Related Research Articles

QNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.

BlackBerry was a brand of smartphones and other related mobile services and devices. The line was originally developed and maintained by the Canadian company BlackBerry Limited from 1999 to 2016, after which it was licensed to various companies.
A computing platform, digital platform, or software platform is an environment in which software is executed. It may be the hardware or the operating system (OS), a web browser and associated application programming interfaces, or other underlying software, as long as the program code is executed using the services provided by the platform. Computing platforms have different abstraction levels, including a computer architecture, an OS, or runtime libraries. A computing platform is the stage on which computer programs can run.

BlackBerry Limited is a Canadian software company specializing in cybersecurity. Founded in 1984, it developed the famous BlackBerry brand of interactive pagers, smartphones and tablets. The company transitioned to providing software and services and holds critical software application patents.

Kanata is a suburb and former city within Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It is located about 22 km (14 mi) west of the city's downtown core. As of 2021, the former City of Kanata had a population of 98,938, with the population centre having a population of 137,118. Before it was amalgamated into Ottawa in 2001, it was one of the fastest-growing cities in Canada and the fastest-growing community in Eastern Ontario. Located just to the west of the National Capital Commission Greenbelt, it is one of the largest of several communities that surround central Ottawa.

Mihal "Mike" Lazaridis is a Canadian businessman, investor in quantum computing technologies, and co-founder of BlackBerry, which created and manufactured the BlackBerry wireless handheld device. In November 2009, Canadian Business ranked Lazaridis as the 11th wealthiest Canadian, with an estimated net worth of CA$2.9 billion.

Garth Alan Gibson is a computer scientist from Carnegie Mellon University. Gibson's developed the RAID taxonomy of redundant data storage systems, along with David A. Patterson and Randy Katz.
Gordon Bell is a Canadian software developer and entrepreneur. He is one of the co-creators of the QNX microkernel real-time operating system.

William "Bill" Reeves is a Canadian animator and technical director known for working with John Lasseter on the animated shorts Luxo Jr. and The Adventures of André and Wally B.
Solace is a middleware company based in Kanata / Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, that manufactures and sells message-oriented middleware appliances and software that routes information between applications, devices and user interfaces.
Dataproducts Corporation was an early manufacturer of computer peripheral equipment.
The J.W. Graham Medal in Computing and Innovation is an award given annually by the University of Waterloo and the University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics to "recognize the leadership and many innovative contributions made to the University of Waterloo, and to the Canadian computer industry." Recipients of this award receive a gold medal and certificate. Recipients are graduates of the University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics from business, education, or government.

BlackBerry 10 (BB10) is a discontinued proprietary mobile operating system for the BlackBerry line of smartphones, both developed by BlackBerry Limited. Released in January 2013, BlackBerry 10 is a complete rework from the company's previous BlackBerry OS software.
Dave Boswell is a Canadian computer scientist who was awarded the J.W. Graham Medal for his contributions to the field in 2003.
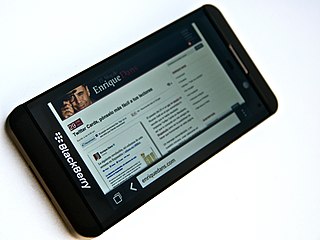
The BlackBerry Z10 was an LTE touchscreen-based smartphone developed by BlackBerry, previously known as RIM. The BlackBerry Z10 was the first of two new BlackBerry phones presented at the BlackBerry 10 event on January 30, 2013. The BlackBerry Z10 was followed by the Z30.
Ian McPhee is a Canadian computer scientist, entrepreneur, and philanthropist. He earned a Bachelor of Mathematics in 1973, and his Masters of Mathematics in 1979.
Kim Davidson is a Canadian computer scientist, and founder and CEO of Side Effects software. He founded the firm in 1987.
Terry Stepien is a Canadian computer scientist, and protege of Wes Graham, an influential professor of Computer Science at Stepien's alma mater, the University of Waterloo. Stepien earned a Bachelor of Mathematics in 1981, and his Masters in 1988.
Tas Tsonis is a computer scientist who continues to play a prominent role in using graphical algorithms, computer science, and computational geometry to automate the personalization of apparel and accessories. He has been granted twelve US patents based on mathematical and graphical algorithms.
References
- ↑ "Recipients of the J. W. Graham Medal in Computing & Innovation". University of Waterloo. 1998. Retrieved 2020-03-01.
- ↑ Bylinsky, Gene (2003-03-17). "Heroes of Manufacturing". Fortune . Fortune Media Group Holdings.
- ↑ "QNX Software Systems founder and CEO Dan Dodge steps down from BlackBerry Ltd". Financial Post. Postmedia Network. 2015-09-08. Retrieved 2020-03-01.
- ↑ Pilieci, Vito (2016-07-29). "QNX founder Dan Dodge now working at Apple Inc.: reports". Ottawa Citizen. Postmedia Network. Retrieved 2020-03-01.