
The Vijayanagara Empire was a medieval Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, members of a pastoralist cowherd community that claimed Yadava lineage.

The Kakatiya dynasty was an Indian dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their territory comprised much of the present day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka, northern Tamil Nadu, and southern Odisha. Their capital was Orugallu, now known as Warangal.
Reddy is a caste that originated in India, predominantly settled in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. They are classified as a forward caste.

Rudrama Devi, also known by her regnal name Rudra-deva Maharaja, was a Kakatiya Queen-regnant who ruled substantial parts of present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh in southern India. She was among the few and the most successful female rulers of Indian history.

Western Ganga was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India which lasted from about 350 to 1000 CE. They are known as "Western Gangas" to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over Kalinga. The general belief is that the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later, moving their capital to Talakadu on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district.

The Kalabhra dynasty, also called Kaḷabrar, Kaḷappirar, Kallupura or Kalvar, were rulers of all or parts of Tamil region sometime between the 3rd century and 6th century CE, after the ancient dynasties of the early Cholas, the early Pandyas and Chera. Information about the origin and reign of the Kalabhras is uncertain and scarce. It is believed by historians that the Kalabhras belonged to the Vellalar community of warriors who were possibly once the feudatories of the Cholas and the Pallavas. Their proposed roots vary from southeast region of modern Karnataka, Kalappalars of Vellalar community, to Kalavar chieftains. This age is generally called "The Augustan age of Tamil Literature", in a 1922 book by the name "Studies in South Indian Jainism" written by M. S. Ramaswami Ayyangar and B. Seshagiri Rao. The Kalabhra era is sometimes referred to as the "dark period" of Tamil history, and information about it is generally inferred from any mentions in the literature and inscriptions that are dated many centuries after their era ended.
Dravida Brahmins, or simply Dravidulu, are Hindu brahmins and a sub-caste of the Telugu Brahmins of Andhra Pradesh in South India, who migrated from Tamil-speaking regions. They are further divided into sub-sects based on the places where they have settled such as Aaraama Dravidulu, Pudur Dravidulu, Konaseema Dravidulu, Peruru Dravidulu, Tummagunta Dravidulu and Dimili Dravidulu.

The Telugu Chodas or Telugu Cholas ruled parts of present-day Andhra Pradesh and Telangana between the 5th and the 13th centuries as samantas of Pallavas and later the Imperial Cholas. Various dynasties exist among them including Velanati, Pottapi, Konidena, Nannuru, Nellore, Kunduru etc. The earliest Choda dynasty in the Telugu area was that of Renati Chodas who ruled Renadu region from late 5th century to 7th century. Some of the Telugu Chodas including Renati Chodas claimed descent from the early Sangam Tamil king Karikala Chola. Telugu Chodas contributed much to the early development of Telugu language and are the first dynasty to use Telugu as their official language. The first and oldest Telugu inscription founded so far is Kalamalla inscription dating to 575 CE put up by Renati Chola king Erikal Mutturaju Dhanunjaya. Telugu Chodas are believed to have been migrated from Tamilakam to Andhra country due to invasion of Tamilakam by Kalabhras and increasing power of Pallavas in northern most part of Tamilakam.
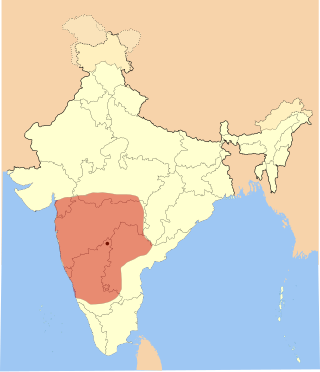
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada dynasty is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the modern Bidar District of Karnataka state, and alternatively the Later Chalukya from its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called Western Chalukyas to differentiate from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Prior to the rise of these Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta empire of Manyakheta controlled most of Deccan and Central India for over two centuries. In 973, seeing confusion in the Rashtrakuta empire after a successful invasion of their capital by the ruler of the Paramara dynasty of Malwa, Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta dynasty ruling from Bijapur region defeated his overlords and made Manyakheta his capital. The dynasty quickly rose to power and grew into an empire under Someshvara I who moved the capital to Kalyani.

