
The Maumee River is a river running from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie in the United States. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana, has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for 137 miles (220 km) through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio’s breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie’s water.
The Maumee Torrent was a catastrophic draining of Lake Maumee, the ancestor of present-day Lake Erie, that occurred during the late Wisconsin glaciation, approximately 21,000 years ago. It happened when the waters of Lake Maumee, possibly in response to an advance of the ice front at the eastern end of the lake, overtopped a "sag" or low spot in the Fort Wayne Moraine, which was a deposit of glacial debris that acted as a natural dam at the site of present-day Fort Wayne, Indiana. This unleashed a massive flow of water that scoured a one- to two-mile-wide outlet running southwest to the Wabash River known as the "Wabash-Erie Channel", which probably followed the course of earlier, less massive drainage. The channel, now a small stream called the Little River, is the largest topographical feature in Allen County, Indiana. As much as 30 feet of fine sand, silt and organic sediments were deposited in the channel before drainage reversed and was captured by the present-day Maumee River. U.S. Route 24 between Fort Wayne and Huntington follows the channel.

Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 Years Before Present (YBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide ice sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.

The geography of Indiana comprises the physical features of the land and relative location of U.S. State of Indiana. Indiana is in the north-central United States and borders on Lake Michigan. Surrounding states are Michigan to the north and northeast, Illinois to the west, Kentucky to the south, and Ohio to the east. The entire southern boundary is the Ohio River.

The Valparaiso Moraine is a recessional moraine that forms an immense U around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It is a band of high, hilly terrain made up of glacial till and sand. It begins near the border of Wisconsin and Illinois and extends south through Lake, McHenry, Cook, DuPage and Will counties in Illinois, and then turns southeast, entering Indiana. From this point, the moraine curves northeast through Lake, Porter, and LaPorte counties of Indiana into Michigan. It continues into Michigan as far as Montcalm County.

The Kankakee Outwash Plain is a flat plain interspersed with sand dunes in the Kankakee River valley in northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois of the United States. It is just south of the Valparaiso Moraine and was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation. As the glacier, stopped at the Valparaiso Moraine, melted, the meltwater was carried away to the outwash plain. On the south side of the moraine, where the elevation drops, the meltwaters eroded away valleys, carrying sand and mud with them. As the muddy meltwater reached the valley where the slope lessened, the water slowed down, depositing the sand on the outwash plain. This created a smooth, flat, and sandy plain. Before its draining, the Kankakee Marsh, located on the outwash plain, was one of the largest freshwater marshes in the United States.

The Calumet Shoreline is an ancient shoreline of Lake Michigan located in the Lake Michigan Basin. It can be clearly seen as a sand ridge along Ridge Road south of Chicago. Closer to the lake from the Calumet Shoreline, there are the Tolleston shorelines and farther from the lake are the Glenwood Shoreline, the Tinley Moraine, and the Valparaiso Moraine. The shoreline is named after the Calumet Region of Northern Indiana.
The Union Moraine begins in Ohio, east of Bellefontaine and the highest point in that state, towards Greenville in Darke County. Traveling southwestward and arcing a little northward, the moraine reaches Union City, Ohio for which it is named. From here, it travels almost directly westward to Muncie, Indiana. From Muncie, the moraine runs northwest ending in the bluffs overlooking Pipe Creek at Bunker Hill,Indiana, just south of Peru on the Wabash River.

The Fort Wayne Moraine is considered contemporary to the last stages of the Valparaiso Moraine. Centered on Fort Wayne, Indiana, the northern leg of the moraine is mostly overlaid by the younger Wabash Moraine angling northeastward through Williams County, Ohio. It only becomes identifiable in Lenawee County, Michigan south and northeast of Adrian before ending in the intermingling of moraines around Ann Arbor. The south and eastern leg of the moraine follows the northern bank of the St. Marys River into the State of Ohio. At the north bend of the St. Marys River, the moraine arcs northeastward through Lima, continuing in a northward arc to reach north of U.S. 30 in Hancock County to pass through Upper Sandusky, again bending to the north to end 15 miles (24 km) to 20 miles (32 km) to the northeast.
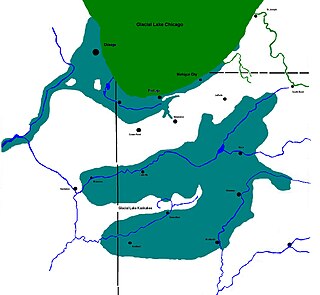
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.

