Katmai National Park and Preserve is an American national park and preserve in southwest Alaska, notable for the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes and for its brown bears. The park and preserve encompass 4,093,077 acres, which is between the sizes of Connecticut and New Jersey. Most of the national park is a designated wilderness area. The park is named after Mount Katmai, its centerpiece stratovolcano. The park is located on the Alaska Peninsula, across from Kodiak Island, with headquarters in nearby King Salmon, about 290 miles (470 km) southwest of Anchorage. The area was first designated a national monument in 1918 to protect the area around the major 1912 volcanic eruption of Novarupta, which formed the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes, a 40-square-mile (100 km2), 100-to-700-foot-deep pyroclastic flow. The park includes as many as 18 individual volcanoes, seven of which have been active since 1900.

The Alaska Peninsula National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge in southwestern Alaska whose use is regulated as an ecological-protection measure. It stretches along the southern coast of the Alaska Peninsula, between the Becharof National Wildlife Refuge on its east and the end of the peninsula at False Pass in the west. In between, however, it is broken into sections by lands of the Aniakchak National Monument and Izembek National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in King Salmon, Alaska and was established to conserve Alaska Peninsula brown bears, caribou, moose, marine mammals, shorebirds, other migratory birds and fish, and to comply with treaty obligations.

The Sammamish River flows through north King County, Washington for about 14 miles (23 km), draining Lake Sammamish into Lake Washington. Along its course, the Sammamish River flows through Redmond, Woodinville, Bothell, and Kenmore.

The Kenai River called Kahtnu in the Dena'ina language, is the longest river in the Kenai Peninsula of southcentral Alaska. It runs 82 miles (132 km) westward from Kenai Lake in the Kenai Mountains, through the Kenai National Wildlife Refuge and Skilak Lake to its outlet into the Cook Inlet of the Pacific Ocean near Kenai and Soldotna.
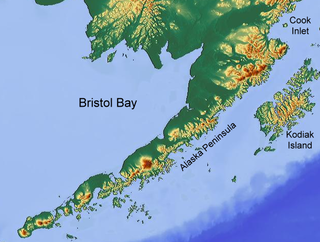
Bristol Bay is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km, (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder, Egegik, Igushik, Kvichak, Meshik, Nushagak, Naknek, Togiak, and Ugashik.

The chum salmon, also known as dog salmon or keta salmon, is a species of anadromous salmonid fish from the genus Oncorhynchus native to the coastal rivers of the North Pacific and the Beringian Arctic, and is often marketed under the trade name silverbrite salmon in North America. The English name "chum salmon" comes from the Chinook Jargon term tzum, meaning "spotted" or "marked"; while keta in the scientific name comes from Russian, which in turn comes from the Evenki language of Eastern Siberia. The term 'Dog Salmon' is most commonly used in Alaska and refers to the Salmon whose flesh Alaskans use to feed their dogs.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

The sockeye salmon, also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, blueback salmon, or simply sockeye, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a Pacific salmon that is primarily red in hue during spawning. They can grow up to 84 cm in length and weigh 2.3 to 7 kg (5–15 lb). Juveniles remain in freshwater until they are ready to migrate to the ocean, over distances of up to 1,600 km (1,000 mi). Their diet consists primarily of zooplankton. Sockeye salmon are semelparous, dying after they spawn. Some populations, referred to as kokanee, do not migrate to the ocean and live their entire lives in fresh water.

Chiginagak Volcano is a stratovolcano on the Alaska Peninsula, located about 15 km NW of Chiginagak Bay.

The coho salmon is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name kizhuch (кижуч).

Oncorhynchus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae, native to coldwater tributaries of the North Pacific basin. The genus contains twelve extant species, namely six species of Pacific salmon and six species of Pacific trout, all of which are migratory mid-level predatory fish that display natal homing and semelparity.

The Ugashik River is a stream, 43 miles (69 km) long, on the Alaska Peninsula of the U.S. state of Alaska. It flows from headwaters near Lower Ugashik Lake and empties into Ugashik Bay, an estuary of the Bering Sea's Bristol Bay.

The Baker River is an approximately 30-mile (48 km), southward-flowing tributary of the Skagit River in northwestern Washington in the United States. It drains an area of the high North Cascades in the watershed of Puget Sound north of Seattle, and east of Mount Baker. With a watershed of approximately 270 square miles (700 km2) in a complex of deep valleys partially inside North Cascades National Park, it is the last major tributary of the Skagit before the larger river reaches its mouth on Skagit Bay. The river flows through Concrete, Washington, near its mouth and has two hydroelectric dams owned by Puget Sound Energy.
The King Salmon River is a 35-mile (56 km) tributary of the Ugashik River in the U.S. state of Alaska. Beginning at Mother Goose Lake in the Aleutian Range, it flows northwest to meet the larger river near the upper reaches of Ugashik Bay. The lake and the upper course of the King Salmon lie within the Alaska Peninsula National Wildlife Refuge. The river's gravel bottom and braided channels are ideal for the many king salmon that spawn in its waters, but they limit navigation to small skiff.

