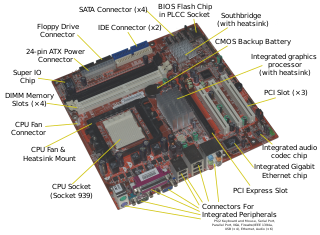
BIOS is non-volatile firmware used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process, and to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs. The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on a personal computer's system board, and it is the first software to run when powered on. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by companies looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a de facto standard.

Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.

In computing, the expansion card, expansion board, adapter card or accessory card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.

The Amiga 2000, or A2000, is a personal computer released by Commodore in March 1987. It was introduced as a "big box" expandable variant of the Amiga 1000 but quickly redesigned to share most of its electronic components with the contemporary Amiga 500 for cost reduction. Expansion capabilities include two 3.5" drive bays and one 5.25" bay that can be used by a 5.25" floppy drive, a hard drive, or CD-ROM once they became available.

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers were made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.

The Elbrus is a line of Soviet and Russian computer systems developed by Lebedev Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering. These computers are used in the space program, nuclear weapons research, and defense systems, as well as for theoretical and researching purposes, such as an experimental Refal and CLU translators.

In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.
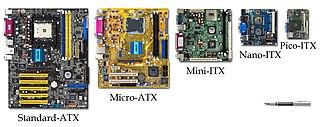
Small Form Factor refers to various computer form factors designed to minimize the volume and footprint of a desktop computer. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs. Their smaller and often lighter construction has made them popular as home theater PCs and as gaming computers for attending LAN parties. Manufacturers also emphasize the aesthetic and ergonomic design of SFFs since users are more likely to place them on top of a desk or carry them around. Advancements in component technology together with reductions in size means a powerful computer is no longer restricted to the huge towers of old.
In computing, the form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented.
The Digital Personal Workstation, code named "sports car", is a family of entry-level to mid-range workstation computers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). These workstations are based on the DEC Alpha and Intel Pentium Pro or Pentium II microprocessors. Members of this family can run the Digital UNIX, OpenVMS and Microsoft Windows NT operating systems. The i-Series, based on Pentium Pro, was introduced first, on 23 September 1996.

Elbrus-2S+ is a multi-core microprocessor based on the Elbrus 2000 architecture developed by Moscow Center of SPARC Technologies (MCST) There are multiple reports regarding the evolution of this technology for the purpose of import substitution in Russia, which was raised by several ministries on July 2014, due to economic sanctions in response to 2014 pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine. In December 2014, it was announced that Mikron start pilot production of a dual-core variant of this microprocessor called Elbrus-2SM using a 90 nanometer CMOS manufacturing process in Zelenograd, Russia.

MCST is a microprocessor company that was set up in 1992. Different types of processors made by MCST were used in personal computers, servers and computing systems. MCST develops microprocessors based on two different instruction set architecture (ISA): Elbrus (computer) and SPARC. MCST is a direct descendant of the Lebedev Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering.
Monoblock PC is a computer workstation based on the Elbrus 2000 architecture. It was developed in Russia as a joint effort between Kraftway and the Moscow Center of SPARC Technologies (MCST).

LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively.

The Elbrus-8S is a Russian 28 nanometer 8-core microprocessor developed by Moscow Center of SPARC Technologies (MCST). The first prototypes were produced by the end of 2014 and serial production started in 2016. The Elbrus-8S is to be used in servers and workstations.

MultiClet is an ongoing innovation project for a microprocessor that claims to be the first post von Neumann, multicellular microprocessor, breaking the paradigm for computing technology that has been in place for more than 60 years. There have been attempts in the past to shift away from the von Neumann architecture, but no one has really taken it to the limit by trying to implement a fully multicellular - dynamically reconfigurable microprocessor. Now 4-cellular dynamically reconfigurable microprocessor is implemented.
Mikron Group, headed by JSC Mikron, is one of the largest manufacturers and exporters of microelectronics in Russia and the CIS. Its facilities are located in Zelenograd, Russia.
Baikal CPU is a line of MIPS and ARM-based microprocessors developed by fabless design firm Baikal Electronics, a spin-off of the Russian supercomputer company T-Platforms.