In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.

The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.

The platysma muscle is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effect on either side of the neck.

The depressor labii inferioris is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip.

The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle of the face. It arises from either zygomatic arch (cheekbone); it inserts at the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by branches of the facial nerve.

The zygomaticus minor muscle is a muscle of facial expression. It originates from the zygomatic bone, lateral to the rest of the levator labii superioris muscle, and inserts into the outer part of the upper lip. It draws the upper lip backward, upward, and outward and is used in smiling. It is innervated by the facial nerve (VII).

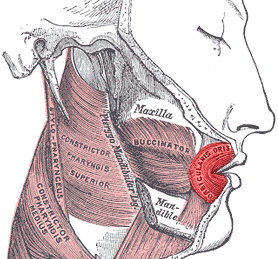
The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.

The levator anguli oris (caninus) is a facial muscle of the mouth arising from the canine fossa, immediately below the infraorbital foramen. It elevates angle of mouth medially. Its fibers are inserted into the angle of the mouth, intermingling with those of the zygomaticus, triangularis, and orbicularis oris. Specifically, the levator anguli oris is innervated by the buccal branches of the facial nerve.

The depressor anguli oris muscle is a facial muscle. It originates from the mandible and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It is associated with frowning, as it depresses the corner of the mouth.
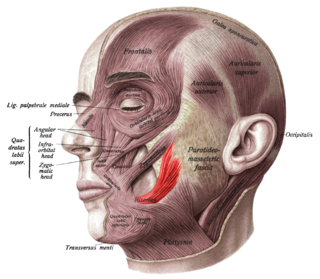
The risorius muscle is a highly variable muscle of facial expression. It has numerous and very variable origins, and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It receives motor innervation from branches of facial nerve. It may be absent or asymmetrical in some people. It pulls the angle of the mouth sidewise, such as during smiling.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The mental nerve is a sensory nerve of the face. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensation to the front of the chin and the lower lip, as well as the gums of the anterior mandibular (lower) teeth. It can be blocked with local anaesthesia for procedures on the chin, lower lip, and mucous membrane of the inner cheek. Problems with the nerve cause chin numbness.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve arises from the facial nerve in the parotid gland at the parotid plexus. It passes anterior-ward deep to the platysma and depressor anguli oris muscles. It provides motor innervation to muscles of the lower lip and chin: the depressor labii inferioris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle, and mentalis muscle. It communicates with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The buccal branches of the facial nerve, are of larger size than the rest of the branches, pass horizontally forward to be distributed below the orbit and around the mouth.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates. They are the only muscles that attach to the dermis.
The buccal fat pad is one of several encapsulated fat masses in the cheek. It is a deep fat pad located on either side of the face between the buccinator muscle and several more superficial muscles. The inferior portion of the buccal fat pad is contained within the buccal space. It should not be confused with the malar fat pad, which is directly below the skin of the cheek. It should also not be confused with jowl fat pads. It is implicated in the formation of hollow cheeks and the nasolabial fold, but not in the formation of jowls.
Jaw reduction or mandible angle reduction is a type of surgery to narrow the lower one-third of the face—particularly the contribution from the mandible and its muscular attachments. There are several techniques for treatment—including surgical and non-surgical methods. A square lower jaw can be considered a masculine trait, especially in Asian countries. As a result, whereas square lower jaws are often considered a positive trait in men, a wide mandible can be perceived as discordant or masculine on women, or sometimes in certain men, particularly when there is asymmetry.
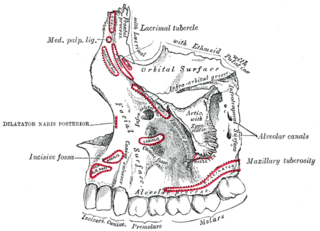
The canine space, is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a thin potential space on the face, and is paired on either side. It is located between the levator anguli oris muscle inferiorly and the levator labii superioris muscle superiorly. The term is derived from the fact that the space is in the region of the canine fossa, and that infections originating from the maxillary canine tooth may spread to involve the space. Infra-orbital is derived from infra- meaning below and orbit which refers to the eye socket.
2.Al-Hoqail RA, Abdel Meguid EM. An anatomical and analytical study of the modiolus: enlightening its relevance to plastic surgery. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2009;33(2):147–152. doi:10.1007/s00266-008-9187-x
3.Pélissier P, Pistre V, Bustamante K, Martin D, Baudet J. Le modiolus. Anatomie comparée, rappels embryologique et physiologique, intérêt chirurgical [The modiolus. Comparative anatomy, embryological and physiological review, surgical importance]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2000;45(1):41–47.
4.Yu SK, Lee MH, Kim HS, Park JT, Kim HJ, Kim HJ. Histomorphologic approach for the modiolus with reference to reconstructive and aesthetic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(4):1414–1417. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e318292c939
















