The Prince Olav Mountains is a mountain range of the Queen Maud Mountains stretching from Shackleton Glacier to Liv Glacier at the head of the Ross Ice Shelf.

Garwood Glacier is a glacier occupying the northwest part of Garwood Valley, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was first mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04), but was not named until 1911, when Thomas Griffith Taylor of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, named it for Edmund J. Garwood, professor of geology and mineralogy at the University of London.
Wilson Hills is a group of scattered hills, nunataks and ridges that extend NW-SE for about 110 kilometres (68 mi) between Matusevich Glacier and Pryor Glacier in Antarctica. They were discovered by Lieutenant Harry Pennell, Royal Navy, on the Terra Nova Expedition in February 1911 during Robert Falcon Scott's last expedition, and named after Dr. Edward A. Wilson, a zoologist with the expedition, who perished with Scott on the return journey from the South Pole.

Explorers Range is a large mountain range in the Bowers Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica, extending from Mount Bruce in the north to Carryer Glacier and McLin Glacier in the south. Named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) for the northern party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64, whose members carried out a topographical and geological survey of the area. The names of several party members are assigned to features in and about this range. All of the geographical features listed below lie situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare.
The Andrews Peaks are a line of rock peaks 3 nautical miles (6 km) long near the head of Arthur Glacier, situated between Mount Warner and Mount Crow in the Ford Ranges of Marie Byrd Land. They were mapped by the United States Antarctic Service (1939–41) and by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos (1959–65), and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Stephen T. Andrews, a United States Antarctic Research Program ionospheric physicist, scientific leader at Byrd Station in 1969.
Ashton Glacier is a glacier 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows east-southeast from Mount Thompson to the northwest side of Lehrke Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land. The glacier was photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), and was probably seen by the USAS ground survey party which explored this coast. A joint party consisting of members of the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition and the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted the glacier in 1947. It was named by the FIDS for L. Ashton, a carpenter with the FIDS at the Port Lockroy and Hope Bay bases in 1944–45 and 1945–46, respectively.

The Gothic Mountains is a group of mountains, 32 kilometres (20 mi) long, in the Queen Maud Mountains of Antarctica, located west of Watson Escarpment and bounded by Scott Glacier, Albanus Glacier, and Griffith Glacier. The mountains were first visited in December 1934 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition (ByrdAE) geological party led by Quin Blackburn. The name was proposed by Edmund Stump, leader of a U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) - Arizona State University geological party which made investigations here in the 1980-81 season. The mountains are composed of granites which have weathered to produce a series of spires and peaks reminiscent of a Gothic cathedral.
Clarsach Glacier is a glacier flowing south between Prague Spur and the Finlandia Foothills in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. The feature was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and was mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1960. Further delineation was made from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1966–67 and from U.S. Landsat imagery taken January 1974. It was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, 1977; in plan view the outline of the glacier resembles a clàrsach, or Irish harp.
Cleaves Glacier is a glacier in the Holland Range, flowing northwest from Mount Reid into the east side of Robb Glacier. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from tellurometer surveys (1961–62) and Navy air photos (1960), and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Harold H. Cleaves, Master of the USNS Pvt. Joseph F. Merrell during Operation Deepfreeze 1964–65.
Frostman Glacier is a broad, low gradient glacier discharging into the south side of Hull Bay just west of the Konter Cliffs, on the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–65, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Thomas O. Frostman, a meteorologist at Plateau Station, 1968.
Tumble Glacier is a glacier extending along the east side of Alexander Island, Antarctica, 7 nautical miles (13 km) long and 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide, which flows east from the cliffs of Mount Egbert, Mount Ethelwulf and Mount Ethelred of the Douglas Range into the west side of the George VI Ice Shelf that occupies George VI Sound immediately south of Mount King. The glacier was first roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under Rymill. Resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, and so named by them because of the extremely broken condition of the lower reaches of the glacier.
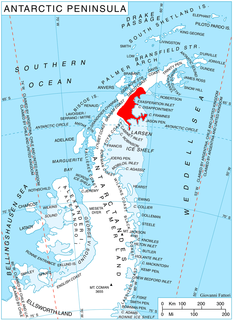
Punchbowl Glacier is a glacier that flows southwards between Poibrene Heights and Metlichina Ridge, and enters the north end of Exasperation Inlet, north of Jorum Glacier, on the east side of Graham Land, Antarctica. Surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947 and 1955. The name applied by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) is descriptive of shape as the glacier is hemmed in by mountains.
Peregrinus Peak is a peak along the north side of Airy Glacier, 3 nautical miles (6 km) southeast of Mount Timosthenes, in central Antarctic Peninsula. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) November 27, 1947. Surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in December 1958. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Petrus Peregrinus de Maricourt, of Luceria, author of Epistola de magnete (1269), the first scientific treatise on the magnet.
Pilon Peak is a prominent peak (1,880 m) standing 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) northeast of Mount Works along the west side of Horne Glacier, in the Everett Range, Concord Mountains. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–62. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander Jerome R. Pilon, U.S. Navy, Operations Officer of Antarctic Development Squadron Six (1967–68), Executive Officer (1968–69), and Commanding Officer (1969–70). Commander Pilon served on the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names of the U.S. Board on Geographic Names, 1976–78.
Goodwin Glacier is a glacier flowing west into Flandres Bay southward of Pelletan Point on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache, 1897–99. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Hannibal Goodwin, an American pastor who invented the first transparent nitrocellulose flexible photographic roll-film in 1887.
Mount Harrington is one of the highest peaks in the east end of the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, Antarctica, rising to 2,610 metres (8,560 ft) on the west side of Whitehall Glacier and 5 nautical miles (9 km) southwest of Mount Northampton. It was named in 1960 by The New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee after geologist Hilary J. Harrington, who led the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) to this region, 1957–58, and also led the NZGSAE in the McMurdo Sound region, 1958–59. Later, he was a United States Antarctic Research Program investigator in the McMurdo Sound region, 1968–69.

Hotine Glacier is a glacier 10 nautical miles (19 km) long which is divided at its mouth by Mount Cloos, flowing west into both Deloncle Bay and Girard Bay on Kiev Peninsula, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache, 1897–99, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Brigadier Martin Hotine, Director of Overseas Surveys.
Roos Glacier is a steep glacier that drains the northwest slopes of Mount Murphy on Walgreen Coast, Marie Byrd Land. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after S. Edward Roos, oceanographer with the Byrd Antarctic Expeditions of 1928-30 and 1933-35. Buettner Peak is a sharp peak rising midway along the north wall of Roos Glacier.
Rotz Glacier is a tributary glacier 9 nautical miles (17 km) long and 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) wide. It flows west from Wakefield Highland, central Antarctic Peninsula, into Airy Glacier at a point due south of Mount Timosthenes. Photographed by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) on November 27, 1947. Surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in December 1958 and November 1960. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Jean Rotz, 16th century French chartmaker and writer on the principles of navigation, who designed an elaborate magnetic compass and became hydrographer to King Henry VIII in 1542.

Leay Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest into Girard Bay to the west of Hotine Glacier, on Kiev Peninsula, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Petra Searle of the Directorate of Overseas Surveys, who has contributed to the work of mapping the Antarctic Peninsula area.


![]()




