A kame delta is a glacial landform formed by a stream of melt water flowing through or around a glacier and depositing material, known as kame deposits. Upon entering a proglacial lake at the end (terminus) of a glacier, the river/stream deposit these sediments. This landform can be observed after the glacier has melted and the delta's asymmetrical triangular shape is visible. Once the glacier melts, the edges of the delta may subside as ice under it melts. Glacial till is deposited on the lateral sides of the delta, as the glacier melts.

A kame is a glacial landform, an irregularly shaped hill or mound composed of sand, gravel and till that accumulates in a depression on a retreating glacier, and is then deposited on the land surface with further melting of the glacier. Kames are often associated with kettles, and this is referred to as kame and kettle topography. The word kame is a variant of comb, which has the meaning "crest" among others. The geological term was introduced by Thomas Jamieson in 1874.

The Eel River is a 94-mile-long (151 km) tributary of the Wabash River in northern Indiana in the United States. Via the Wabash and Ohio rivers, its waters flow to the Mississippi River and ultimately the Gulf of Mexico. The Eel River rises southeast of Huntertown in Allen County and flows southwest through Allen, Whitley, Kosciusko, Wabash, Miami, and Cass counties to join the Wabash at Logansport. The river was called Kineepikwameekwa Siipiiwi - "river of the snake fish" by the Miami people, who inhabited the area at the time of European contact, the English rendered it as Ke-na-po-co-mo-co.
Fluvio refers to things related to rivers and glacial refers to something that is of ice. Fluvio-glacial refers to the meltwater created when a glacier melts. Fluvio-glacial processes can occur on the surface and within the glacier. The deposits that happen within the glacier are revealed after the entire glacier melts or partially retreats. Fluvio-glacial landforms and erosional surfaces include: outwash plains, kames, kame terraces, kettle holes, eskers, varves, and proglacial lakes.

Northwest Indiana comprises Lake, Porter, LaPorte, Newton and Jasper counties in Indiana. This region neighbors Lake Michigan and is part of the Chicago metropolitan area. According to the 2010 Census, Northwest Indiana has a population of 819,537 and is the state's second largest urban area after the Indianapolis Metropolitan Area. It is also the home of the Indiana Dunes, parts of which have been preserved through conservation efforts. The town of Ogden Dunes houses the Hour Glass, a museum showcasing the ecological and conservation efforts of O. D. Frank.
The Maumee Torrent was a catastrophic draining of Lake Maumee, the ancestor of present-day Lake Erie, that occurred during the late Wisconsin glaciation, approximately 21,000 years ago. It happened when the waters of Lake Maumee, possibly in response to an advance of the ice front at the eastern end of the lake, overtopped a "sag" or low spot in the Fort Wayne Moraine, which was a deposit of glacial debris that acted as a natural dam at the site of present-day Fort Wayne, Indiana. This unleashed a massive flow of water that scoured a one- to two-mile-wide outlet running southwest to the Wabash River known as the "Wabash-Erie Channel", which probably followed the course of earlier, less massive drainage. The channel, now a small stream called the Little River, is the largest topographical feature in Allen County, Indiana. As much as 30 feet of fine sand, silt and organic sediments were deposited in the channel before drainage reversed and was captured by the present-day Maumee River. U.S. Route 24 between Fort Wayne and Huntington follows the channel.

Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 Years Before Present (YBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide ice sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.

Sims Corner Eskers and Kames National Natural Landmark and nearby McNeil Canyon Haystack Rocks and Boulder Park natural landmarks contain excellent examples of Pleistocene glacial landforms. Sims Corner Eskers and Kames National Natural Landmark includes classic examples of ice stagnation landforms such as glacial erratics, terminal moraines, eskers, and kames. It is located on the Waterville Plateau of the Columbia Plateau in north central Washington state in the United States.

The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.

The Valparaiso Moraine is a recessional moraine that forms an immense U around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It is a band of high, hilly terrain made up of glacial till and sand. It begins near the border of Wisconsin and Illinois and extends south through Lake, McHenry, Cook, DuPage and Will counties in Illinois, and then turns southeast, entering Indiana. From this point, the moraine curves northeast through Lake, Porter, and LaPorte counties of Indiana into Michigan. It continues into Michigan as far as Montcalm County.

The Tinley Moraine is a moraine around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation and is younger than the higher and wider terminal moraine called the Valparaiso Moraine, which is located farther from the lake than the Tinley Moraine. Compared to the Valparaiso Moraine, the Tinley Moraine is much narrower and occupies a similar swath, about 6 miles (10 km) closer to Lake Michigan, and passes through the communities of Flossmoor, Western Springs, and Arlington Heights. The moraine probably was named after the village of Tinley Park, a village southwest of Chicago that lies on the moraine.

