The Queen Elizabeth Range is a rugged mountain range of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica.

The Usarp Mountains are a major Antarctic mountain range, lying west of the Rennick Glacier and trending north to south for about 190 kilometres (118 mi). The feature is bounded to the north by Pryor Glacier and the Wilson Hills.
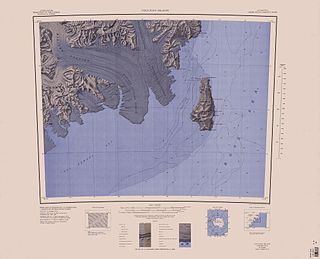
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.


The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

Il Polo Glacier is a small glacier draining northward between Polar Times Glacier and Polarforschung Glacier into the Publications Ice Shelf, Antarctica. It was delineated in 1952 by John H. Roscoe from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and was named by Roscoe for Il Polo, a polar journal published by the Istituto Geografico, Forlì, Italy.
The Porthos Range is the second range south in the Prince Charles Mountains of Antarctica, extending for about 30 miles in an east-to-west direction between Scylla Glacier and Charybdis Glacier. First visited in December 1956 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party under W.G. Bewsher (1956-57) and named after Porthos, a character in Alexandre Dumas, père's novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.
On the continent of Antarctica, the Aramis Range is the third range south in the Prince Charles Mountains, situated 11 miles southeast of the Porthos Range and extending for about 30 miles in a southwest–northeast direction. It was first visited in January 1957 by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party led by W.G. Bewsher, who named it for a character in Alexandre Dumas' novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.
Willey Glacier is a heavily crevassed glacier north of Creswick Peaks in Palmer Land, flowing west from Creswick Gap into George VI Sound. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Lawrence E. Willey, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) geologist at Fossil Bluff and Stonington Island stations, 1966–69 and 1973, and awarded the Polar Medal for services to Antarctic Survey in 1976.
Ball Glacier is a glacier 7 nautical miles (13 km) long with the head located between Mount Lister and Mount Hooker on the east side of the Royal Society Range. The glacier flows northeast between Craw Ridge and Tasman Ridge into Blue Glacier. It was named by the New Zealand Geographic Board after Gary Ball, a New Zealand mountaineer who climbed Mount Lister with an Italian field party, 1976–77, and camped on this glacier; he was field assistant with R.H. Findlay's New Zealand Antarctic Research Program party to this area, 1980–81.
Barcus Glacier is a glacier in the Hutton Mountains that drains east-southeast, to the north of Mount Nash and Mount Light, into Keller Inlet in Palmer Land. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from ground surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for James R. Barcus, ionospheric physics researcher at Byrd Station in the summers of 1966–67 and 1967–68.
Mount Borland is a large, gently-domed mountain, standing 5 nautical miles (9 km) south of Mount Twigg near the head of Lambert Glacier. It was sighted by Flying Officer J. Seaton, RAAF, during an Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions photographic flight in November 1956, and named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for R.A. Borland, a meteorologist at Mawson Station in 1958.
Bucher Glacier is a small glacier draining the west slopes of Rudozem Heights and flowing to Bourgeois Fjord just north of Bottrill Head on the German Peninsula, Fallières Coast on the west side of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1958 for Edwin Bucher, Swiss glaciologist and author of many publications on snow and avalanches.
Nash Ridge is a high, massive ridge of eastern Eisenhower Range, about 10 nautical miles (18 km) long and 5 nautical miles (9 km) wide, projecting between the flow of the O'Kane and Priestley Glaciers, in Victoria Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1955–63. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Harold A. Nash, biologist at McMurdo Station in the 1965-66 and 1966–67 seasons.
Mount Weller is a mountain, 1,080 m, standing west of Auster Glacier and 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) east of Reference Peak in Enderby Land. It was plotted from air photos taken by ANARE in 1956 and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for G.E. Weller, a meteorologist at Mawson Station in 1961.
Strange Glacier is a glacier in the Latady Mountains, draining southeast along the south side of Crain Ridge to enter Gardner Inlet between Schmitt Mesa and Mount Austin, in Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Donald L. Strange, hospital corpsman at South Pole Station in 1964.

Turner Glacier is a glacier on the east side of Mount Liotard flowing northeast into Ryder Bay, Adelaide Island. The glacier was surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1948, and photographed from the air by Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (FIDASE), 1956–57. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1977 after Andrew John Turner, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) builder, Halley Station, 1973–74; Signy Island, 1974–75; Rothera Station, 1976–77, 1978–80; and Faraday Station, 1982–83.
Gallup Glacier is a broad glacier, about 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing east between Mount Rosenwald and Mount Black to enter Shackleton Glacier, Antarctica, just north of Matador Mountain. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Commander F.S. Gallup, Jr., U.S. Navy, Commanding Officer of Squadron VX-6 during Operation Deep Freeze 1965.
Hewitt Glacier is a glacier, 15 nautical miles (28 km) long, descending the eastern slopes of the Holland Range, Antarctica, between Lewis Ridge and Mount Tripp to enter Richards Inlet. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (1959–60) for Leonard R. Hewitt, leader at Scott Base, 1959.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Twigg". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Twigg". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 





