
Bosnia and Herzegovina, abbreviated BiH or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. The capital and largest city is Sarajevo. Bosnia and Herzegovina borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. It is not entirely landlocked; in the south it has a narrow coast on the Adriatic Sea within the Mediterranean, which is about 20 kilometres long and surrounds the town of Neum. Bosnia, which is the inland region of the country, has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions of the country, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, which is the smaller, southern region of the country, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous.
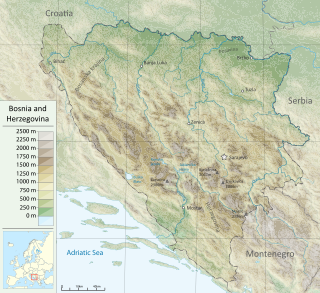
Bosnia and Herzegovina is located in Southeastern Europe, in the western Balkans. It has a 932 km (579 mi) border with Croatia to the north and southwest, a 357 km (222 mi) border with Serbia to the east, and a 249 km (155 mi) border with Montenegro to the southeast. It borders the Adriatic Sea along its 20 km (12 mi) coastline.

The Iapydes were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the Colapis (Kupa) and Oeneus (Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans.

Tuzla is the third-largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the administrative center of Tuzla Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 110,979 inhabitants.

The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated between Central and Southeast Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the lowlands, the plain that remained when the Pliocene Epoch Pannonian Sea dried out.

Prijedor is a city and municipality located in the Republika Srpska entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 89,397 inhabitants within its administrative limits. Prijedor is situated in the north-western part of the Bosanska Krajina geographical region.

Brčko is a city and the administrative seat of Brčko District, in northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. It lies on the banks of Sava river across from Croatia. As of 2013, it has a population 39,893 inhabitants.

Bosnia is the northern region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, encompassing roughly 81% of the country; the other region, the southern part, is Herzegovina.

The Greek Catholic Church of Croatia and Serbia, sometimes called, in reference to its Byzantine Rite, the Byzantine Catholic Church of Croatia and Serbia, is a particular Eastern Catholic church in full communion with the Catholic Church. It consists of the Greek Catholic Eparchy of Križevci, covering Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and the Greek Catholic Eparchy of Ruski Krstur, covering Serbia. The Eparchy of Križevci was headed by Bishop Nikola Kekić until his retirement in March 2019, and since then the eparchy is governed by apostolic administrator Milan Stipić. The Eparchy of Ruski Krstur is headed by Bishop Đura Džudžar since his appointment in 2003.
Yugoslavian languages or languages of Yugoslavia are the languages spoken in the former Yugoslav states. They are mainly Indo-European languages and dialects, namely dominant South Slavic varieties as well as Albanian, Aromanian, Bulgarian, Czech, German, Italian, Venetian, Balkan Romani, Romanian, Rusyn, Slovak and Ukrainian languages. There are also pockets where non-Indo-European languages such as Hungarian, Turkish, etc. varieties are spoken.

Daesitiates were an Illyrian tribe that lived in the territory of today's central Bosnia, during the time of the Roman Republic. Along with the Maezaei, the Daesitiates were part of the western group of Pannonians in Roman Dalmatia. They were prominent from the end of the 4th century BC up until the beginning of the 3rd century CE. Evidence of their daily activities can be found in literary sources, as well as in the rich material finds from Central Bosnian cultural group that is commonly associated with tribe of Daesitiates.

The Drina is a 346 km (215 mi) long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps which belongs to the Danube river watershed. Its name is derived from the Roman name of the river which in turn is derived from Greek.

The Balkan mixed forests are a terrestrial ecoregion of southeastern Europe according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm.

Posavina is a geographical region that stretches along the Sava river, encompassing only the inner areas of the Sava river basin, that are adjacent or near to the Sava river itself, namely catch region spanning from the Julian Alps in the northwest to the confluence with the Danube in the southeast. It passes through several countries of former Yugoslavia, namely Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia.
The Ruthenian Catholic Apostolic Administration of Bosnia-Hercegovina was a short-lived (1914-1924) pre-diocesan Eastern Catholic jurisdiction, covering Bosnia and Hercegovina.

The geology of Bosnia & Herzegovina is the study of rocks, minerals, water, landforms and geologic history in the country. The oldest rocks exposed at or near the surface date to the Paleozoic and the Precambrian geologic history of the region remains poorly understood. Complex assemblages of flysch, ophiolite, mélange and igneous plutons together with thick sedimentary units are a defining characteristic of the Dinaric Alps, also known as the Dinaride Mountains, which dominate much of the country's landscape.

The geology of Croatia has some Precambrian rocks mostly covered by younger sedimentary rocks and deformed or superimposed by tectonic activity.
