The Marseilles moraine is a terminal moraine that encircles the southern tip of Lake Michigan in North America. It begins near Elgin, Illinois, and extends south and west of Chicago metropolitan area, turning eastward 30 miles (48 km) to 40 miles (64 km) south of the lake in Kankakee and Iroqouis counties, entering Indiana. It formed during the Wisconsin glaciation. The glacier had been in retreat when it stopped for an extended period, depositing glacial till and sand creating the hills of the moraine.

Lake Arkona was a stage of the lake waters in the Huron-Erie-Ontario basin following the end of the Lake Maumee levels and before the Lake Whittlesey stages, named for Arkona, Ontario, about 50 miles (80 km) east of Sarnia.

The Lake Border Moraine is a complex group of moraines bordering the southern end of Lake Michigan. It can be traced north along the eastern shore of the lake basin and across the highlands between the northern Lake Michigan and Saginaw Bay. It continues around the Saginaw Basin into the " thumb " of Michigan, and south through southeastern Michigan on the eastern side of the "thumb." Along Lake Michigan, north to Holland the system is close to the shore. From Holland north to Oceana County it is 15 miles (24 km) to 25 miles (40 km) east of the shore. In Oceana County it forms the prominent "clay banks" along the shoreline of Lake Michigan. It again bears inland from Hart, where more recent moraines reside between it and Lake Michigan. It runs north of the great interlobate moraine that exists between the Lake Michigan and Saginaw lobes of the Laurentian ice sheet. A little north of Cadillac turns to the east. A short distance from Cadillac, it splits with the southern ridge or outer member heading to the Saginaw basin. The northern ridge heads towards Lake Huron, but turns south before reaching the shore. In Newaygo and Lake counties it rest on an earlier interlobate moraine. It separates in Wexford and Missaukee counties to continue south along the west side of the Saginaw basin.

Lake Warren was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Erie basin around 12,700 years before present (YBP) when Lake Whittlesey dropped in elevation. Lake Warren is divided into three stages: Warren I 690 feet (210 m), Warren II 680 feet (210 m), and Warren III 675 feet (206 m), each defined by the relative elevation above sea level.

The Packerton Moraine in north-central Indiana has been considered by most persons who have studied it to be a large interlobate moraine between the Saginaw and the Erie lobes. The northeast-southwest direction of the eskers north of Disko, Wabash County, and the southeast-northwest trend south of there indicated that the part of the Packerton moraine south of Disko was built by the Erie lobe and the part north of Disko by the Saginaw lobe. An esker, Miami County shows a northeast-southwest alignment, providing evidence that Packerton moraine in Miami County was built by the Erie lobe. A small area in the northwestern was deposited by the Saginaw lobe. It is named the Packerton moraine from the village of Packerton in Kosciusko County. Thirteen kames and eskers complexes are mixed with sand and gravel. The till is, sandier, especially in the part deposited by the Saginaw lobe, than in the lobe passed over some source of sand, whereas the Erie lobe did not. Water-laid or wind-blown sands are found throughout the moraine. The bulk of the sand seems to have been water-deposited, but locally the sand appears to have been reworked by the wind. Few of the sand deposits exhibit dunal forms.
Lake Wayne formed in the Lake Erie and Lake St. Clair basins around 12,500 years before present (YBP) when Lake Arkona dropped in elevation. About 20 feet (6.1 m) below the Lake Warren beaches it was early described as a lower Lake Warren level. Based on work in Wayne County, near the village of Wayne evidence was found that Lake Wayne succeeded Lake Whittlesey and preceded Lake Warren. From the Saginaw Basin the lake did not discharge water through Grand River but eastward along the edge of the ice sheet to Syracuse, New York, thence into the Mohawk valley. This shift in outlets warranted a separate from Lake Warren. The Wayne beach lies but a short distance inside the limits of the Warren beach. Its character is not greatly different when taken throughout its length in Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania and New York. At the type locality in Wayne County, Michigan, it is a sandy ridge, but farther north, and to the east through Ohio it is gravel. The results of the isostatic rebound area similar to the Lake Warren beaches.

The Erie Plain is a lacustrine plain that borders Lake Erie in North America. From Buffalo, New York, to Cleveland, Ohio, it is quite narrow, but broadens considerably from Cleveland around Lake Erie to Southern Ontario, where it forms most of the Ontario peninsula. The Erie Plain was used in the United States as a natural gateway to the North American interior, and in both the United States and Canada the plain is heavily populated and provides very fertile agricultural land.


























