG does not measure response to individual visual stimuli.

The LEA Vision Test System is a series of pediatric vision tests designed specifically for children who do not know how to read the letters of the alphabet that are typically used in eye charts. There are numerous variants of the LEA test which can be used to assess the visual capabilities of near vision and distance vision, as well as several other aspects of occupational health, such as contrast sensitivity, visual field, color vision, visual adaptation, motion perception, and ocular function and accommodation (eye).

Fixation disparity is a tendency of the eyes to drift in the direction of the heterophoria. While the heterophoria refers to a fusion-free vergence state, the fixation disparity refers to a small misalignment of the visual axes when both eyes are open in an observer with normal fusion and binocular vision. The misalignment may be vertical, horizontal or both. The misalignment is much smaller than that of strabismus. While strabismus prevents binocular vision, fixation disparity keeps binocular vision, however it may reduce a patient's level of stereopsis. A patient may have a different fixation disparity at distance than near. Observers with a fixation disparity are more likely to report eye strain in demanding visual tasks; therefore, tests of fixation disparity belong to the diagnostic tools used by eye care professionals: remediation includes vision therapy, prism eye glasses, or visual ergonomics at the workplace.
Stargardt disease is the most common inherited single-gene retinal disease. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants (STGD1). However, there are Stargardt-like diseases with mimicking phenotypes that are referred to as STGD3 and STGD4, and have a autosomal dominant inheritance due to defects with ELOVL4 or PROM1 genes, respectively. It is characterized by macular degeneration that begins in childhood, adolescence or adulthood, resulting in progressive loss of vision.
Sattler's layer, named after Hubert Sattler, an Austrian ophthalmologist, is one of five layers of medium-diameter blood vessels of the choroid, and a layer of the eye. It is situated between the Bruch's membrane, choriocapillaris below, and the Haller's layer and suprachoroidea above, respectively. The origin seems to be related to a continuous differentiation throughout the growth of the tissue and even further differentiation during adulthood.
The International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV) is an association that promotes research and applications of electrophysiological methods in clinical diagnosis of ophthalmological diseases. The society was founded in 1958 as the International Society for Clinical Electroretinography (ISCERG) and holds annual meetings that take place at changing locations. The official journal is Documenta Ophthalmologica. The society also establishes standards for electrophysiological diagnosis.

Crowding is a perceptual phenomenon where the recognition of objects presented away from the fovea is impaired by the presence of other neighbouring objects. It has been suggested that crowding occurs due to mandatory integration of the crowded objects by a texture-processing neural mechanism, but there are several competing theories about the underlying mechanisms. It is considered a kind of grouping since it is "a form of integration over space as target features are spuriously combined with flanker features."

Chloroquine retinopathy is a form of toxic retinopathy caused by the drugs chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine, which are sometimes used in the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. This eye toxicity limits long-term use of the drugs.
Cyclotropia is a form of strabismus in which, compared to the correct positioning of the eyes, there is a torsion of one eye about the eye's visual axis. Consequently, the visual fields of the two eyes appear tilted relative to each other. The corresponding latent condition – a condition in which torsion occurs only in the absence of appropriate visual stimuli – is called cyclophoria.
Instrument myopia is the tendency of a person with normal eyes to focus them too close when looking into an optical instrument at its image. Optical instruments include viewfinders, telescopes, binoculars, and microscopes. For example, through a microscope, a person might focus the eyes to one meter distance although it can present an image at six meters distance.

Louise Littig Sloan was an American ophthalmologist and vision scientist. She is credited for being a pioneer of the sub-division of clinical vision research, contributing more than 100 scientific articles in which she either authored or co-authored. Her most notable work was in the area of visual acuity testing where she developed and improved equipment. Sloan received her Ph.D. from Bryn Mawr College in experimental psychology. She spent a short period of time in both Bryn Mawr's experimental psychology program as well as the Department of Ophthalmology at Harvard Medical School. The majority of her career, however, was spent at Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute where she directed the Wilmer Laboratory of Physiological Optics for 44 years. In 1971, Sloan was the second woman awarded the prestigious Edgar D. Tillyer Award by Optica (formerly Optical Society for her many achievements in the field of vision.

Congenital blindness refers to blindness present at birth. Congenital blindness is sometimes used interchangeably with "Childhood Blindness." However, current literature has various definitions of both terms. Childhood blindness encompasses multiple diseases and conditions present in ages up to 16 years old, which can result in permanent blindness or severe visual impairment over time. Congenital blindness is a hereditary disease and can be treated by gene therapy. Visual loss in children or infants can occur either at the prenatal stage or postnatal stage. There are multiple possible causes of congenital blindness. In general, 60% of congenital blindness cases are contributed from prenatal stage and 40% are contributed from inherited disease. However, most of the congenital blindness cases show that it can be avoidable or preventable with early treatment.

The TCO Certified certification was initially created by the Swedish Confederation of Professional Employees (TCO) to guarantee that computer products purchased by employers maintain ecological standards and were sufficiently ergonomic to prevent long term health issues for users. It became known during the 1990s as a certification for computer displays. Dating back to 1992, TCO is one of the oldest certifications for end user electronics.














