Related Research Articles

QNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.
VxWorks is a real-time operating system developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.

An Embedded Operating System (EOS) is an operating system designed specifically for embedded computer systems. These systems aim to enhance functionality and reliability to perform dedicated tasks. When the multitasking method employed allows for timely task execution, such an OS may qualify as a real-time operating system (RTOS).
The Embedded Configurable Operating System (eCos) is a free and open-source real-time operating system intended for embedded systems and applications which need only one process with multiple threads. It is designed to be customizable to precise application requirements of run-time performance and hardware needs. It is implemented in the programming languages C and C++ and has compatibility layers and application programming interfaces for Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) and The Real-time Operating system Nucleus (TRON) variant μITRON. eCos is supported by popular SSL/TLS libraries such as wolfSSL, thus meeting all standards for embedded security.
Nucleus RTOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS) produced by the Embedded Software Division of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business, supporting 32- and 64-bit embedded system platforms. The operating system (OS) is designed for real-time embedded systems for medical, industrial, consumer, aerospace, and Internet of things (IoT) uses. Nucleus was released first in 1993. The latest version is 3.x, and includes features such as power management, process model, 64-bit support, safety certification, and support for heterogeneous computing multi-core system on a chip (SOCs) processors.
Wind River Systems, Inc., also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California–based company, subsidiary of Aptiv PLC. The company develops embedded system and cloud software consisting of real-time operating systems software, industry-specific software, simulation technology, development tools and middleware.

Multiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
The ITRON project is the first of several sub-architectures of the TRON project.
An operating system abstraction layer (OSAL) provides an application programming interface (API) to an abstract operating system making it easier and quicker to develop code for multiple software or hardware platforms. It can make an application less dependent on any one specific operating system.
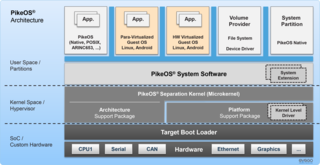
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which features a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring compliance with industry standards for quality, safety, and security across various sectors. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security.
Novell Embedded Systems Technology (NEST) was a series of APIs, data formats and network protocol stacks written in a highly portable fashion intended to be used in embedded systems. The idea was to allow various small devices to access Novell NetWare services, provide such services, or use NetWare's IPX protocol as a communications system. Novell referred to this concept as "Extended Networks", and when the effort was launched they boasted that they wanted to see one billion devices connected to NetWare networks by year 2000. NEST was launched in mid-1994 countering Microsoft's similar Microsoft at Work efforts, which had been launched in 1993.
Lynx Software Technologies, Inc. is a San Jose, California software company founded in 1988. Lynx specializes in secure virtualization and open, reliable, certifiable real-time operating systems (RTOSes). Originally known as Lynx Real-Time Systems, the company changed its name to LynuxWorks in 2000 after acquiring, and merging with, ISDCorp, an embedded systems company with a strong Linux background. In May 2014, the company changed its name to Lynx Software Technologies.
TI-RTOS is an embedded tools ecosystem created and offered by Texas Instruments (TI) for use across a range of their embedded system processors. It includes a real-time operating system (RTOS) component-named TI-RTOS Kernel, networking connectivity stacks, power management, file systems, instrumentation, and inter-processor communications like DSP/BIOS Link. It is free and open-source software, released under a BSD license.
FlexOS is a discontinued modular real-time multiuser multitasking operating system (RTOS) designed for computer-integrated manufacturing, laboratory, retail and financial markets. Developed by Digital Research's Flexible Automation Business Unit in Monterey, California, in 1985.
wolfSSL is a small, portable, embedded SSL/TLS library targeted for use by embedded systems developers. It is an open source implementation of TLS written in the C programming language. It includes SSL/TLS client libraries and an SSL/TLS server implementation as well as support for multiple APIs, including those defined by SSL and TLS. wolfSSL also includes an OpenSSL compatibility interface with the most commonly used OpenSSL functions.

T-Kernel is an open source real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for 32-bit microcontrollers. It is standardized by the T-Engine Forum, which distributes it under a T-License agreement. There is also a corresponding Micro T-Kernel (μT-Kernel) implementation designed for embedded systems with 16-bit or 8-bit microcontrollers.
NuttX is a free and open-source real-time operating system (RTOS) with an emphasis on technical standards compliance and on having a small footprint. Scalable from 8-bit to 64-bit microcontroller environments, the main governing standards in NuttX are from the Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Further standard application programming interfaces (APIs) from Unix and other common RTOSes are adopted for functions unavailable under these standards, or inappropriate for deeply embedded environments, such as the fork system call.

Integrated Systems Inc. (ISI) was an embedded software company founded by Naren Gupta in 1980/1981. Summit Partners invested in 1987, the company listed in 1990, and it was acquired by Wind River Systems in 2000.
References
- 1 2 "pSOSystem and the NEST Development Environment - Designing Embedded Applications with NetWare Connectivity" (White paper). Integrated Systems, Inc. (ISI). 1998. Archived from the original on 1998-02-19.
- ↑ "Novell Announces RTOS Vendor Program Which Brings Integrated Networking Solutions to the Embedded Systems Marketplace" (Press Release). Orem, UT, USA: Novell, Inc. 1995-05-23. Archived from the original on 2018-08-18. Retrieved 2018-08-18.
"Because Novell used Integrated Systems' FlexOS during the development and testing of NEST, we are in the unique position of supporting it through both our real-time product lines pSOSystem for deeply embedded markets, and FlexOS for point of sale," said Moses Joseph, vice president of marketing for Integrated Systems. "Developers using the FlexOS development kit and the expanded pSOSystem/NEST package for everything from home security and entertainment to office automation and global communications applications, now have quick and easy access to the widest variety of standard networking protocols.