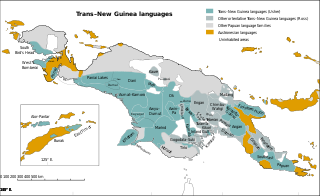
Trans–New Guinea (TNG) is an extensive family of Papuan languages spoken on the island of New Guinea and neighboring islands, a region corresponding to the country Papua New Guinea as well as parts of Indonesia.

Kaiser-Wilhelmsland formed part of German New Guinea, the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago, the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea.

The Highlands Highway, sometimes known as the Okuk Highway, is the main land highway in Papua New Guinea. It connects several major cities and is vital for the movement of people and goods between the populous Highlands region and the coast.

The Purari is a river that originates in the south central highlands especially in Kandep District of Enga Province of Papua New Guinea, flowing 630 kilometres (391 mi) though Gulf Province to the Gulf of Papua. The Purari has a 33,670 km2 (13,000 sq mi) drainage basin and is the third largest river in Papua New Guinea. The discharge varies through the year, averaging around 3,000 m3/s (110,000 cu ft/s)–4,000 m3/s (140,000 cu ft/s) at the delta.

Mount Hagen is the third largest city in Papua New Guinea, with a population of 46,250. It is the capital of the Western Highlands Province and is located in the large fertile Wahgi Valley in central mainland Papua New Guinea, at an elevation of 1,677 m (5,502 ft).
Kundiawa is the capital of Simbu Province, Papua New Guinea, with a population of 8,147. It lies along the Highlands Highway approximately halfway between Goroka and Mount Hagen, respectively the capitals of the Eastern Highlands and Western Highlands provinces.

Mount Giluwe is the second highest mountain in Papua New Guinea at 4,367 metres (14,327 ft), and the fifth highest peak on the island of New Guinea. It is located in the Southern Highlands province and is an old shield volcano with vast alpine grasslands. Ancient volcanic plugs form its two summits, with the central peak the highest and an east peak about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) away at 4,300 m (14,108 ft). Giluwe has the distinction of being the highest volcano on the Australian continent and Oceania, and is thus one of the Volcanic Seven Summits.
Michael James LeahyMBE was an Australian explorer and gold prospector, famed for his exploration of the Highlands area of Papua New Guinea. He photographed, filmed and published many of his explorations widely.
East New Guinea Highlands is a 1960 proposal by Stephen Wurm for a family of Papuan languages spoken in Papua New Guinea that formed part of his 1975 expansion of Trans–New Guinea.
Melpa is a Papuan language spoken by about 130,000 people predominantly in Mount Hagen and the surrounding district of Western Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea.

Wabag is the capital of Enga Province, Papua New Guinea. It is the least populous provincial capital in the country. It is on the Lai River; the Highlands Highway passes through the town, between Mount Hagen and Porgera. Europeans first visited the site in 1938-39 A radio camp and airstrip were established in 1938-39 but restrictions on transportation and the surrounding land's infertility long inhibited Wabag's development.
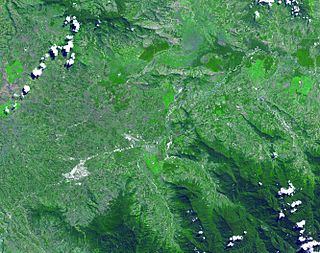
Kuk Swamp is an archaeological site in Papua New Guinea, that lies in the Wahgi Valley of the highlands. The swamp developed in a former lake basin, as it was filled by an alluvial fan or deposits of water-transported material. Archaeological evidence for early agricultural drainage systems was found here, beginning about 9,000 years ago. It includes draining ditches of three major classes, which were used to convert the area to an anthropogenic grassland. The native crop taro was grown here.
James Lindsay Taylor was an Australian born, Papua New Guinean explorer. He is most noted for leading patrols (explorations) into the Highlands of Papua New Guinea in the 1930s. In particular the 1933 patrol in the Wahgi Valley with the brothers Dan and Mick Leahy and surveyor Ken Spinks; and for the Hagen-Sepik patrol with John Black in 1938–39.

The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya, Indonesia, 16,024 ft (4,884 m), the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home to many intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities. The highlands run generally east-west the length of the island, which is divided politically between Indonesia in the west and Papua New Guinea in the east.

The Chimbu–Wahgi languages are a language family of New Guinea. They are sometimes included in the Trans–New Guinea proposal; Usher links them with the Engan languages in a Central New Guinea Highlands family.
Frederick William Shaw Mayer MBE, also well known as "Masta Pisin" or the "Bird Man" in New Guinea, was an Australian ornithologist, aviculturist and zoological collector. He is notable for his work in New Guinea, especially with birds-of-paradise.
Jimi District is a district of the Jiwaka Province of Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Tabibuga. The population of the district was 71,379 at the 2011 census. Before May 2012, it was part of the Western Highlands Province. It is home to the Jimi Valley and the village of Koinambe.
Wahgi is a Trans–New Guinea language of the Chimbu–Wahgi branch spoken by approximately 100,000 people in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. Like other Chimbu languages, Wahgi has some unusual lateral consonants.
Nii is a Trans–New Guinea language of the Chimbu–Wahgi branch spoken in the highlands of Papua New Guinea.
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.










