The Multicultural History Society of Ontario (MHSO) is a not-for-profit educational institution and archives located in Toronto, Canada. Established in 1976, the Multicultural History Society of Ontario collects, preserves, and makes available records of histories of migration and ethnicity. [1]
The MHSO was established in 1976 by Professor Robert F. Harney of the University of Toronto and a few close colleagues. They believed that the chronicling of immigrant and ethnic stories was essential to understanding Ontario history.
Professor Harney, a renowned scholar in the field of migration and ethnic studies, served as the MHSO's Academic Director from its establishment until his death in 1989.
Born in Salem, Massachusetts, Harney received a Bachelor of Arts degree from Harvard University and an M.A. and Ph.D. from the University of California, Berkeley. For twenty-five years, he taught history at the University of Toronto, where he stimulated and steered a generation of students. In 1989, he was appointed to the newly endowed Professorship and Program in Ethnic, Immigration, and Pluralism Studies. Following his death, this collaborative graduate program was renamed the Robert F. Harney Professorship and Program in his honour.
The MHSO has produced and distributed publications, mounted and circulated exhibitions, and staged conferences, public lectures, and special events. In recent years, it has focused on virtual programming. The MHSO also provides professional and technical services and training to teachers and students, scholars and community historians, heritage and cultural organizations, and members of ethnocultural and indigenous communities.
An example of MHSO services is the case of Dr. Joseph Pivato whom Robert Harney invited to be Research Fellow for 1984 and edited the book, Contrasts: Comparative Essays on Italian-Canadian Writing (1985) and later held The Mariano Elia Chair in Italian-Canadian Studies at York University (1987–88). And thus inspired by Robert Harney he promoted research and publications in ethnic minority writing in Canada.
The MHSO is the creator of an extensive collection of archival materials which document immigrant and ethnic experiences in Canada. Assisted by ethnic and indigenous associations and community researchers, the Society undertook oral history interviews, and collected historical photographs and personal and institutional textual records during the first decades of its operation.
More recently, it has undertaken additional collection activities in connection with specific projects. In the early 21st century, as a result of these efforts, more than 50 ethnocultural communities and First Nations, and some 240 municipalities in every region of the province are represented in the MHSO's archival holdings. [2]

The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for "ethnic pluralism", with the two terms often used interchangeably, and for cultural pluralism in which various ethnic groups collaborate and enter into a dialogue with one another without having to sacrifice their particular identities. It can describe a mixed ethnic community area where multiple cultural traditions exist or a single country within which they do. Groups associated with an indigenous, aboriginal or autochthonous ethnic group and settler-descended ethnic groups are often the focus.

William Kymlicka is a Canadian political philosopher best known for his work on multiculturalism and animal ethics. He is currently Professor of Philosophy and Canada Research Chair in Political Philosophy at Queen's University at Kingston, and Recurrent Visiting Professor in the Nationalism Studies program at the Central European University in Budapest, Hungary. For over 20 years, he has lived a vegan lifestyle, and he is married to the Canadian author and animal rights activist Sue Donaldson.
According to the 2021 Canadian census, over 450 "ethnic or cultural origins" were self-reported by Canadians. The major panethnic origin groups in Canada are: European (52.5%), North American (22.9%), Asian (19.3%), North American Indigenous (6.1%), African (3.8%), Latin, Central and South American (2.5%), Caribbean (2.1%), Oceanian (0.3%), and Other (6%). Statistics Canada reports that 35.5% of the population reported multiple ethnic origins, thus the overall total is greater than 100%.
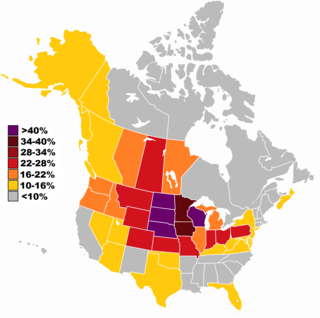
German Canadians are Canadian citizens of German ancestry or Germans who emigrated to and reside in Canada. According to the 2016 census, there are 3,322,405 Canadians with full or partial German ancestry. Some immigrants came from what is today Germany, while larger numbers came from German settlements in Eastern Europe and Imperial Russia; others came from parts of the German Confederation, Austria-Hungary and Switzerland.

"Cultural mosaic" is the mix of ethnic groups, languages, and cultures that coexist within society. The idea of a cultural mosaic is intended to suggest a form of multiculturalism, different from other systems such as the melting pot, which is often used to describe nations like the United States' assimilation.
The Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy at the University of Toronto is an interdisciplinary academic centre with various research and educational programs committed to the field of globalization. Located in Toronto, Ontario, it offers master's degrees in global affairs and public policy, as well as in European, Russian and Asia-Pacific studies. The school is a member of the Association of Professional Schools of International Affairs (APSIA), a group of schools that educate students in international affairs. Admission to the Munk School is highly competitive; the Master of Global Affairs program typically receives between 500 and 600 applicants per year but offers only 80 first-year places.

