
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors.

A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. The electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules.

A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, Fresnel reflectors, lenses, or the mirrors of a heliostat.

Spain is one of the first countries to deploy large-scale solar photovoltaics, and is the world leader in concentrated solar power (CSP) production.

First Solar, Inc. is a public traded American manufacturer of solar panels, and a provider of utility-scale PV power plants and supporting services that include finance, construction, maintenance and end-of-life panel recycling. First Solar uses rigid thin-film modules for its solar panels, and produces CdTe panels using cadmium telluride (CdTe) as a semiconductor. The company was founded in 1990 by inventor Harold McMaster as Solar Cells, Inc. and the Florida Corporation in 1993 with JD Polk. In 1999 it was purchased by True North Partners, LLC, who rebranded it as First Solar, Inc.

Solar power includes solar farms as well as local distributed generation, mostly on rooftops and increasingly from community solar arrays. In 2023, utility-scale solar power generated 164.5 terawatt-hours (TWh), or 3.9% of electricity in the United States. Total solar generation that year, including estimated small-scale photovoltaic generation, was 238 TWh.
A photovoltaic system, also called a PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. Many utility-scale PV systems use tracking systems that follow the sun's daily path across the sky to generate more electricity than fixed-mounted systems.
Skyline Solar was a Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) company based in Mountain View, California. The company developed medium-concentration photovoltaic systems to produce electricity for commercial, industrial and utility scale solar markets. The company was founded in 2007 by Bob MacDonald, Bill Keating and Eric Johnson. The operation of the company appears to have ceased in late 2012 and the website is deactivated.

Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) is a photovoltaic technology that generates electricity from sunlight. Unlike conventional photovoltaic systems, it uses lenses or curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto small, highly efficient, multi-junction (MJ) solar cells. In addition, CPV systems often use solar trackers and sometimes a cooling system to further increase their efficiency.
Cool Earth Solar has developed concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) technology to build solar power plants. The company is headquartered in Livermore, California, US, and in 2008 closed its Series A round of funding with Quercus Trust as the lead investor. The company was founded in 2006 by Dr. Eric Cummings. Energy industry veteran Rob Lamkin joined the company as CEO in 2007.
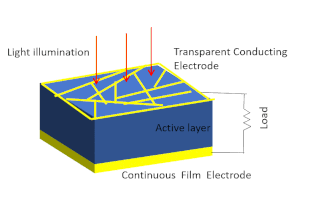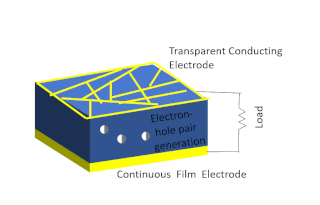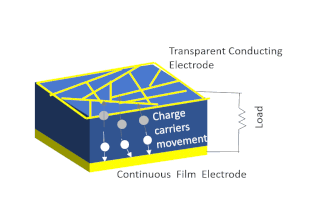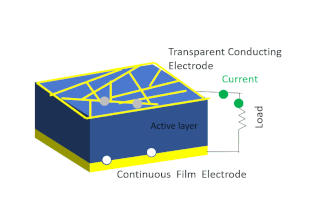
Solar-cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell.
Amonix, Inc. was a solar power system developer based in Seal Beach, California. The company manufactured concentrator photovoltaic (CPV) products designed for installation in sunny and dry climates. CPV products convert sunlight into electrical energy in the same way that conventional solar photovoltaic technology does, except that they use optics to focus the solar radiation before the light is absorbed by solar cells. According to a comparative study of energy production of solar technologies, CPV systems require no water for energy production and produce more energy per megawatt (MW) installed than traditional PV systems. Amonix had nearly 70 megawatts of CPV solar power systems deployed globally, including Southwestern U.S. and Spain.

Antonio Luque López is a Spanish scientist and entrepreneur in the field of photovoltaic solar energy. In 1979 he founded the Institute of Solar Energy of the Technical University of Madrid (IES-UPM) and was its director till his retirement in 2017; he is currently its honorary president as well as professor emeritus in this university. He invented the bifacial solar cell in the late 1970s, today one of the mainstream solar cell technologies, and founded Isofoton in 1981 for its industrial production. He is, arguably, one of the fathers of the science and technology of concentrator photovoltaics and has been active in the research and development of high-efficiency photovoltaic conversion devices, inventing the intermediate band solar cell.

The Alamosa Solar Generating Plant is a 35.3 MWp (30.0 MWAC) concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) power station, the largest in the world when it was completed, in May 2012. It is currently the world's third largest operating CPV facility. The output is being sold to Public Service of Colorado, a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, under a long term Power Purchase Agreement.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to solar energy:

Suncore Photovoltaic Technology Company Limited ("Suncore") is a solar energy company that specializes in concentrator photovoltaics (CPV), an emerging photovoltaic (PV) technology. The company manufactures, develops, and finances CPV systems for ground mounted applications. Its products include CPV solar power systems, receivers, trackers and turnkey service.

Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, are solar panels mounted on a structure that floats on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake such as drinking water reservoirs, quarry lakes, irrigation canals or remediation and tailing ponds. A growing number of such systems exist in China, France, Indonesia, India, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, Singapore, Thailand, and the United States. Floating solar is a type of "offshore solar" energy which also includes fixed-bottom foundations.
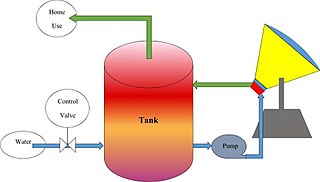
The combination of photovoltaic (PV) technology, solar thermal technology, and reflective or refractive solar concentrators has been a highly appealing option for developers and researchers since the late 1970s and early 1980s. The result is what is known as a concentrated photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) system which is a hybrid combination of concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) and photovoltaic thermal (PVT) systems.
The Eubank Landfill Solar Array is a photovoltaic power station in Albuquerque, New Mexico that consists of 1.0 MWAC of concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) and 1.0 MWAC of flat-panel silicon photovoltaics (PV). It is the only utility-scale CPV system utilizing Suncore third-generation technology that is operational and grid-connected in the US. A portion of the output is being sold to PNM under a Power Purchase Agreement.











