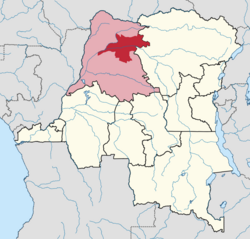
Équateur was a province in the northwest of Belgian Congo and the independent Republic of the Congo, now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had its origins in the Équateur District of the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. It was upgraded to provincial status in 1917. Between 1933 and 1947 it was named Coquilhatville. In 1962 it was divided into three smaller provinces, but there were recombined in 1966. Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo until 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces.

Équateur District was a former district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. In 1914, it became part of former Équateur Province. The district went through various changes of extent and name over the years. The original district roughly corresponds to the current provinces of Équateur and Tshuapa.

Tshuapa is one of the 21 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Tshuapa, Équateur, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi, and Sud-Ubangi provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Équateur province. Tshuapa was formed from the Tshuapa District whose town of Boende was elevated to capital city of the new province.

Kasai District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, named after the Kasai River. It was formed around 1885 and went through several large changes in extent in the years that followed. The 1933 version of the district roughly corresponded to the former Kasai-Occidental province and the present Kasaï and Kasaï-Central provinces.

Tshuapa District, was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in 1933 in the Coquilhatville Province. At its greatest extent it roughly corresponded to the present provinces of Équateur and Tshuapa.

Haut-Lomami District was a district of the pre-2015 Katanga Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The district dates back to the days of the Belgian Congo. At its greatest extent it roughly corresponded to the northern part of the current Lualaba Province and to the present Haut-Lomami Province.
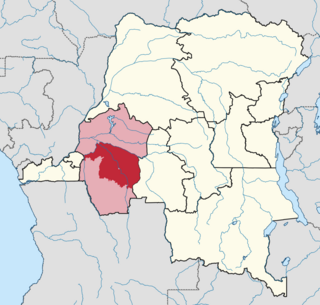
Kwilu District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded to the present province of Kwilu.

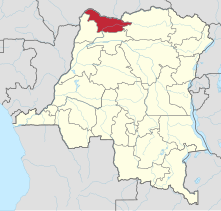
Bas-Uele District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was formed from part of Uele District in 1912 and was later merged into Uele District, then split out again. There were various boundary changes. It roughly corresponded in area to the present Bas-Uélé province.

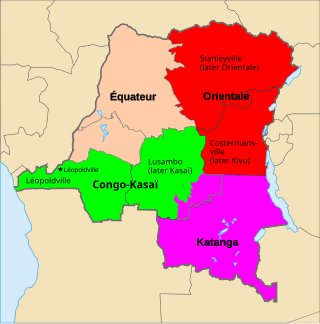
The Districts of the Belgian Congo were the primary administrative divisions when Belgium annexed the Congo Free State in 1908, each administered by a district commissioner. In 1914 they were distributed among four large provinces, with some boundary changes. In 1933 the provinces were restructured into six, again with boundary changes. The number of districts fluctuated between 12 and 26 through splits and consolidations, first rising, then falling, then rising again.

Stanleyville District was a district of the Belgian Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various changes in extent. Between 1933 and 1963 it had roughly the same extent as the current Tshopo province.
Ubangi District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various significant changes in extent.
Bangala District was a district of the Congo Free State and the Belgian Congo. It went through various significant changes in extent. The eastern part very roughly corresponded to the present province of Mongala.
Lulonga District was a district of the Belgian Congo created in 1912 and dissolved in 1933. Today part of Lulonga is in the current province of Équateur, and part in the province of Tshuapa.
Congo-Ubangi District, was a district of the Belgian Congo created in 1933 in the Coquilhatville Province. It had been dissolved by 1954.
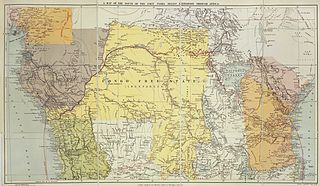
The Districts of the Congo Free State were the primary administrative divisions of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908. There were various boundary changes in the period before the Congo Free State was annexed by Belgium to become the Belgian Congo.

Tanganika District was a district of the pre-2015 Katanga Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The district dates back to the days of the Belgian Congo. At its greatest extent it roughly corresponded to the present Tanganyika Province, with a small portion in the southwest now in Haut-Lomami Province.

Sud-Kivu District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded in area to the present South Kivu province.

Nord-Kivu District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded in area to the present North Kivu province.
Luapula-Moero District was a district of the pre-2015 Katanga Province in the Belgian Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded in area to the present Haut-Katanga Province.