Italian Canadians are Canadian-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who migrated to Canada as part of Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Canada. According to the 2021 Census of Canada, 1,546,390 Canadians claimed full or partial Italian ancestry. They comprise a subgroup of Southern European Canadians which is a further subgroup of European Canadians. The census enumerates the entire Canadian population, which consists of Canadian citizens, landed immigrants and non-permanent residents and their families living with them in Canada. Residing mainly in central urban industrial metropolitan areas, Italian Canadians are the seventh largest self-identified ethnic group in Canada behind French, English, Irish, Scottish, German and Chinese Canadians.
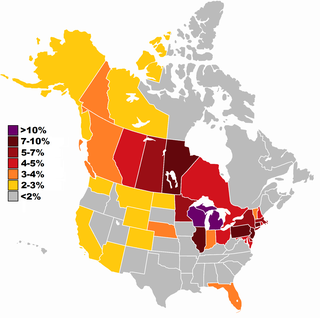
Polish Canadians are citizens of Canada with Polish ancestry, and Poles who immigrated to Canada from abroad. At the 2016 Census, there were 1,106,585 Canadians who claimed full or partial Polish heritage.
Finnish Canadians are Canadian citizens of Finnish ancestry or Finns who emigrated to and reside in Canada. In 2016, 143,645 Canadians claimed Finnish ancestry. Finns started coming to Canada in the early 1880s, and in much larger numbers in the early 20th century and well into the mid-20th century. Finnish immigration to Canada was often a direct result of economic depressions and wars, or in the aftermath of major conflicts like the Finnish Civil War. Canada was often chosen as a final destination because of the similarity in climate and natural conditions, while employment in logging or homesteading attracted landless farmers in the early 20th century. Migratory movements of Finns between Canada and the United States was very common as well.
Native American studies is an interdisciplinary academic field that examines the history, culture, politics, issues, spirituality, sociology and contemporary experience of Native peoples in North America, or, taking a hemispheric approach, the Americas. Increasingly, debate has focused on the differences rather than the similarities between other Ethnic studies disciplines such as African American studies, Asian American Studies, and Latino/a Studies.

Australian studies forms part of the academic field of cultural studies. It involves an examination of what constructs Australia's national identity. This area of scholarship traditionally involves the study of Australian history, society and culture but can be extended to the study of Australian politics and economics. This area of scholarship also includes the study of Australia's Indigenous population, Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders.

Nationalism studies is an interdisciplinary academic field devoted to the study of nationalism and related issues. While nationalism has been the subject of scholarly discussion since at least the late eighteenth century, it is only since the early 1990s that it has received enough attention for a distinct field to emerge.

Canadians are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Canadian.

Howard Adelman is a Canadian philosopher and former university professor. He retired as Professor Emeritus of Philosophy at York University in 2003. Adelman was one of the founders of Rochdale College, as well as the founder and director of York's Centre for Refugee Studies. He was editor of Refuge for ten years, and since his retirement he has received several honorary university and governmental appointments in Canada and abroad. Adelman was the recipient of numerous awards and grants, and presented the inaugural lecture in a series named in his honor at York University in 2008.
Multiculturalism in Canada was officially adopted by the government during the 1970s and 1980s. The Canadian federal government has been described as the instigator of multiculturalism as an ideology because of its public emphasis on the social importance of immigration. The 1960s Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism is often referred to as the origin of modern political awareness of multiculturalism, resulting in Canada being one of the most multicultural nations in the world. The official state policy of multiculturalism is often cited as one of Canada's significant accomplishments, and a key distinguishing element of Canadian identity and Canadian values.

Joseph Pivato is a Canadian writer and academic who first established the critical recognition of Italian-Canadian literature and changed perceptions of Canadian writing. From 1977 to 2015 he was professor of Comparative Literature at Athabasca University, Canada. He is now Professor Emeritus.
Multicultural media in Canada, also referred to as “ethnic media” or “third media”, is media that responds to the needs of ethnic minorities of Canada. The objective of such media in Canada is to create a voice for a community of a particular ethnic background, challenge social injustices, and foster cultural pride for minority and immigrant Canadians.

The Chinese Canadian community in the Greater Toronto Area was first established around 1877, with an initial population of two laundry owners. While the Chinese Canadian population was initially small in size, it dramatically grew beginning in the late 1960s due to changes in immigration law and political issues in Hong Kong. Additional immigration from Southeast Asia in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and related conflicts and a late 20th century wave of Hong Kong immigration led to the further development of Chinese ethnic enclaves in the Greater Toronto Area. The Chinese established many large shopping centres in suburban areas catering to their ethnic group. There are 679,725 Chinese in the Greater Toronto Area as of the 2021 census, second only to New York City for largest Chinese community in North America.
South Asian Canadians in the Greater Toronto Area form 19% of the region's population, numbering 1.1 million as of 2021. Comprising the largest visible minority group in the region, Toronto is the destination of over half of the immigrants coming from India to Canada, and India is the single largest source of immigrants in the Greater Toronto Area. South Asian Canadians in the region also include significant Pakistanis, Bangladeshis, Sri Lankans, and Nepalis, all representing several different ethnolinguistic backgrounds.
Eve Tuck is an Unangax̂ scholar in the field of Indigenous studies and educational research. Tuck is the associate professor of critical race and indigenous studies at the Ontario Institute for Studies in Education at the University of Toronto.