Related Research Articles
The Geintizinacea comprises a superfamily of Upper Devonian to Upper Permian uniserial fusulinids, the chamber walls consisting of a dark microgranular inner layer and radially fibrous outer layer. Advanced forms show secondary lateral thickening
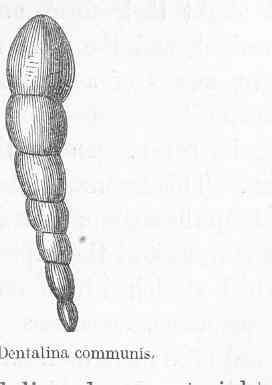
Lagenida is an order of benthic foraminiferal protists in which the tests (shells) are monolamellar, with walls composed of optically and ultra-structurally radiate calcite, with the crystallographic c-axes perpendicular to the surface. Lagenids first appear in the Upper Silurian and continue to the Recent. They are currently divided into two superfamilies, the older Robuloidacea which range from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) and the younger Nodosariacea, ranging from the Permian to Recent.
Parathuramminacea comprises a superfamily within the foraminiferal order Fusulinida, characterized by tests (shells) that are unilocular, globular to elongate or irregular, or that may consist of a series or cluster of such chambers. Forms are either free or attached.
Involutinida is an order of foraminifera included in the Spirillinata found in the fossil record from the early Permian to early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian).
The Rzehakinidae is a family of Lower Cretaceous to recent formaminifera that resemble the calcareous imperforate Miliolidae but which are constructed of finely agglutinated material that veneers an organic base. Tests are with two, or less commonly three, chambers per whorl, which are commonly added in various planes. In form they are generally ovoid.

Cibicides is a genus of cosmopolitan benthic foraminifera known from at least as far back as the Paleocene that extends down to the present.
Discorbis is a genus of benthic Foraminifera, that made its first appearance during the Eocene. Its present distribution is cosmopolitan.
Rosalina is a genus of foraminifera included in the rotaliid family Rosalinidae.
Neoconorbina is a genus of recent (Holocene) discorbacean foraminifers related to Rosalina with a low conical trochoidal test, circular in outline. The conical side is the spiral side, on which all three whorls are visible, the final chamber taking up most of the periphery. The umbilical side is flat to concave. exposing only the three to four chambers of the final whorl around an open umbilicus. Chambers on the umbilical side have triangular to platelike umbilical extensions as with other rasalinids. The wall of is calcite, finely and densely perforate on the spiral side, more coarsely perforate on the umbilical side; surface smooth; aperture at the umbilical margin of the chamber, beneath the platelike extension, or folium.
The Ammodiscacea is a superfamily of foraminifera in the order Textulariida. tests are made of agglutinated grains and consist of a proloculus followed by an enrolled tubular second chamber open at the distal end, that lacks internal septa but which may have growth constrictions.
The Hormosinacea is a superfamily of agglutinated foraminifera in the Textulariida, with a range that extends from the Middle Ordovician, that unites seven families characterized by multilocular tests,, in a uniserial arrangement.
Schwagerina is an extinct genus of fusulinacean Foraminifera that is used as an Early Permian index fossil. The overall shape of the shell or test is fusiform to subcylindrical, the spirotheca, or outer test wall, is thick, and composed of tectum and alveolar keriotheca; the septa are fluted throughout the length of the shell, intense to top of chambers in some, only in lower parts in others; axial fillings highly variable, chomata distinct or thin and discontinuous.
Sigmoilina is a miliolid genus, referring to the foraminiferal order Miliolida, characterized by an assymmetricall biconvex test formed by strongly overlapping chambers, one-half coil in length, that form a sigmoid (S-shaped) curve in cross section. The strongly overlapping chambers obliterate earlier ones from view resulting in the compressed biloculine appearance, differing from the squat, depressed biloculine form of Pyrgo and Biloculina. The test, as for all Miliolida, is porcelaneous and imperphorate, the terminal aperture, with tooth, the only point of egress and ingress for the animal.
Triloculinella is a genus of Miliolacean forams with a fusiform to asymmetrically globular test. Inner chambers, one-half coil in length, are crypto-quinqueloculine to quinqueloculine in arrangement; The final three to five visible from the exterior. The aperture is an arch at the end of the final chamber, largely covered by a broad apertural flap, which distinguishes the genus from Triloculina, Quinqueloculina and such, characterized by a more narrow tooth. The wall, as for all miliolids, is calcareous, imperforate, porcelaneous.

Hauerinidae is a large and diverse family of miliolid forams that includes genera distributed among various subfamilies in the Treatise as well as genera named and described since.

Fischerinidae is a foraminiferal family now in the miliolid superfamily Cornuspiracea that comprises genera that can be free or attached, in which the proloculus is followed by an undivided tubular or spreading second chamber. Commonly, especially in free, i.e. unattached, forms the second chamber is looped around in coils. As diagnostic for the Miliolida the test wall is of imperphorate porcelaneous calcite. The aperture, which is the avenue of egress and ingress for the protoplasm, is terminal; can be rounded or slitlike.
Hemigordiopsidae is a miliolid family included in the Cornuspiracea that has a range extending from the Early Carboniferous (Visean) to the present.
Cornuspiracea comprise a superfamily of miliolid forams in which the test may be free or attached, planispiral or trochospiral, evolute or involute, spreading or discoidal. The proloculus, or initial chamber, is followed by undivided spiral passage or enrolled tubular chamber, later may be irregularly coiled, unicoiled, or show zigzag growth pattern and may be distinctly chambered. The test wall is composed of imperforate porcelaneous calcite, a character of the Miliolida

Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera.
Alfred R. Loeblich Jr (1914–1994) was an American micropaleontologist. He was married to Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich and the two co-authored a number of important works on the Foraminifera and related organisms.
References
- Alfred R. Loeblich Jr and Helen Tappan, 1964. Sarcodina Chiefly "Thecamoebians" and Foraminiferida; Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, part C Protista 2. Geological Society of America and University of Kansas Press. R.C. Moore (ed)
- Alfred R. Loeblich Jr and Helen Tappan,1988. Forminiferal Genera and their Classification. Van Nostrand Reinhold.