The Portable Operating System Interface is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines system and user-level application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers.

An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.

QNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.
pSOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS), created in about 1982 by Alfred Chao, and developed and marketed for the first part of its life by his company Software Components Group (SCG). In the 1980s, pSOS rapidly became the RTOS of choice for all embedded systems based on the Motorola 68000 series family architecture, because it was written in 68000 assembly language and was highly optimised from the start. It was also modularised, with early support for OS-aware debugging, plug-in device drivers, Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) stacks, language libraries, and disk subsystems. Later came source code level debugging, multiprocessing support, and further computer networking extensions.
VxWorks is a real-time operating system developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.

An Embedded Operating System (EOS) is an operating system designed specifically for embedded computer systems. These systems aim to enhance functionality and reliability to perform dedicated tasks. When the multitasking method employed allows for timely task execution, such an OS may qualify as a real-time operating system (RTOS).
Versatile Real-Time Executive (VRTX) is a real-time operating system (RTOS) developed and marketed by the company Mentor Graphics. VRTX is suitable for both traditional board-based embedded systems and system on a chip (SoC) architectures. It has been superseded by the Nucleus RTOS.
RTLinux is a hard realtime real-time operating system (RTOS) microkernel that runs the entire Linux operating system as a fully preemptive process. The hard real-time property makes it possible to control robots, data acquisition systems, manufacturing plants, and other time-sensitive instruments and machines from RTLinux applications. The design was patented. Despite the similar name, it is not related to the Real-Time Linux project of the Linux Foundation.

Real-time application interface (RTAI) is a real-time extension for the Linux kernel, which lets users write applications with strict timing constraints for Linux. Like Linux itself the RTAI software is a community effort. RTAI provides deterministic response to interrupts, POSIX-compliant and native RTAI real-time tasks. RTAI supports several architectures, including IA-32, x86-64, PowerPC, ARM, and MIPS.
Adeos is a nanokernel hardware abstraction layer (HAL), or hypervisor, that operates between computer hardware and the operating system (OS) that runs on it. It is distinct from other nanokernels in that it is not only a low level layer for an outer kernel. Instead, it is intended to run several kernels together, which makes it similar to full virtualization technologies. It is free and open-source software released under a GNU General Public License (GPL).
Nucleus RTOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS) produced by the Embedded Software Division of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business, supporting 32- and 64-bit embedded system platforms. The operating system (OS) is designed for real-time embedded systems for medical, industrial, consumer, aerospace, and Internet of things (IoT) uses. Nucleus was released first in 1993. The latest version is 3.x, and includes features such as power management, process model, 64-bit support, safety certification, and support for heterogeneous computing multi-core system on a chip (SOCs) processors.

Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality performed by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
LEON is a radiation-tolerant 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) microprocessor core that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), without any involvement by Sun. Later versions have been designed by Gaisler Research, under a variety of owners. It is described in synthesizable VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL). LEON has a dual license model: An GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and GNU General Public License (GPL) free and open-source software (FOSS) license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system on a chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.

FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 40 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License.
Eclipse ThreadX is a highly deterministic, embedded real-time operating system (RTOS) programmed mostly in the language C. Originally it was named ThreadX when Express Logic first developed it, later it was renamed to Azure RTOS after Express Logic was purchased by Microsoft, most recently it was renamed again to Eclipse ThreadX after it transitioned to open source model under the stewardship of the Eclipse Foundation.
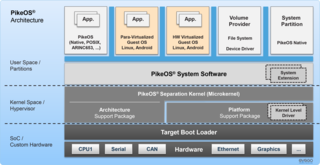
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which features a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring compliance with industry standards for quality, safety, and security across various sectors. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security.
LynxSecure is a least privilege real-time separation kernel hypervisor from Lynx Software Technologies designed for safety and security critical applications found in military, avionic, industrial, and automotive markets.

OpenComRTOS is a commercial network-centric, formally developed real-time operating system (RTOS), aimed mainly at the embedded system market.

T-Kernel is an open source real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for 32-bit microcontrollers. It is standardized by the T-Engine Forum, which distributes it under a T-License agreement. There is also a corresponding Micro T-Kernel (μT-Kernel) implementation designed for embedded systems with 16-bit or 8-bit microcontrollers.









