Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. Although usually just a cosmetic ailment, in some cases they cause fatigue, pain, itching, and nighttime leg cramps. These veins typically develop in the legs, just under the skin. Their complications can include bleeding, skin ulcers, and superficial thrombophlebitis. Varices in the scrotum are known as varicocele, while those around the anus are known as hemorrhoids. The physical, social, and psychological effects of varicose veins can lower their bearers' quality of life.

Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.

A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck, chest, groin, or through veins in the arms.
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram.

In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.

The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.
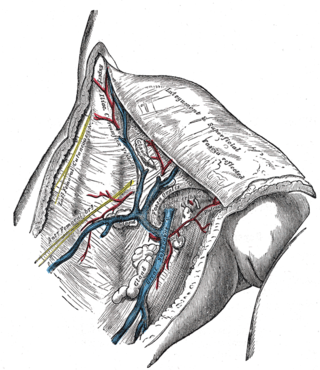
The great saphenous vein (GSV) or long saphenous vein is a large, subcutaneous, superficial vein of the leg. It is the longest vein in the body, running along the length of the lower limb, returning blood from the foot, leg and thigh to the deep femoral vein at the femoral triangle.
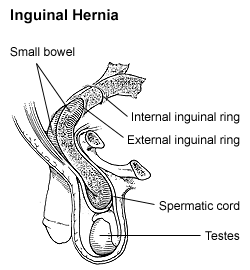
An inguinal hernia or groin hernia is a hernia (protrusion) of abdominal cavity contents through the inguinal canal. Symptoms, which may include pain or discomfort especially with or following coughing, exercise, or bowel movements, are absent in about a third of patients. Symptoms often get worse throughout the day and improve when lying down. A bulging area may occur that becomes larger when bearing down. Inguinal hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the intestine is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness of the area.
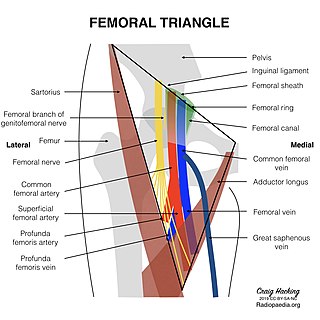
In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus as the continuation of the popliteal vein. The great saphenous vein, and the deep femoral vein drain into the femoral vein in the femoral triangle when it becomes known as the common femoral vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. Its major tributaries are the deep femoral vein, and the great saphenous vein. The femoral vein contains valves.
The small saphenous vein is a relatively large superficial vein of the posterior leg.
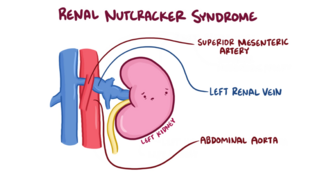
The nutcracker syndrome (NCS) results most commonly from the compression of the left renal vein (LRV) between the abdominal aorta (AA) and superior mesenteric artery (SMA), although other variants exist. The name derives from the fact that, in the sagittal plane and/or transverse plane, the SMA and AA appear to be a nutcracker crushing a nut.
Femoral hernias are hernias which occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of all hernias. While femoral hernias can occur in both males and females, almost all develop in women due to the increased width of the female pelvis. Femoral hernias are more common in adults than in children. Those that do occur in children are more likely to be associated with a connective tissue disorder or with conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure. Seventy percent of pediatric cases of femoral hernias occur in infants under the age of one.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
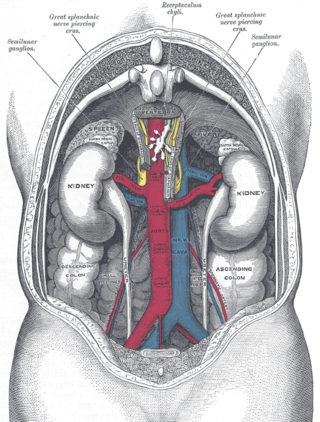
Ovarian vein syndrome is a rare condition in which dilation of the ovarian vein compresses the ureter. This causes chronic or colicky abdominal pain, back pain and/or pelvic pain. The pain can worsen on lying down or between ovulation and menstruation. There can also be an increased tendency towards urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis. The right ovarian vein is most commonly involved, although the disease can be left-sided or affect both sides. It is currently classified as a form of pelvic congestion syndrome.

Congenital stenosis of vena cava is a congenital anomaly in which the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava has an aberrant interruption or coarctation.

The anterior accessory saphenous vein is a special anterior tributary of the great saphenous vein (GSV), draining the antero-lateral face of the thigh.

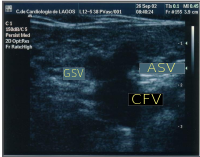
Ultrasonography of suspected or previously confirmed chronic venous insufficiency of leg veins is a risk-free, non-invasive procedure. It gives information about the anatomy, physiology and pathology of mainly superficial veins. As with heart ultrasound (echocardiography) studies, venous ultrasonography requires an understanding of hemodynamics in order to give useful examination reports. In chronic venous insufficiency, sonographic examination is of most benefit; in confirming varicose disease, making an assessment of the hemodynamics, and charting the progression of the disease and its response to treatment. It has become the reference standard for examining the condition and hemodynamics of the lower limb veins. Particular veins of the deep venous system (DVS), and the superficial venous system (SVS) are looked at. The great saphenous vein (GSV), and the small saphenous vein (SSV) are superficial veins which drain into respectively, the common femoral vein and the popliteal vein. These veins are deep veins. Perforator veins drain superficial veins into the deep veins. Three anatomic compartments are described, (N1) containing the deep veins, (N2) containing the perforator veins, and (N3) containing the superficial veins, known as the saphenous compartment. This compartmentalisation makes it easier for the examiner to systematize and map. The GSV can be located in the saphenous compartment where together with the Giacomini vein and the accessory saphenous vein (ASV) an image resembling an eye, known as the 'eye sign' can be seen. The ASV which is often responsible for varicose veins, can be located at the 'alignment sign', where it is seen to align with the femoral vessels.

Pain in the hip is the experience of pain in the muscles or joints in the hip/ pelvic region, a condition commonly arising from any of a number of factors. Sometimes it is closely associated with lower back pain.
In medicine, vein graft failure (VGF) is a condition in which vein grafts, which are used as alternative conduits in bypass surgeries, get occluded.

Ultrasonography in suspected deep vein thrombosis focuses primarily on the femoral vein and the popliteal vein, because thrombi in these veins are associated with the greatest risk of harmful pulmonary embolism.