
The little ringed plover is a small plover. The genus name Charadrius is a Late Latin word for a yellowish bird mentioned in the fourth-century Vulgate. It derives from Ancient Greek kharadrios a bird found in river valleys. The specific dubius is Latin for doubtful, since Sonnerat, writing in 1776, thought this bird might be just a variant of common ringed plover.

Isopogon, commonly known as conesticks, conebushes or coneflowers, is a genus of about forty species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae, and are endemic to Australia. They are shrubs with rigid leaves, bisexual flowers in a dense spike or "cone" and the fruit is a small, hairy nut.

Trichius fasciatus, also known as the Eurasian Bee Beetle, is a beetle species belonging to the family Scarabaeidae, subfamily Cetoniinae.

Monochamus is a genus of longhorn beetles found throughout the world. They are commonly known as sawyer beetles or sawyers, as their larvae bore into dead or dying trees, especially conifers such as pines. They are the type genus of the Monochamini, a tribe in the huge long-horned beetle subfamily Lamiinae, but typically included in the Lamiini today.

Isopogon dubius, commonly known as pincushion coneflower, is a species of plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a shrub with sharply-pointed, deeply lobed or pinnate leaves and more or less spherical heads of pink to reddish pink flowers.
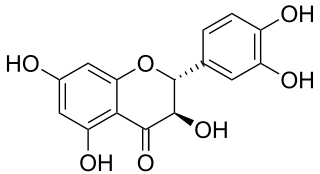
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols.

Tylopilus tabacinus is a species of bolete fungus in the family Boletaceae. It is characterized by a tawny-brown cap measuring up to 17.5 cm (6.9 in) in diameter, and a reticulated stem up to 16.5 cm (6.5 in) long by 6 cm (2.4 in) thick. A characteristic microscopic feature is the distinctive crystalline substance encrusted on the hyphae in the surface of the cap. The species is known from the eastern United States from Florida north to Rhode Island, and west to Mississippi, and from eastern Mexico. It is a mycorrhizal species, and associates with oak and beech trees.
Monochamus tuberosus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1884. It contains the varietas Monochamus tuberosus var. orientalis.
Monochamus adamitus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1857. It is known from Tanzania, Sierra Leone, Angola, Ghana, Mozambique, the Ivory Coast, Senegal, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, and Zimbabwe.

Monochamus sutor is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, originally under the genus Cerambyx. It has a wide, natural distribution throughout Europe, and has also been introduced into Belgium and the Netherlands. Adults measure between 15 to 24 mm, and larvae measure up to 45 mm (1.8 in).

Monochamus bimaculatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1888. It is known from Myanmar, Vietnam, India, Malaysia, Taiwan, Laos, and Thailand. It contains the varietas Monochamus bimaculatus var. ingranulatus.

The spotted pine sawyer is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by John Lawrence LeConte in 1852.

Monochamus galloprovincialis, the pine sawyer beetle, also referred to as the black pine sawyer beetle, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Olivier in 1795, originally under the genus Cerambyx. It has a wide distribution, occurring naturally throughout Europe and the Caucasus. It has also been introduced into the Canary Islands. It serves as a vector for the parasitic nematode species Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and also acts as a host to the parasitoid wasp species Dolichomitus tuberculatus.
Monochamus ruficornis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Hintz in 1913, originally under the genus Monohammus. It is known from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Cameroon. It contains the varietas Monochamus ruficornis var. dissolutus.
Monochamus ruspator is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1781, originally under the genus Lamia. It has a wide distribution throughout Africa.

Monochamus spectabilis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Perroud in 1855, originally under the genus Lophoptera. It has a wide distribution throughout Africa. It contains the varietas Monochamus spectabilis var. immaculipennis.
Monochamus thomsoni is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Chevrolat in 1855, originally under the genus Monohammus. It has a wide distribution throughout Africa. It contains the varietas Monochamus thomsoni var. buea.
Monochamus vagus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1888, originally under the genus Monohammus. It is known from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It contains the varietas Monochamus vagus var. bomasi.

Pseudonemophas versteegi is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Ritsema in 1881, originally under the genus Monochamus. It is known from India, Sumatra, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, and China. It contains the varietas Pseudonemophas versteegi var. albescens.













