Related Research Articles

Bacterial lawn is a term used by microbiologists to describe the appearance of bacterial colonies when all the individual colonies on a Petri dish agar plate merge to form a field or mat of bacteria. Bacterial lawns find use in screens for antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage titering.

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology.

Bacteriological water analysis is a method of analysing water to estimate the numbers of bacteria present and, if needed, to find out what sort of bacteria they are. It represents one aspect of water quality. It is a microbiological analytical procedure which uses samples of water and from these samples determines the concentration of bacteria. It is then possible to draw inferences about the suitability of the water for use from these concentrations. This process is used, for example, to routinely confirm that water is safe for human consumption or that bathing and recreational waters are safe to use.
A fecal coliform is a facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-sporulating bacterium. Coliform bacteria generally originate in the intestines of warm-blooded animals. Fecal coliforms are capable of growth in the presence of bile salts or similar surface agents, are oxidase negative, and produce acid and gas from lactose within 48 hours at 44 ± 0.5°C. The term "thermotolerant coliform" is more correct and is gaining acceptance over "fecal coliform".

Antibiotic sensitivity testing or antibiotic susceptibility testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It is used because bacteria may have resistance to some antibiotics. Sensitivity testing results can allow a clinician to change the choice of antibiotics from empiric therapy, which is when an antibiotic is selected based on clinical suspicion about the site of an infection and common causative bacteria, to directed therapy, in which the choice of antibiotic is based on knowledge of the organism and its sensitivities.
A colony-forming unit is a unit used in microbiology. It estimates the number of bacteria or fungal cells in a sample which are viable, able to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions. Counting with colony-forming units requires culturing the microbes and counts only viable cells, in contrast with microscopic examination which counts all cells, living or dead. The visual appearance of a colony in a cell culture requires significant growth, and when counting colonies it is uncertain if the colony arose from one cell or a group of cells. Expressing results as colony-forming units reflects this uncertainty.
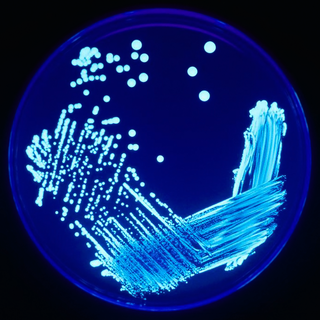
In microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested.
Total viable organism is a term used in microbiology to quantify the amount of microorganisms present in a sample. Each sample is usually cultured on a variety of agar plates often containing different types of selective media. The colony-forming units (CFUs) are calculated after allowing time for growth.

The 3M Petrifilm plate is an all-in-one plating system made by the Food Safety Division of the 3M Company. They are heavily used in many microbiology-related industries and fields to culture various micro-organisms and are meant to be a more efficient method for detection and enumeration compared to conventional plating techniques. A majority of its use is for the testing of foodstuffs.
Total viable count (TVC), gives a quantitative estimate of the concentration of microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast or mould spores in a sample. The count represents the number of colony forming units (cfu) per g of the sample.

Etest is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections.
Plate Count Agar (PCA), also called Standard Methods Agar (SMA), is a microbiological growth medium commonly used to assess or to monitor "total" or viable bacterial growth of a sample. PCA is not a selective medium.

A serial dilution is the stepwise dilution of a substance in solution. Usually the dilution factor at each step is constant, resulting in a geometric progression of the concentration in a logarithmic fashion. A ten-fold serial dilution could be 1 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M ... Serial dilutions are used to accurately create highly diluted solutions as well as solutions for experiments resulting in concentration curves with a logarithmic scale. A tenfold dilution for each step is called a logarithmic dilution or log-dilution, a 3.16-fold (100.5-fold) dilution is called a half-logarithmic dilution or half-log dilution, and a 1.78-fold (100.25-fold) dilution is called a quarter-logarithmic dilution or quarter-log dilution. Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including biochemistry, pharmacology, microbiology, and physics.
A dip slide is a test for the presence of microorganisms in liquids. The use of dip slides is the method most frequently used to measure and observe microbial activity in liquid-based systems. It is often used in testing cooling systems. Dip slides are often used to determine the presence of slime forming bacteria in cooling & industrial water systems. The Health and Safety Executive's (HSE) recommends the use of dipslides to monitor the general activity of aerobic bacteria. The dip slide test consists of a sterile culture medium on a plastic carrier that is dipped into the liquid to be sampled. The culture is then incubated, allowing for microbial growth. Most Dip slides consist of 1 - 2 agars attached to a flexible plastic paddle, this allows full contact of the agar onto the desired area for testing. Most Dipslides come in a circular clear shatterproof tube that can be inserted into a dip-slide incubator.
Cell counting is any of various methods for the counting or similar quantification of cells in the life sciences, including medical diagnosis and treatment. It is an important subset of cytometry, with applications in research and clinical practice. For example, the complete blood count can help a physician to determine why a patient feels unwell and what to do to help. Cell counts within liquid media are usually expressed as a number of cells per unit of volume, thus expressing a concentration.
Virtual colony count (VCC) is a kinetic, 96-well microbiological assay originally developed to measure the activity of defensins. It has since been applied to other antimicrobial peptides including LL-37. It utilizes a method of enumerating bacteria called quantitative growth kinetics, which compares the time taken for a bacterial batch culture to reach a threshold optical density with that of a series of calibration curves. The name VCC has also been used to describe the application of quantitative growth kinetics to enumerate bacteria in cell culture infection models. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can be done on 96-well plates by diluting the antimicrobial agent at varying concentrations in broth inoculated with bacteria and measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration that results in no growth. However, these methods cannot be used to study some membrane-active antimicrobial peptides, which are inhibited by the broth itself. The virtual colony count procedure takes advantage of this fact by first exposing bacterial cells to the active antimicrobial agent in a low-salt buffer for two hours, then simultaneously inhibiting antimicrobial activity and inducing exponential growth by adding broth. The growth kinetics of surviving cells can then be monitored using a temperature-controlled plate reader. The time taken for each growth curve to reach a threshold change in optical density is then converted into virtual survival values, which serve as a measure of antimicrobial activity.

A spiral plater is an instrument used to dispense a liquid sample onto a Petri dish in a spiral pattern. Commonly used as part of a CFU count procedure for the purpose of determining the number of microbes in the sample. In this setting, after spiral plating, the Petri dish is incubated for several hours after which the number of colony forming microbes (CFU) is determined. Spiral platers are also used for research, clinical diagnostics and as a method for covering a Petri dish with bacteria before placing antibiotic discs for AST.
Agar dilution is one of two methods used by researchers to determine the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of antibiotics. It is the dilution method most frequently used to test the effectiveness of new antibiotics when a few antibiotics are tested against a large panel of different bacteria.
In microbiology, the term isolation refers to the separation of a strain from a natural, mixed population of living microbes, as present in the environment, for example in water or soil flora, or from living beings with skin flora, oral flora or gut flora, in order to identify the microbe(s) of interest. Historically, the laboratory techniques of isolation first developed in the field of bacteriology and parasitology, before those in virology during the 20th century.
References
- ↑ Miles, AA; Misra, SS; Irwin, JO (Nov 1938). "The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood". The Journal of Hygiene. 38 (6): 732–49. doi:10.1017/s002217240001158x. PMC 2199673 . PMID 20475467.
- ↑ Hedges, AJ (Jun 25, 2002). "Estimating the precision of serial dilutions and viable bacterial counts". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 76 (3): 207–14. doi:10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00022-3. PMID 12051477.