The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) is a joint program of the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Geophysical Institute of the University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAFGI), and the State of Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys (ADGGS). AVO was formed in 1988, and uses federal, state, and university resources to monitor and study Alaska's volcanology, hazardous volcanoes, to predict and record eruptive activity, and to mitigate volcanic hazards to life and property. The Observatory website allows users to monitor active volcanoes, with seismographs and webcameras that update regularly. AVO now monitors more than 20 volcanoes in Cook Inlet, which is close to Alaskan population centers, and the Aleutian Arc due to the hazard that plumes of ash pose to aviation.

Issaquah Creek is a small stream flowing through the city of Issaquah and nearby communities, in the U.S. state of Washington. Its headwaters are on the slopes of Cougar, Squak, Tiger, and Taylor mountains in the Issaquah Alps. Tributaries of Issaquah Creek include Holder Creek, Carey Creek, Fifteen-mile Creek, McDonald Creek, East Fork Issaquah Creek, and North Fork Issaquah Creek. The creek empties into the south end of Lake Sammamish. The lake's outlet is the Sammamish River, which in turn empties into Lake Washington and ultimately Puget Sound.
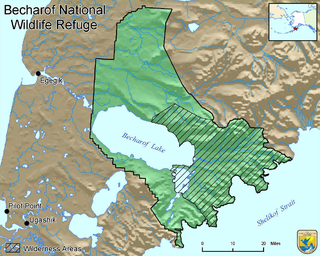
Becharof National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in the Aleutian Range of the Alaska Peninsula of southwestern Alaska. It is adjacent to Katmai National Park and Preserve. This national wildlife refuge, which covers an area of 1,200,000 acres (4,900 km2), was established in 1980 to conserve major brown bears, salmon, migratory birds, caribou, marine birds, and mammals and to comply with treaty obligations. It lies primarily in the east-central part of Lake and Peninsula Borough, but extends eastward into the mainland portion of Kodiak Island Borough. The refuge is administered from offices in King Salmon.

Dominated by the Ahklun Mountains in the north and the cold waters of Bristol Bay to the south, Togiak National Wildlife Refuge confronts the traveler with a kaleidoscope of landscapes. The natural forces that have shaped this land range from the violent and powerful to the geologically patient. Earthquakes and volcanoes filled the former role, and their marks can still be found, but it was the gradual advance and retreat of glacial ice that carved many of the physical features of this refuge.
The Tuya River is a major tributary of the Stikine River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. From its source at High Tuya Lake in Tuya Mountains Provincial Park just south of Ash Mountain, the highest peak of the Tuya Range, the Tuya River flows south about 200 km (120 mi) to meet the Stikine River in the Grand Canyon of the Stikine. The Tuya River's main tributary is the Little Tuya River. The Tuya River divides the Tanzilla Plateau on the east from the Kawdy Plateau, to the northwest, and the Nahlin Plateau, to the southwest. All three are considered sub-plateaus of the Stikine Plateau. The Tuya River's watershed covers 3,575 km2 (1,380 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is estimated at 36.9 m3/s (1,300 cu ft/s). The mouth of the Tuya River is located about 24 km (15 mi) northeast of Telegraph Creek, British Columbia, about 67 km (42 mi) southwest of Dease Lake, British Columbia, and about 210 km (130 mi) east of Juneau, Alaska. The Tuya River's watershed's land cover is classified as 35.7% shrubland, 31.4% conifer forest, 14.0% mixed forest, 7.2% herbaceous, and small amounts of other cover.

The kokanee salmon, also known as the kokanee trout, little redfish, silver trout, kikanning, Kennerly's salmon, Kennerly's trout, or Walla, is the non-anadromous form of the sockeye salmon. There is some debate as to whether the kokanee and its sea-going relative are separate species; geographic isolation, failure to interbreed, and genetic distinction point toward a recent divergence in the history of the two groups. The divergence most likely occurred around 15,000 years ago when a large ice melt created a series of freshwater lakes and rivers across the northern part of North America. While some members of the salmon and trout family (salmonids) went out to sea (anadromous), others stayed behind in fresh water (non-anadromous). The separation of the sockeye and the kokanee created a unique example of sympatric speciation that is relatively new in evolutionary terms. While they occupy the same areas and habitats during the breeding season, when ocean-going sockeye salmon return to freshwater to spawn, the two populations do not mate with each other in some regions, suggesting speciation.