A voivodeship or voivodate is the area administered by a voivode (governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval states, much as the title of voivode was equivalent to that of a duke. Other roughly equivalent titles and areas in medieval Eastern Europe included ban and banate.

Military districts are formations of a state's armed forces which are responsible for a certain area of territory. They are often more responsible for administrative than operational matters, and in countries with conscript forces, often handle parts of the conscription cycle.

The Land Forces are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 110,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stretches back a millennium – since the 10th century. Poland's modern army was formed after Poland regained independence following World War I in 1918.

The 7th Infantry Division was the name of several units of the Polish Army.

KS Lublinianka is a Polish professional football club based in Lublin. It was founded in 1921 as WKS Lublin and was supported by the Lublin garrison of the Polish Army. In 1923, WKS Lublin was renamed to Klub Sportowy Lublinianka. In 1938 the club won the Football Junior Championships of Poland. They spent eleven seasons in the Polish First League and in the 1969–70 season they reached the quarterfinals of the Polish Cup. Lublinianka currently plays in the IV liga Lublin.

The Polish People's Army constituted the second formation of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in 1943–1945, and in 1945–1989 the armed forces of the Polish communist state, ruled by the Polish Workers' Party and then the Polish United Workers' Party. The communist-led Polish armed forces, allowed and facilitated by Joseph Stalin, were the result of efforts made in the early 1940s in the Soviet Union by Wanda Wasilewska and Zygmunt Berling.

Franciszek Ksawery Latinik was a Polish military officer, Colonel of Austro-Hungarian Army and Major General of the Polish Army.

Polish Historical Society is a Polish professional scientific society for historians.
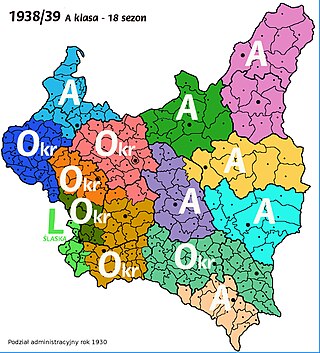
In the Second Polish Republic, there was not a national, Second Division, as we know it today, although the creation of the second division was proposed on several occasions. On Sunday, 26 September 1937 in Częstochowa, a conference of regional teams from across the nation took place, to discuss the creation of the league. Officials of several clubs arrived, such as Brygada Częstochowa, Gryf Toruń, Śmigły Wilno, Rewera Stanisławów, Dąb Katowice, Unia Sosnowiec, Strzelec Janowa Dolina, and WKS Grodno. Also, invited were officials of HCP Poznań, Podgorze Kraków, Naprzód Lipiny and Union Touring Łódź, but for unknown reasons they did not show up. The officials talked about creation of a National B-League, but nothing came out of this project. Instead, in the years 1921-1939, several Voivodeships held their own games and those leagues were known as A-Classes. In 1927, the elite Polish Football League was created, which by the late 1930s consisted of 10 teams. The teams that did not make it to the Ekstraklasa, played in the A-Classes.

Narodowa Organizacja Wojskowa was one of the Polish resistance movements in World War II. Created in October 1939, it did not merge with the Service for Poland's Victory (SZP)/Union of Armed Struggle (ZWZ); later Home Army (AK). Nevertheless, it recognized the Polish government in exile, which was located in London. The National Military Organization was politically related to the National Party (SN). In 1942/1943 it split into two parts; one merged with the Home Army, while another formed the National Armed Forces (NSZ). After the Warsaw Uprising, most of NOW members formed the National Military Union (NZW).

Silesian Military District was one of three military districts in Poland, the other two being the Pomeranian Military District and the Warsaw Military District. All three were disbanded by the end of 2011 due to the restructuring of the Polish Army. Its headquarters was in Wrocław.
10th Infantry Division was a unit of the Polish Army during the interbellum period, which took part in the 1939 German Invasion of Poland. It was created in 1919 from the former Polish 4th Rifle Division. Stationed in Łódź and commanded in 1939 by General Franciszek Dindorf-Ankowicz, it was part of Łódź Army. Its task was to defend the fortified area along the upper Warta river, near the interwar border of Poland and Germany.

A Dowództwo Okręgu Korpusu was a military district of the Ministry of Military Affairs of the Second Polish Republic. It served as an organizational, mobilisational, and administrative body of the Polish Army and all local military units of the country were subject to the Corps commands. Also, the DOKs ran all Military Draft Offices of Poland. The system of DOKs was modeled after the French Army, and according to Polish planners, each district located along either Soviet or German border was supposed to field one army. It meant that all districts except for District X, were subject to this rule. The borders of the DOKs did not reflect the Administrative division of Second Polish Republic.
President of Poland's Football Cup was an annual football competition, taking place in the Second Polish Republic in the years 1936–1939. It was sponsored by President Ignacy Mościcki, and unlike today's Polish Cup, it did not feature clubs. Instead, it was a competition of the local districts of the PZPN.
Armored trains of Poland mostly date to the World War I period. Many of them were modernized over the next two decades, and took part in most military conflicts of the Second Polish Republic, namely the Greater Poland Uprising, the Polish-Ukrainian War, the Polish-Bolshevik War, the Silesian Uprisings and the Polish September Campaign in World War II. Armored trains were also used by the Polish Armed Forces in the West as well as in the post-war period by the Polish Railroad Guards and the People's Army of Poland.
The Warsaw Military District was one of three military districts in Poland, the other two being the Pomeranian Military District and the Silesian Military District. It was the regional executive body of the Ministry of National Defense of Poland in the capital of Warsaw in operational and defense matters and military administration existing from 1945 to 1998.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Poland refers to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and its members in Poland. At year-end 1989, there were fewer than 100 members in Poland. In 2022, there were 2,184 members in 11 congregations.

Military Special Courts or WSS was the underground court of the Polish Underground State during World War II. The only such extensive court system in German-occupied Europe.












