
Thurston Island is a largely ice-covered, glacially dissected island, 135 nautical miles long and 55 nautical miles wide, lying between Amundsen Sea and Bellingshausen Sea a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. The island is separated from the mainland by Peacock Sound, which is occupied by the west portion of Abbot Ice Shelf.

Joinville Island is the largest island of the Joinville Island group, about 40 nautical miles long in an east–west direction and 12 nautical miles wide, lying off the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by the Antarctic Sound.

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 40 nautical miles in a north–south direction.
The Robertson Islands or Robertsons Islands are a group of islands extending 6 km southward of the south-eastern extremity of Coronation Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. They were discovered and roughly charted by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer in December 1821 and named by James Weddell in 1823.

Joinville Island group is a group of antarctic islands, lying off the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which Joinville Island group is separated by the Antarctic Sound.

Seymour Island or Marambio Island, is an island in the chain of 16 major islands around the tip of the Graham Land on the Antarctic Peninsula. Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. It lies within the section of the island chain that resides off the west side of the peninsula's northernmost tip. Within that section, it is separated from Snow Hill Island by Picnic Passage, and sits just east of the larger key, James Ross Island, and its smaller, neighboring island, Vega Island.
Iceberg Bay is a bay 3 miles (5 km) wide, which indents the south coast of Coronation Island between Cape Hansen and Olivine Point, in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. It was named by Matthew Brisbane, who roughly charted the south coast of Coronation Island under the direction of James Weddell in 1823. Beaufoy Ridge and Sunshine Glacier lie close north of Iceberg Bay.
Wood Bay is a large bay which is bounded by Cape Johnson and Aviator Glacier Tongue on the north, and Cape Washington on the south, along the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered in 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, and named by him for Lieutenant James F.L. Wood of the ship HMS Erebus.
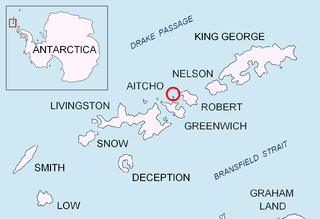
Emeline Island is a conspicuous rocky island rising to over 100 m (328 ft) in the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island extends 550 by 320 m with a surface area of 18 hectares. The area was visited by early 19th century seal hunters.
Whalers Bluff is a bluff rising sharply to 210 m east of Port Jebsen, Signy Island, in the South Orkney Islands. The name "Consulens Hat," of unknown origin, was applied to the highest point of the bluff on a 1913 chart by Norwegian whaling captain M. Thoralf Moe. The bluff was named in 1990 by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) and calls to mind the earlier activities of whalers in this area.
The Demas Range is a range about 8 nautical miles long that forms the lower east margin of the Berry Glacier in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The range trends north–south culminating in Mount Goorhigian, 1,115 metres (3,658 ft) high.
Violante Inlet is an ice-filled inlet 16 nautical miles long, in an east–west direction, and 12 to 15 nautical miles wide, lying between Cape Fanning and Cape Herdman along the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica.
Strombus Ridge is a ridge curving eastward from Thulla Point toward Jane Col on Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. The feature is 0.3 nautical miles (0.6 km) south of Jensen Ridge. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after the whaling ship Strombus, from Tonsberg, Norway, used on the last whaling expedition to Signy Island, 1935–36.

Gibbon Bay is a bay 2 km (1.2 mi) long and wide, entered between Rayner Point and The Turret along the east coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The bay was first seen in December 1821 by Captain George Powell and Captain Nathaniel Palmer, but was more accurately delineated on a 1912 chart by Captain Petter Sorlle. It was recharted in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II and named for the ship's surgeon, Dr G.M. Gibbon.

Marshall Bay is a bay 2 nautical miles (4 km), lying between Cape Vik and Cape Hansen on the south side of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. It was roughly charted in 1912–13 by Petter Sørlle, a Norwegian whaling captain. The bay was recharted in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II, who gave the name for surgeon Dr. E.H. Marshall, a member of the Marine Executive Staff of the Discovery Committee.
Stene Point is a point lying 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) of Cape Vik on the south coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney islands. Surveyed by DI personnel in 1933, and resurveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948–49. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for K.O. Stene, captain of the floating factory Normanna which operated in the South Orkney Islands in 1912–13.
Rayner Point is a point marked by a rocky peak forming the north side of the entrance to Gibbon Bay on the east coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands. Charted in 1912-13 by Captain Petter Sorlle, a Norwegian whaler. Recharted in 1933 by DI personnel on the Discovery II and named for George W. Rayner, member of the zoological staff of the Discovery Committee.

Lynch Island is an island lying in the eastern part of Marshall Bay, close off the south coast of Coronation Island in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica.
Roald Glacier is a glacier which flows from the vicinity of Mount Noble and Mount Sladen eastward into Gibbon Bay, on the east coast of Coronation Island in the South Orkney Islands. Chartered and named by the Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorle in the period 1912–15. Surveyed in 1948-49 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS).
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Noble". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Noble". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 






