
The Auckland Islands are an archipelago of New Zealand, lying 465 kilometres (290 mi) south of the South Island. The main Auckland Island, occupying 510 km2 (200 sq mi), is surrounded by smaller Adams Island, Enderby Island, Disappointment Island, Ewing Island, Rose Island, Dundas Island, and Green Island, with a combined area of 626 km2 (240 sq mi). The islands have no permanent human inhabitants.

The New Zealand sea lion, also known as Hooker's sea lion, and whakahao in Māori, is a species of sea lion that primarily breeds on New Zealand's subantarctic Auckland and Campbell islands and to some extent around the coast of New Zealand's South and Stewart islands. The New Zealand sea lion numbers around 10,000 and is perhaps the world's rarest sea lion species. They are the only species of the genus Phocarctos.
The Dobson River is a river in the South Island of New Zealand. It flows south between the Neumann and Ohau ranges for 45 kilometres (28 mi) from its source to the east of Mount Hopkins, in the Southern Alps, before joining with the Hopkins River, close to the latter's entry into the northern end of Lake Ohau in the Mackenzie Country. The river flows over wide shingle beds, and has no rapids of interest to whitewater enthusiasts. It was named by Julius von Haast in the 1860s for his father-in-law, Edward Dobson, who was the Canterbury Provincial Engineer.

Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku is an uninhabited subantarctic island of New Zealand, and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers 112.68 square kilometres (43.51 sq mi) of the group's 113.31 km2 (43.75 sq mi), and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island, Isle de Jeanette-Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the southernmost extremity of New Zealand. The island is mountainous, rising to over 500 metres (1,640 ft) in the south. A long fjord, Perseverance Harbour, nearly bisects it, opening out to sea on the east coast.

Jacquemart Island, one of the islets surrounding Campbell Island in New Zealand, lies 1 km (0.62 mi) south of Campbell Island and is the southernmost island of New Zealand.

Dent Island is a subantarctic 26-hectare (64-acre) rock stack, lying 3 km west of Campbell Island and belonging to the Campbell Island group. Dent Island is located at 52°31.15′S169°3.75′E. It was named by the French 1874 Transit of Venus Expedition to Campbell Island because of its resemblance to a tooth.

The Campbell Islands are a group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. They lie about 600 km south of Stewart Island. The islands have a total area of 113.31 km2 (43.75 sq mi), consisting of one big island, Campbell Island, and several small islets, notably Dent Island, Isle de Jeanette Marie, Folly Island, Jacquemart Island, and Monowai Island. Ecologically, they are part of the Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion. The islands are one of five subantarctic island groups collectively designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.

Curio Bay is a coastal embayment in the Southland District of New Zealand, best known as the site of a petrified forest some 180 million years old. It also hosts a yellow-eyed penguin colony, arguably the rarest of penguin species, with approximately 1600 breeding pairs in the extant population. The bay, along with neighbouring Porpoise Bay, is home to the endemic Hector's dolphin. Southern right whales are occasionally observed offshore, as on numerous parts of the country's coast. Located near the southernmost point of the South Island, Curio Bay is one of the major attractions in the Catlins, attracting around 100,000 visitors per year. The town of Waikawa has an information center for tourists.

Snow Park was a dedicated snowsports terrain park in South Island, New Zealand. It described itself as the "first dedicated freestyle terrain park in the world" when it opened in 2002, and featured a number of half-pipes, jumps and rails, instead of traditional ski runs. It closed in 2013 and was sold to the Southern Hemisphere Proving Grounds, a vehicle testing facility.

The austral snipes, also known as the New Zealand snipes or tutukiwi, are a genus, Coenocorypha, of tiny birds in the sandpiper family, which are now only found on New Zealand's outlying islands. There are currently three living species and six known extinct species, with the Subantarctic snipe having three subspecies, including the Campbell Island snipe discovered as recently as 1997. The genus was once distributed from Fiji, New Caledonia and Norfolk Island, across New Zealand and southwards into New Zealand's subantarctic islands, but predation by introduced species, especially rats, has drastically reduced their range.
Shipley Glacier is a glacier, 25 miles (40 km) long, in the north-central Admiralty Mountains of Antarctica. The glacier drains the northern slopes of Mount Adam and flows along the east wall of DuBridge Range to Pressure Bay on the north coast of Victoria Land. Some of the glacier bypasses Pressure Bay and reaches the sea west of Flat Island. The seaward end of the glacier was first mapped by the Northern Party, led by Victor Campbell, of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. Named by Campbell for Sir Arthur Shipley, master of Christ's College, Cambridge, England, at the suggestion of Priestley. The entire glacier was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS), 1960–63.
Folly Island or the Folly Islands is a subantarctic island located in New Zealand's Campbell Island group.

Perseverance Harbour, also known as South harbour, is a large indentation in the coast of Campbell Island, one of New Zealand's subantarctic outlying islands. The harbour is a long lateral fissure which reaches the ocean in the island's southeast, and is overlooked by the island's highest point, Mount Honey. The Campbell Island Meteorological Station lies at the western end of the harbour.
Venus Bay is located on Perseverance Harbour on New Zealand's subantarctic Campbell Island. It was named for an 1874 French astronomical expedition to view the Transit of Venus, which set up camp at the site. As a result of the expedition, many of Campbell island's lanforms have French names, including Mount Fizeau and Mount Dumas.
Mount Fizeau is located on New Zealand's subantarctic Campbell Island. It was named by members of the 1874 French astronomical expedition to view the Transit of Venus, which set up on the island at Venus Bay. Mount Fizeau rises to a height of 497 metres, and is the second-highest point on the island.
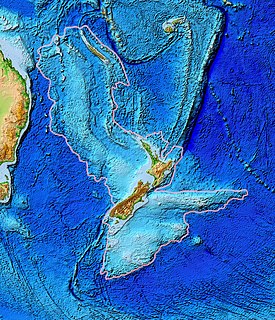
Zealandia, also known as the New Zealand continent or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago. It has variously been described as a continental fragment, a microcontinent, a submerged continent, and a continent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995.
This is a list of the extreme points of the Commonwealth of Nations — the points that are farther north, south, east or west, or higher or lower in elevation than any other location.
Mount Dumas is a mountain on Campbell Island, the main island of the Campbell Island group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. Campbell Island is an ancient volcano, with steep coastal cliffs that expose some of the lava flows. Mount Dumas is located at the island's southern end.










