
The Siegfried Line, known in German as the Westwall, was a German defensive line built during the late 1930s. Started in 1936, opposite the French Maginot Line, it stretched more than 630 km (390 mi) from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the western border of Nazi Germany, to the town of Weil am Rhein on the border with Switzerland. The line featured more than 18,000 bunkers, tunnels and tank traps.
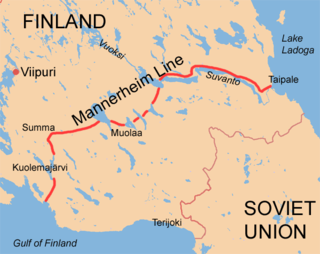
The Mannerheim Line was a defensive fortification line on the Karelian Isthmus built by Finland against the Soviet Union. While this was never an officially designated name, during the Winter War it became known as the Mannerheim Line, after Finnish Army's then commander-in-chief Field Marshal Baron Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim. The line was constructed in two phases: 1920–1924 and 1932–1939. By November 1939, when the Winter War began, the line was by no means complete.

The Battle of Rostov (1941) took place on the Eastern Front of World War II around Rostov-on-Don and was fought between Army Group South of Nazi Germany and the Southern Front of the Soviet Union.

The Mius is a river in Eastern Europe that flows through Ukraine and Russia. It is 258 kilometres (160 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 6,680 square kilometres (2,580 sq mi).

Dragon's teeth are pyramidal anti-tank obstacles of reinforced concrete first used during the Second World War to impede the movement of tanks and mechanised infantry. The idea was to slow down and channel tanks into killing zones where they could easily be disposed of by anti-tank weapons.

The second Smolensk operation was a Soviet strategic offensive operation conducted by the Red Army as part of the Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1943. Staged almost simultaneously with the Lower Dnieper Offensive, the offensive lasted two months and was led by General Andrei Yeremenko, commanding the Kalinin Front, and Vasily Sokolovsky, commanding the Western Front. Its goal was to clear the German presence from the Smolensk and Bryansk regions. Smolensk had been under German occupation since the first Battle of Smolensk in 1941.

Czechoslovakia built a system of border fortifications as well as some fortified defensive lines inland, from 1935 to 1938 as a defensive countermeasure against the rising threat of Nazi Germany. The objective of the fortifications was to prevent the taking of key areas by an enemy—not only Germany but also Hungary and Poland—by means of a sudden attack before the mobilization of the Czechoslovak Army could be completed, and to enable effective defense until allies—Britain and France, and possibly the Soviet Union—could help.

The 383rd 'Miners' Rifle Division was a formation of the Red Army, created during the Second World War. The division was officially created on 18 August 1941. It was given the name Shakhterskaya, as it was originally composed completely of miners from the Donets Basin, Ukrainian SSR. During the course of the war, its losses were continually replaced, and thus it began to consist not only of miners from Donbas.

The Soviet city of Taganrog, now part of the Rostov Oblast of the Russian Federation, had an eventful history during World War II, from 1941 to 1945.
The 31st Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army during the interwar period and World War II.

The Donbas strategic offensive was the second of two strategic operations of the Soviet Red Army on the Eastern Front of World War II, with the goal of liberating the Donetsk Basin, or Donbas, from the forces of Nazi Germany.

The Árpád Line was a line of fortifications built in 1941-44 in the north-eastern and eastern Carpathian Mountains, along the border of Kingdom of Hungary. It was named after Árpád, the head of the Hungarian tribes. The main function of the Line was to protect Northern Transylvania and Carpathian Ruthenia from the east.

The 87th Guards Rifle Division was created on 16 April 1943 from the veterans of the 300th Rifle Division, in recognition of that division's leading role in the penetration of the German/Romanian defenses south of Stalingrad in the opening stages of Operation Uranus, its subsequent defense against Army Group Don's attempt to relieve the German Sixth Army at Stalingrad, and later for its pursuit of the defeated German forces along the Don River to Rostov-na-Donu as far as the Mius River. The 87th Guards continued a record of distinguished service through the rest of the Great Patriotic War, first in the southern sector of the front, where it participated in the liberation of the Donbas region and the Crimea, and then, after a major redeployment, in the north-central sector, advancing through the Baltic states and into East Germany. After the war it was restructured into a rifle brigade, before being reestablished as 87th Guards Rifle Division in October 1953. In June 1957, it was reorganized as a motor rifle division, but appears to have been disbanded in 1959.

The flexible defense is a military theory about the design of modern fortifications. The examples of "flexible" defense-lines are not based on dense lines of heavily armed, large and expensive concrete fortifications as the systems such as the Maginot Line were. Their protective capacity hinges on multiple lines of obstacles and small shelters fitting into the environment. They are "flexible" because soldiers are not locked in pillboxes, but fight instead in easily replaceable open earth-wood made positions, while bunkers serve only as shelters during bombardments. As a result, they are able to adapt to the opponent's movements, and there are no easily targeted large buildings in these lines.

Vasily Afanasyevich Khomenko was a Soviet army commander, and lieutenant general.

The Izyum–Barvenkovo offensive was a Soviet offensive operation of the Southwestern Front against part of German Army Group South during the World War II. The aim of the operation was to tie down German reserves during the Battle of Kursk and overrun the German forces located in Donbas. Soviet troops managed to cross the Donets river and seize the bridgehead, but the German counterattacks stopped the further advance.
The Donbas Operation was a frontline defensive operation of the Soviet Red Army in the territory of Donbas on the Eastern Front of the Second World War in Europe. It was an integral part of the Donbas–Rostov Strategic Defensive Operation.
The Rostov Defensive Operation on November 5–16, 1941 was a front–line defensive operation of the Soviet troops of the Southern Front, an integral part of the Donbas–Rostov Strategic Defensive Operation of the Great Patriotic War.
The Donbas–Rostov Strategic Defensive Operation was a defensive operation of the Southern Front and the left wing of the South–Western Front of the Red Army on the territory of Donbas during the World War II. During it, the Donbas and Rostov front–line defensive operations were carried out.
The 230th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army, originally formed as one of the first reserve rifle divisions following the German invasion of the USSR. After being hastily organized, it joined the fighting front along the lower Dniepr River as part of 6th Army. After the German victory east of Kyiv, it retreated into the Donbas as part of 12th Army and spent the winter in the fighting around Rostov-on-Don. When the German 1942 summer offensive began, it was driven back, now as part of 37th Army, and largely encircled near Millerovo. While not destroyed, by late August it was so depleted that it was disbanded.














