Related Research Articles

Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services.

A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with the most common being an organism altered in a way that "does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural recombination". A wide variety of organisms have been genetically modified (GM), from animals to plants and microorganisms. Genes have been transferred within the same species, across species, and even across kingdoms. New genes can be introduced, or endogenous genes can be enhanced, altered, or knocked out.

Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome.

The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.

Leroy "Lee" Edward Hood is an American biologist who has served on the faculties at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the University of Washington. Hood has developed ground-breaking scientific instruments which made possible major advances in the biological sciences and the medical sciences. These include the first gas phase protein sequencer (1982), for determining the sequence of amino acids in a given protein; a DNA synthesizer (1983), to synthesize short sections of DNA; a peptide synthesizer (1984), to combine amino acids into longer peptides and short proteins; the first automated DNA sequencer (1986), to identify the order of nucleotides in DNA; ink-jet oligonucleotide technology for synthesizing DNA and nanostring technology for analyzing single molecules of DNA and RNA.

In genetic engineering, a gene gun or biolistic particle delivery system is a device used to deliver exogenous DNA (transgenes), RNA, or protein to cells. By coating particles of a heavy metal with a gene of interest and firing these micro-projectiles into cells using mechanical force, an integration of desired genetic information can be introduced into desired cells. The technique involved with such micro-projectile delivery of DNA is often referred to as biolistics, short for "biological ballistics".
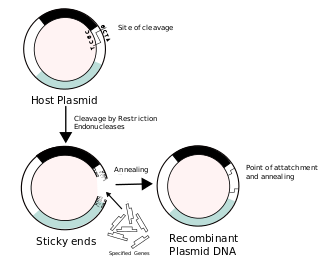
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome.
Tom Maniatis, is an American professor of molecular and cellular biology. He is a professor at Columbia University, and serves as the Scientific Director and CEO of the New York Genome Center.

In immunology, epitope mapping is the process of experimentally identifying the binding site, or epitope, of an antibody on its target antigen. Identification and characterization of antibody binding sites aid in the discovery and development of new therapeutics, vaccines, and diagnostics. Epitope characterization can also help elucidate the binding mechanism of an antibody and can strengthen intellectual property (patent) protection. Experimental epitope mapping data can be incorporated into robust algorithms to facilitate in silico prediction of B-cell epitopes based on sequence and/or structural data.

DNA shuffling, also known as molecular breeding, is an in vitro random recombination method to generate mutant genes for directed evolution and to enable a rapid increase in DNA library size. Three procedures for accomplishing DNA shuffling are molecular breeding which relies on homologous recombination or the similarity of the DNA sequences, restriction enzymes which rely on common restriction sites, and nonhomologous random recombination which requires the use of hairpins. In all of these techniques, the parent genes are fragmented and then recombined.
Psychiatric genetics is a subfield of behavioral neurogenetics and behavioral genetics which studies the role of genetics in the development of mental disorders. The basic principle behind psychiatric genetics is that genetic polymorphisms are part of the causation of psychiatric disorders.

Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder involving the kidneys, ears, and neck. It often has also been described as Melnick-Fraser syndrome.

Genetically modified plants have been engineered for scientific research, to create new colours in plants, deliver vaccines, and to create enhanced crops. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. Many plant cells are pluripotent, meaning that a single cell from a mature plant can be harvested and then under the right conditions form a new plant. This ability is most often taken advantage by genetic engineers through selecting cells that can successfully be transformed into an adult plant which can then be grown into multiple new plants containing transgene in every cell through a process known as tissue culture.

Eyes absent homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EYA1 gene.

Pramod Tandon is an India Plant Biotechnologist and academic. He is a former Professor of Botany & Vice-Chancellor of North-Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Shillong and Chief Executive Officer of Biotech Park, Lucknow. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour Padma Sri in 2009, for his contributions to science.

Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing. In medicine the technique is used to diagnose and monitor disease, detect risk, and decide which therapies will work best for individual patients, and in agricultural biosecurity similarly to monitor crop- and livestock disease, estimate risk, and decide what quarantine measures must be taken.
Avadhesha Surolia is a glycobiologist at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore. He was born in Kishangarh, Rajasthan, India. Presently, he is an honorary professor at the Molecular Biophysics Unit, IISc and holds the Bhatnagar fellowship of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). He is known for his work on lectin structure and interactions, orientation and dynamics of cell surface carbohydrate receptors and protein folding, diabetes, antimalarials and anti-cancer agents based on curcumin, flavonoids, etc. In addition, neuropathic pain, neurodegenerative disorders and the link between immunity and obsessive–compulsive disorder are areas of his current interest

Andrea Crisanti is an Italian full professor of microbiology at the University of Padua and politician. He previously was professor of Molecular Parasitology at Imperial College London. He is best known for the development of genetically manipulated mosquitoes with the objective to interfere with either their reproductive rate or the capability to transmit diseases such as malaria.
Keiichi Itakura is an organic chemist and a Professor in the Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology at the Beckman Research Institute at City of Hope National Medical Center.

Shiladitya DasSarma is a molecular biologist well-known for contributions to the biology of halophilic and extremophilic microorganisms. He is a Professor in the University of Maryland Baltimore. He earned a PhD degree in Biochemistry from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a BS degree in Chemistry from Indiana University Bloomington. Prior to taking a faculty position, he conducted research at the Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and Pasteur Institute, Paris.
References
- ↑ Oto, M; Miyake, S; Yuasa, Y (2013-03-25). "Optimization of nonradioisotopic single strand conformation polymorphism analysis with a conventional minislab gel electrophoresis apparatus". Anal. Biochem. 213 (1): 19–22. doi:10.1006/abio.1993.1379. PMID 8238876.
- ↑ Oto, M (2013-03-25). "Identification of Mutated p53 in Cancers by Nongel-Sieving Capillary Electrophoretic SSCP Analysis". Methods Mol Med. 27: 127–38. doi:10.1385/1-59259-689-4:127. ISBN 978-1-59259-689-8. PMID 21374295.
- ↑ Tomita, N; Oto, M (2013-03-25). "Molecular genetic diagnosis of familial tumors". Int J Clin Oncol. 9 (4): 246–56. doi:10.1007/s10147-004-0421-5. PMID 15375700. S2CID 25875725.
- ↑ PB