
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e. in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft.

Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC worldwide is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of air traffic, and provide information and other support for pilots. In some countries, ATC plays a security or defensive role, or is operated by the military.

In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is 200 feet (61 m) over the ground, within a 1⁄2 mile (800 m) of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically improves the weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Later versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes.

The basic principles of air navigation are identical to general navigation, which includes the process of planning, recording, and controlling the movement of a craft from one place to another.
A non-directional (radio) beacon (NDB) is a radio transmitter at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. As the name implies, the signal transmitted does not include inherent directional information, in contrast to other navigational aids such as low frequency radio range, VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and TACAN. NDB signals follow the curvature of the Earth, so they can be received at much greater distances at lower altitudes, a major advantage over VOR. However, NDB signals are also affected more by atmospheric conditions, mountainous terrain, coastal refraction and electrical storms, particularly at long range.
In aviation, lowest safe altitude (LSALT) is an altitude that is at least 500 feet above any obstacle or terrain within a defined safety buffer region around a particular route that a pilot might fly. The safety buffer allows for errors in the air by including an additional area that a pilot might stray into by flying off track. By flying at or above this altitude a pilot complies with terrain clearance requirements on that particular flight leg.

In the United States, airways or air routes are defined by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in two ways:
Minimum Obstacle Clearance Altitude, or MOCA, is the lowest published altitude in effect between fixes on VOR airways or route segments that meets obstacle clearance requirements for the entire route segment. Within the United States, this altitude also assures acceptable navigational signal coverage only within 22 nm of a VOR. The MOCA seen on the NACO en route chart, may have been computed by adding the required obstacle clearance (ROC) to the controlling obstacle in the primary area or computed by using a TERPS chart if the controlling obstacle is located in the secondary area. This figure is then rounded to the nearest 100 foot increment, i.e. 2,049 feet becomes 2,000, and 2,050 feet becomes 2,100 feet. An extra 2,000 feet is added in mountainous areas, 1,000 in non-mountainous. The MOCA is based upon obstacle clearance over the terrain or over manmade objects, adequacy of navigation facility performance, and communications requirements. The MOCA is always at or below the Minimum en route altitude (MEA), and may put an aircraft below air traffic control radar coverage and also below Minimum reception altitude (MRA) for navigation aids; as a result, it is typically used only in emergencies, especially to get below icing.
Minimum en route altitude (MEA), alternately spelled as Minimum enroute altitude, is the lowest published altitude between radio navigation fixes that assures acceptable navigational signal coverage and meets obstacle clearance requirements between those fixes.

In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply.

A marker beacon is a particular type of VHF radio beacon used in aviation, usually in conjunction with an instrument landing system (ILS), to give pilots a means to determine position along an established route to a destination such as a runway.
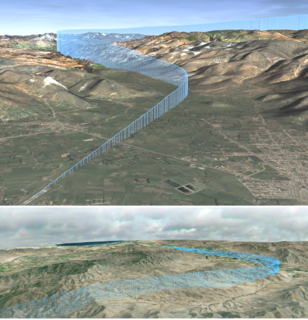
Required navigation performance (RNP) is a type of performance-based navigation (PBN) that allows an aircraft to fly a specific path between two 3D-defined points in space.

Area navigation is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from the beacons. This can conserve flight distance, reduce congestion, and allow flights into airports without beacons. Area navigation used to be called "random navigation", hence the acronym RNAV.
In aviation, a standard terminal arrival route or standard terminal arrival (STAR) is a published flight procedure followed by aircraft on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan just before reaching a destination airport.
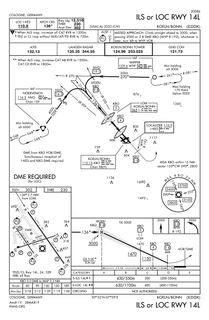
Approach plates are the printed charts of instrument approach procedures that pilots use to fly instrument approaches during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. Each country maintains its own instrument approach procedures according to International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards.
Standard instrument departure (SID) routes, also known as departure procedures (DP), are published flight procedures followed by aircraft on an IFR flight plan immediately after takeoff from an airport.
In aviation, a minimum crossing altitude (MCA) is the lowest altitude at which a navigational fix can be crossed when entering or continuing along an airway that will allow an aircraft to clear all obstacles while carrying out a normal climb to the required minimum en route IFR altitude (MEA) of the airway in question beyond the fix.

Maximum elevation figure (MEF) is a type of visual flight rule (VFR) information that indicates the elevation of the highest geographical feature within a GEOREF quadrangle area. It is of interest to pilots, who want to be aware of the highest mountain peaks and tall towers nearby, so that they can fly above them to avoid controlled flight into terrain.
ICAO performance-based navigation (PBN) specifies that aircraft required navigation performance (RNP) and area navigation (RNAV) systems performance requirements be defined in terms of accuracy, integrity, availability, continuity, and functionality required for the proposed operations in the context of a particular airspace, when supported by the appropriate navigation infrastructure.