Uthiramerur is a panchayat town in Kancheepuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is situated 90 km south west of Chennai, the capital of Tamil
Vadama, meaning "Northerners", are a sub-sect of the Iyer community of Tamil Brahmins. While some believe that their name is an indication of the fact that they were the most recent Brahmin migrants to the Tamil country others interpret the usage of the term "Vadama" as a reference to their strict adherence to the Sanskrit language and Vedic rituals which are of northerly origin.
The Western Ganga Dynasty was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka. Its members are known as Western Gangas to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over modern Orissa. The Western Gangas ruled as a sovereign power from the middle of fourth century to middle of sixth century, initially from Kolar, later moving their capital to Talakad on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district. Though territorially a small kingdom, the Western Ganga contribution to polity, culture and literature of the modern south Karnataka region is considered noteworthy. The Ganga kings showed benevolent tolerance to all faiths but are most famous for their patronage towards Jainism resulting in the construction of fine monuments in such places as Shravanabelagola and Kambadahalli.
Jayapa or Jaya was a military commander under the Kakatiya king Ganapati-deva, whose core territory included the Telugu-speaking region in present-day Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Pratāparudra, also known as Rudradeva II, was the last monarch of the Kakatiya dynasty of India. He ruled the eastern part of Deccan, with his capital at Warangal.

Togere Venkatasubbasastry Venkatachala Sastry, commonly known as T. V. Venkatachala Shastry, is a Kannada-language writer, grammarian, critic, editor and lexicographer. He has authored in excess of 100 books, translations and has edited collections of essays, biographical sketches and felicitation volumes. Recipient of the Kannada Sahitya Akademi Award (honorary), Sastry is an authority on Kannada language grammar and its various facets ranging from the metre scale on which he has written extensively to the history of Kannada literature spanning two millennia.

Sondekoppa Srikanta Sastri was an Indian historian, Indologist, and polyglot. He authored around 12 books, over two hundred articles, several monographs and book reviews over four decades in English, Kannada, Telugu and Sanskrit. These include "Sources of Karnataka History", "Geopolitics of India & Greater India", "Bharatiya Samskruthi" and "Hoysala Vastushilpa". S. Srikanta Sastri was a polyglot well versed in fourteen languages spanning Greek, Latin, Pali, Prakrit, Sanskrit and German among others. He was Head of the Department of History & Indology at Maharaja College, University of Mysore between 1940 and 1960. He was conferred the Kannada Literary Academy award in 1970 and was subsequently honoured by Governor of Karnataka Mohanlal Sukhadia in 1973 during mythic society diamond jubilee function. A Festschrift was brought forth and presented to him during his felicitation function in 1973 titled "Srikanthika" with articles on History and Indology by distinguished scholars. His work on Indus Valley civilization and town planning at Harappa and Mohenjodaro were published in successive articles and drew considerable attention. His articles on The Aryan Invasion theory, the date of Adi Sankaracharya, Oswald Spengler's view on Indian culture, Jaina epistemology, Proto-Vedic religion of Indus Valley Civilization and evolution of the Gandabherunda insignia remain relevant today.
Gunda III, also known as Gundyana or Gundana, was a member of the Kakatiya dynasty of southern India. He served the Rashtrakuta king Krishna II, and died during Krishna's invasion of the Vengi Chalukya kingdom. He is the earliest known member of the Kakatiya family to have been in the Telugu-speaking region.
Beta II alias Tribhuvana-malla was a member of the Kakatiya dynasty of southern India. As a Kalyani Chalukya vassal, he obtained control of the Sabbi-1000 province centred around Vemulavada. He commissioned a Shaivite shrine, and also donated land for a Jaina temple.
Durga-raja was a member of the Kakatiya dynasty of southern India. He is attested by only one record - the 1098 CE Kazipet dargah inscription, which was issued during the reign of his father Beta II. According to one theory, he probably ruled for a short period and rebelled against his Kalyani Chalukya overlord, before being subjugated by his brother Prola II who remained loyal to the Chalukyas.

Ganapati-deva was the longest reigning monarch of the Kakatiya dynasty of southern India. He brought most of the Telugu-speaking region in present-day Andhra Pradesh and Telangana under the Kakatiya influence by war or diplomacy.












