Related Research Articles

The GNU Debugger (GDB) is a portable debugger that runs on many Unix-like systems and works for many programming languages, including Ada, Assembly, C, C++, D, Fortran, Haskell, Go, Objective-C, OpenCL C, Modula-2, Pascal, Rust, and partially others.

GPE is a graphical user interface environment for handheld computers, such as palmtops and personal digital assistants (PDAs), running some Linux kernel-based operating system. GPE is a complete environment of software components and applications which makes it possible to use a Linux handheld for tasks such as personal information management (PIM), audio playback, email, and web browsing.

The GNU Project is a free software, mass collaboration project announced by Richard Stallman on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices by collaboratively developing and publishing software that gives everyone the rights to freely run the software, copy and distribute it, study it, and modify it. GNU software grants these rights in its license.

GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.
The Embedded Configurable Operating System (eCos) is a free and open-source real-time operating system intended for embedded systems and applications which need only one process with multiple threads. It is designed to be customizable to precise application requirements of run-time performance and hardware needs. It is implemented in the programming languages C and C++ and has compatibility layers and application programming interfaces for Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) and The Real-time Operating system Nucleus (TRON) variant μITRON. eCos is supported by popular SSL/TLS libraries such as wolfSSL, thus meeting all standards for embedded security.

μClinux is a variation of the Linux kernel, previously maintained as a fork, that targets microcontrollers without a memory management unit (MMU). It was integrated into the mainline kernel as of 2.5.46; the project continues to develop patches and tools for microcontrollers. The homepage lists Linux kernel releases for 2.0, 2.4 and 2.6.
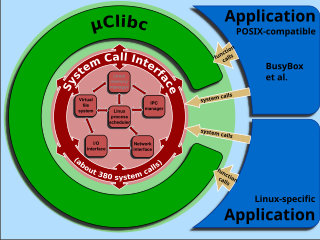
In computing, uClibc is a small C standard library intended for Linux kernel-based operating systems for embedded systems and mobile devices. uClibc was written to support μClinux, a version of Linux not requiring a memory management unit and thus suited for microcontrollers.

The NXP ColdFire is a microprocessor that derives from the Motorola 68000 family architecture, manufactured for embedded systems development by NXP Semiconductors. It was formerly manufactured by Freescale Semiconductor which merged with NXP in 2015.
Computer operating systems based on the Linux kernel are used in embedded systems such as consumer electronics, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), networking equipment, machine control, industrial automation, navigation equipment, spacecraft flight software, and medical instruments in general.

iPodLinux is a μClinux-based Linux distribution designed specifically to run on Apple Inc.'s iPod. When the iPodLinux kernel is booted it takes the place of Apple's iPod operating system and automatically loads Podzilla, an alternative GUI and launcher for a number of additional included programs such as a video player, an image viewer, a command line shell, games, emulators for video game consoles, programming demos, and other experimental or occasionally unfinished software.
Lineo was a thin client and embedded systems company spun out of Caldera Thin Clients by 20 July 1999.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.

Gnash is a media player for playing SWF files. Gnash is available both as a standalone player for desktop computers and embedded devices, as well as a plugin for the browsers still supporting NPAPI. It is part of the GNU Project and is a free and open-source alternative to Adobe Flash Player. It was developed from the gameswf project.

Real-Time Executive for Multiprocessor Systems (RTEMS), formerly Real-Time Executive for Missile Systems, and then Real-Time Executive for Military Systems, is a real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for embedded systems. It is free and open-source software.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license.

The Embeddable Linux Kernel Subset (ELKS), formerly known as Linux-8086, is a Linux-like operating system kernel. It is a subset of the Linux kernel, intended for 16-bit computers with limited processor and memory resources such as machines powered by Intel 8086 and compatible microprocessors not supported by 32-bit Linux.
LatticeMico32 is a 32-bit microprocessor reduced instruction set computer (RISC) soft core from Lattice Semiconductor optimized for field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). It uses a Harvard architecture, which means the instruction and data buses are separate. Bus arbitration logic can be used to combine the two buses, if desired.

The GNU General Public Licenses are a series of widely used free software licenses, or copyleft licenses, that guarantee end users the freedoms to run, study, share, and/or modify the software. The GPL was the first copyleft license available for general use. It was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the Lesser General Public License, and even further distinct from the more widely-used permissive software licenses such as BSD, MIT, and Apache.

The Linux kernel is a free and open source, UNIX-like kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system (OS) which was created to be a free replacement for Unix. Since the late 1990s, it has been included in many operating system distributions, many of which are called Linux. One such Linux kernel operating system is Android which is used in many mobile and embedded devices.
References
- ↑ "MiniGUI - Introduction". Archived from the original on 2009-02-01. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ "MiniGUI - Resources". Archived from the original on 2005-12-18. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ "MiniGUI - Evolution". Archived from the original on 2009-02-01. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ Yongming, Wei (2005-10-27). "A technical introduction to MiniGUI". linuxdevices.com. Archived from the original on 2012-09-12. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ "MiniGUI - Introduction (features)". Archived from the original on 2009-01-30. Retrieved 2008-12-28.