The Kankakee Outwash Plain is a flat plain interspersed with sand dunes in the Kankakee River valley in northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois of the United States. It is just south of the Valparaiso Moraine and was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation. As the glacier, stopped at the Valparaiso Moraine, melted, the meltwater was carried away to the outwash plain. On the south side of the moraine, where the elevation drops, the meltwaters eroded away valleys, carrying sand and mud with them. As the muddy meltwater reached the valley where the slope lessened, the water slowed down, depositing the sand on the outwash plain. This created a smooth, flat, and sandy plain. Before its draining, the Kankakee Marsh, located on the outwash plain, was one of the largest freshwater marshes in the United States.

Boulder Park National Natural Landmark, along with the nearby McNeil Canyon Haystack Rocks and Sims Corner Eskers and Kames natural landmarks, illustrate well-preserved examples of classic Pleistocene ice stagnation landforms that are found in Washington. These landforms include numerous glacial erratics and haystack rocks that occur near and on the Withrow Moraine, which is the terminal moraine of the Okanogan ice lobe.

The Kankakee Torrent was a catastrophic flood that occurred about 19,000 BP calibrated years ago in the Midwestern United States. It resulted from a breach of moraines forming a large glacial lake fed by the melting of the Late Wisconsin Laurentide Ice Sheet. The point of origin of the flood was from Lake Chicago. The landscape south of Chicago still shows the effects of the torrent, particularly at Kankakee River State Park and on the Illinois River at Starved Rock State Park.
The Mississinawa Moraine begins in Ohio east of Lima in Hardin County, then running in a shallow arc to the south of Grand Lake St. Marys and St. Marys in Mercer County towards Fort Recovery, Ohio. Just west of Fort Recovery, the moraine again arches southward towards the Mississinewa River. The moraine follows the eastern bank of the river northwestward to where it enters the Wabash River at Wabash, Indiana. Angling towards the north and a little east, the Mississinawa moraine merges with the Packerton Moraine north of the Eel River in Whitley County near Columbia City. The moraine does not end here, but continues in a northeasterly direction through the three corners area of Michigan, Indiana, and Ohio until reaching Ann Arbor, Michigan where numerous moraines intermingle. Note: There are two common spellings of the name. Mississinawa is commonly used in the older reports. Mississinewa is the modern usage and the spelling used on modern maps and projects associated with the river. Both spellings are used interchangeably in this article, based on the source material.
The Union Moraine begins in Ohio, east of Bellefontaine and the highest point in that state, towards Greenville in Darke County. Traveling southwestward and arcing a little northward, the moraine reaches Union City, Ohio for which it is named. From here, it travels almost directly westward to Muncie, Indiana. From Muncie, the moraine runs northwest ending in the bluffs overlooking Pipe Creek at Bunker Hill,Indiana, just south of Peru on the Wabash River.
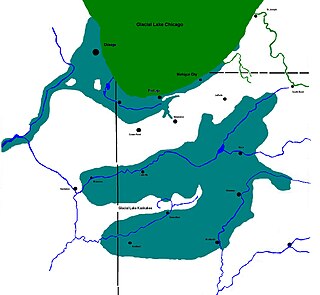
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.

The Marseilles moraine is a terminal moraine that encircles the southern tip of Lake Michigan in North America. It begins near Elgin, Illinois, and extends south and west of Chicago metropolitan area, turning eastward 30 miles (48 km) to 40 miles (64 km) south of the lake in Kankakee and Iroqouis counties, entering Indiana. It formed during the Wisconsin glaciation. The glacier had been in retreat when it stopped for an extended period, depositing glacial till and sand creating the hills of the moraine.

The Lake Border Moraine is a complex group of moraines bordering the southern end of Lake Michigan. It can be traced north along the eastern shore of the lake basin and across the highlands between the northern Lake Michigan and Saginaw Bay. It continues around the Saginaw Basin into the " thumb " of Michigan, and south through southeastern Michigan on the eastern side of the "thumb." Along Lake Michigan, north to Holland the system is close to the shore. From Holland north to Oceana County it is 15 miles (24 km) to 25 miles (40 km) east of the shore. In Oceana County it forms the prominent "clay banks" along the shoreline of Lake Michigan. It again bears inland from Hart, where more recent moraines reside between it and Lake Michigan. It runs north of the great interlobate moraine that exists between the Lake Michigan and Saginaw lobes of the Laurentian ice sheet. A little north of Cadillac turns to the east. A short distance from Cadillac, it splits with the southern ridge or outer member heading to the Saginaw basin. The northern ridge heads towards Lake Huron, but turns south before reaching the shore. In Newaygo and Lake counties it rest on an earlier interlobate moraine. It separates in Wexford and Missaukee counties to continue south along the west side of the Saginaw basin.