
A tablet is a pharmaceutical oral dosage form or solid unit dosage form. Tablets may be defined as the solid unit dosage form of medication with suitable excipients. It comprises a mixture of active substances and excipients, usually in powder form, that are pressed or compacted into a solid dose. The main advantages of tablets are that they ensure a consistent dose of medicine that is easy to consume.

Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the absorption or emission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths. Although spectrophotometry is most commonly applied to ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation, modern spectrophotometers can interrogate wide swaths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including x-ray, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and/or microwave wavelengths.
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication. They may be used to enhance the active ingredient’s therapeutic properties; to facilitate drug absorption; to reduce viscosity; to enhance solubility; to improve long-term stabilization ; or to add bulk to solid formulations that have small amounts of potent active ingredients. During the manufacturing process, excipients can improve the handling of active substances and facilitate powder flow. The choice of excipients depends on factors such as the intended route of administration, the dosage form, and compatibility with the active ingredient.
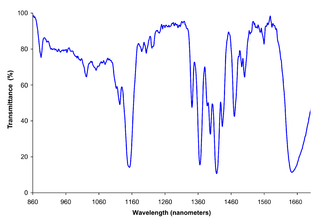
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar, pulse oximetry, functional neuroimaging, sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics, rehabilitation, neonatal research, brain computer interface, urology, and neurology. There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical, food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry, combustion research and knowledge.
Micronization is the process of reducing the average diameter of a solid material's particles. Traditional techniques for micronization focus on mechanical means, such as milling and grinding. Modern techniques make use of the properties of supercritical fluids and manipulate the principles of solubility.

In the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, encapsulation refers to a range of dosage forms—techniques used to enclose medicines—in a relatively stable shell known as a capsule, allowing them to, for example, be taken orally or be used as suppositories. The two main types of capsules are:
A particle counter is used for monitoring and diagnosing particle contamination within specific clean media, including air, water and chemicals. Particle counters are used in a variety of applications in support of clean manufacturing practices, industries include: electronic components and assemblies, pharmaceutical drug products and medical devices, and industrial technologies such as oil and gas.

An orally disintegrating tablet or orally dissolving tablet (ODT) is a drug dosage form available for a limited range of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. ODTs differ from traditional tablets in that they are designed to be dissolved on the tongue rather than swallowed whole. The ODT serves as an alternative dosage form for patients who experience dysphagia or for where compliance is a known issue and therefore an easier dosage form to take ensures that medication is taken. Common among all age groups, dysphagia is observed in about 35% of the general population, as well as up to 60% of the elderly institutionalized population and 18-22% of all patients in long-term care facilities ODTs may have a faster onset of effect than tablets or capsules, and have the convenience of a tablet that can be taken without water. During the last decade, ODTs have become available in a variety of therapeutic markets, both OTC and by prescription.
Chemical imaging is the analytical capability to create a visual image of components distribution from simultaneous measurement of spectra and spatial, time information. Hyperspectral imaging measures contiguous spectral bands, as opposed to multispectral imaging which measures spaced spectral bands.
Pharmaceutical formulation, in pharmaceutics, is the process in which different chemical substances, including the active drug, are combined to produce a final medicinal product. The word formulation is often used in a way that includes dosage form.

High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) serves as an extension of thin-layer chromatography (TLC), offering robustness, simplicity, speed, and efficiency in the quantitative analysis of compounds. This TLC-based analytical technique enhances compound resolution for quantitative analysis. Some of these improvements involve employing higher-quality TLC plates with finer particle sizes in the stationary phase, leading to improved resolution. Additionally, the separation can be further refined through repeated plate development using a multiple development device. As a result, HPTLC provides superior resolution and lower Limit of Detection (LODs).
Transmission Raman spectroscopy (TRS) is a variant of Raman spectroscopy which is advantageous in probing bulk content of diffusely scattering samples. Although it was demonstrated in the early days of Raman spectroscopy it was not exploited in practical settings until much later, probably due to limitations of technology at the time. It was rediscovered in 2006, where the authors showed that it was capable of allowing Raman spectroscopy through many millimetres of tabletted or powdered samples. In addition, this research has also identified several highly beneficial analytical properties of this approach, including the ability to probe bulk content of powders and tissue in the absence of subsampling and to reject Raman and fluorescence components originating from the surface of the sample.
Acoustic resonance spectroscopy (ARS) is a method of spectroscopy in the acoustic region, primarily the sonic and ultrasonic regions. ARS is typically much more rapid than HPLC and NIR. It is non destructive and requires no sample preparation as the sampling waveguide can simply be pushed into a sample powder/liquid or in contact with a solid sample.
Reading Scientific Services Ltd. (RSSL) is a British company providing scientific analysis, consultancy, product development and training to the global food, drink, healthcare, pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical and consumer goods sectors. It has been inspected by regulatory authorities including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and the United Kingdom Accreditation Service.

Pharmaceutical manufacturing is the process of industrial-scale synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs as part of the pharmaceutical industry. The process of drug manufacturing can be broken down into a series of unit operations, such as milling, granulation, coating, tablet pressing, and others.

Malvern Panalytical is a Spectris plc company. The company is a manufacturer and supplier of laboratory analytical instruments. It has been influential in the development of the Malvern Correlator, and it remains notable for its work in the advancement of particle sizing technology. The company produces technology for materials analysis and principal instruments designed to measure the size, shape and charge of particles. Additional areas of development include equipment for rheology measurements, chemical imaging and chromatography. In 2017, they merged with PANalytical to form Malvern Panalytical Ltd.

Tableting is a method of pressing medicine or candy into tablets. Confectionery manufacture shares many similarities with pharmaceutical production.

Effervescent or carbon tablets are tablets which are designed to dissolve in water and release carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is generated by a reaction of a compound containing bicarbonate, such as sodium bicarbonate or magnesium bicarbonate, with an acid such as citric acid or tartaric acid. Both compounds are present in the tablet in powder form and start reacting as soon as they dissolve in water.
Ultrapure water (UPW), high-purity water or highly purified water (HPW) is water that has been purified to uncommonly stringent specifications. Ultrapure water is a term commonly used in manufacturing to emphasize the fact that the water is treated to the highest levels of purity for all contaminant types, including: organic and inorganic compounds; dissolved and particulate matter; volatile and non-volatile; reactive, and inert; hydrophilic and hydrophobic; and dissolved gases.

AFM-IR or infrared nanospectroscopy is one of a family of techniques that are derived from a combination of two parent instrumental techniques. AFM-IR combines the chemical analysis power of infrared spectroscopy and the high-spatial resolution of scanning probe microscopy (SPM). The term was first used to denote a method that combined a tuneable free electron laser with an atomic force microscope equipped with a sharp probe that measured the local absorption of infrared light by a sample with nanoscale spatial resolution.










