Related Research Articles

GNU Hurd is a collection of microkernel servers written as part of GNU, for the GNU Mach microkernel. It has been under development since 1990 by the GNU Project of the Free Software Foundation, designed as a replacement for the Unix kernel, and released as free software under the GNU General Public License. When the Linux kernel proved to be a viable solution, development of GNU Hurd slowed, at times alternating between stasis and renewed activity and interest.

In computer science, a microkernel is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system (OS). These mechanisms include low-level address space management, thread management, and inter-process communication (IPC).
Mach is a kernel developed at Carnegie Mellon University by Richard Rashid and Avie Tevanian to support operating system research, primarily distributed and parallel computing. Mach is often considered one of the earliest examples of a microkernel. However, not all versions of Mach are microkernels. Mach's derivatives are the basis of the operating system kernel in GNU Hurd and of Apple's XNU kernel used in macOS, iOS, iPadOS, tvOS, and watchOS.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
L4 is a family of second-generation microkernels, used to implement a variety of types of operating systems (OS), though mostly for Unix-like, Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) compliant types.
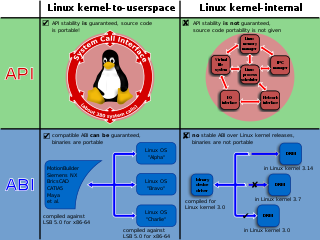
In computing, a system call is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services, creation and execution of new processes, and communication with integral kernel services such as process scheduling. System calls provide an essential interface between a process and the operating system.
Capability-based security is a concept in the design of secure computing systems, one of the existing security models. A capability is a communicable, unforgeable token of authority. It refers to a value that references an object along with an associated set of access rights. A user program on a capability-based operating system must use a capability to access an object. Capability-based security refers to the principle of designing user programs such that they directly share capabilities with each other according to the principle of least privilege, and to the operating system infrastructure necessary to make such transactions efficient and secure. Capability-based security is to be contrasted with an approach that uses traditional UNIX permissions and Access Control Lists.

XNU is the computer operating system (OS) kernel developed at Apple Inc. since December 1996 for use in the Mac OS X operating system and released as free and open-source software as part of the Darwin OS, which, in addition to being the basis for macOS, is also the basis for Apple TV Software, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, visionOS, and tvOS.
Computer operating systems based on the Linux kernel are used in embedded systems such as consumer electronics, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), networking equipment, machine control, industrial automation, navigation equipment, spacecraft flight software, and medical instruments in general.
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the same kernel.
AppImage is an open-source format for distributing portable software on Linux. It aims to allow the installation of binary software independently of specific Linux distributions, a concept often referred to as upstream packaging. As a result, one AppImage can be installed and run across Ubuntu, Arch Linux, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux without needing to use different files. It aims to be a format that is self-contained, rootless, and independent of the underlying Linux distribution.
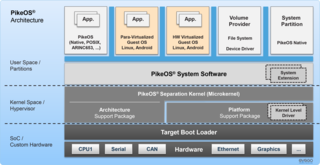
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which features a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring compliance with industry standards for quality, safety, and security across various sectors. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security.
Independent Group of Unix-Alikes and Networking Activists (IGUANA) are developers of the Wombat system.

Gernot Heiser is a Scientia Professor and the John Lions Chair for operating systems at UNSW Sydney, where he leads the Trustworthy Systems group (TS).

The kernel is a computer program at the core of a computer's operating system and generally has complete control over everything in the system. The kernel is also responsible for preventing and mitigating conflicts between different processes. It is the portion of the operating system code that is always resident in memory and facilitates interactions between hardware and software components. A full kernel controls all hardware resources via device drivers, arbitrates conflicts between processes concerning such resources, and optimizes the utilization of common resources e.g. CPU & cache usage, file systems, and network sockets. On most systems, the kernel is one of the first programs loaded on startup. It handles the rest of the startup as well as memory, peripherals, and input/output (I/O) requests from software, translating them into data-processing instructions for the central processing unit.
Open Kernel Labs is a privately owned company that develops microkernel-based hypervisors and operating systems for embedded systems. The company was founded in 2006 by Steve Subar and Gernot Heiser as a spinout from NICTA. It was headquartered in Chicago, while research and development was located in Sydney, Australia. The company was acquired by General Dynamics in September 2012.

The Linux console is a system console internal to the Linux kernel. A system console is the device which receives all kernel messages and warnings and which allows logins in single user mode. The Linux console provides a way for the kernel and other processes to send text output to the user, and to receive text input from the user. The user typically enters text with a computer keyboard and reads the output text on a computer monitor. The Linux kernel supports virtual consoles – consoles that are logically separate, but which access the same physical keyboard and display. The Linux console are implemented by the VT subsystem of the Linux kernel, and do not rely on any user space software. This is in contrast to a terminal emulator, which is a user space process that emulates a terminal, and is typically used in a graphical display environment.
The REX Operating System is a real-time operating system (RTOS) developed by Qualcomm for the ARM processor based mobile phone Dual-Mode Subscriber Station (DMSS) or Advanced Mode Subscriber Software (AMSS) development. As of 2007, most Korean cell phones ran on REX.
L4Linux is a variant of the Linux kernel for operating systems, that is altered to the extent that it can run paravirtualized on an L4 microkernel, where the L4Linux kernel runs a service. L4Linux is not a fork but a variant and is binary compatible with the Linux x86 kernel, thus it can replace the Linux kernel of any Linux distribution.
A virtual kernel architecture (vkernel) is an operating system virtualisation paradigm where kernel code can be compiled to run in the user space, for example, to ease debugging of various kernel-level components, in addition to general-purpose virtualisation and compartmentalisation of system resources. It is used by DragonFly BSD in its vkernel implementation since DragonFly 1.7, having been first revealed in September 2006, and first released in the stable branch with DragonFly 1.8 in January 2007.
References
- 1 2 "Beta release of Kenge, Iguana and Wombat" . Retrieved 2010-03-12.
- 1 2 Leslie, Ben; van Schaik, Carl; Heiser, Gernot (April 2005). "Wombat: A portable user-mode Linux for embedded systems". Proceedings of Linux.conf.au (2005). Canberra. Archived from the original (pdf) on 2016-10-21. Retrieved 2016-10-21– via ts.data61.csiro.au/publications/papers/Leslie_vSH_05.abstract.