
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division.

Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.

Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like Escherichia coli as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism which causes many common types of fermentation. S. cerevisiae cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding.

Schizosaccharomyces pombe, also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs.
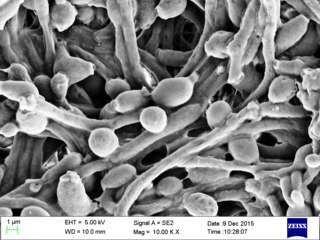
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood–brain barrier in mice.

Karyogamy is the final step in the process of fusing together two haploid eukaryotic cells, and refers specifically to the fusion of the two nuclei. Before karyogamy, each haploid cell has one complete copy of the organism's genome. In order for karyogamy to occur, the cell membrane and cytoplasm of each cell must fuse with the other in a process known as plasmogamy. Once within the joined cell membrane, the nuclei are referred to as pronuclei. Once the cell membranes, cytoplasm, and pronuclei fuse, the resulting single cell is diploid, containing two copies of the genome. This diploid cell, called a zygote or zygospore can then enter meiosis, or continue to divide by mitosis. Mammalian fertilization uses a comparable process to combine haploid sperm and egg cells (gametes) to create a diploid fertilized egg.

In cellular biology, pinocytosis, otherwise known as fluid endocytosis and bulk-phase pinocytosis, is a mode of endocytosis in which small molecules dissolved in extracellular fluid are brought into the cell through an invagination of the cell membrane, resulting in their containment within a small vesicle inside the cell. These pinocytotic vesicles then typically fuse with early endosomes to hydrolyze the particles.

Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps.

Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that employ a huge variety of reproductive strategies, ranging from fully asexual to almost exclusively sexual species. Most species can reproduce both sexually and asexually, alternating between haploid and diploid forms. This contrasts with most multicellular eukaryotes such as mammals, where the adults are usually diploid and produce haploid gametes which combine to form the next generation. In fungi, both haploid and diploid forms can reproduce – haploid individuals can undergo asexual reproduction while diploid forms can produce gametes that combine to give rise to the next generation.
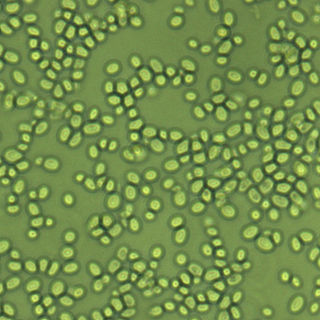
Nakaseomyces glabratus is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Nakaseomyces, previously known as Candida glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, N. glabratus strains of both mating types are commonly found. N. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes, N. glabratus is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by N. glabratus can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.
Microbial genetics is a subject area within microbiology and genetic engineering. Microbial genetics studies microorganisms for different purposes. The microorganisms that are observed are bacteria, and archaea. Some fungi and protozoa are also subjects used to study in this field. The studies of microorganisms involve studies of genotype and expression system. Genotypes are the inherited compositions of an organism. Genetic Engineering is a field of work and study within microbial genetics. The usage of recombinant DNA technology is a process of this work. The process involves creating recombinant DNA molecules through manipulating a DNA sequence. That DNA created is then in contact with a host organism. Cloning is also an example of genetic engineering.

Angelika Amon was an Austrian American molecular and cell biologist, and the Kathleen and Curtis Marble Professor in Cancer Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Amon's research centered on how chromosomes are regulated, duplicated, and partitioned in the cell cycle. Amon was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2017.

Bruce William Stillman is a biochemist and cancer researcher who has served as the Director of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) since 1994 and President since 2003. He also served as the Director of its NCI-designated Cancer Center for 25 years from 1992 to 2016. During his leadership, CSHL has been ranked as the No. 1 institution in molecular biology and genetics research by Thomson Reuters. Stillman's research focuses on how chromosomes are duplicated in human cells and in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae; the mechanisms that ensure accurate inheritance of genetic material from one generation to the next; and how missteps in this process lead to cancer. For his accomplishments, Stillman has received numerous awards, including the Alfred P. Sloan, Jr. Prize in 2004 and the 2010 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize, both of which he shared with Thomas J. Kelly of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, as well as the 2019 Canada Gairdner International Award for biomedical research, which he shared with John Diffley.
Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, and is part of the Warburg effect in tumor cells. While aerobic fermentation does not produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in high yield, it allows proliferating cells to convert nutrients such as glucose and glutamine more efficiently into biomass by avoiding unnecessary catabolic oxidation of such nutrients into carbon dioxide, preserving carbon-carbon bonds and promoting anabolism.
Beatrice B. "Bebe" Magee is an American biochemist and geneticist with expertise in molecular mycology and fungal genetics. She earned her B. A. in chemistry from Brandeis University in 1962 and her M. A. in biochemistry from the University of California, Berkeley, in 1964. She has been co-author on over 40 publications in peer-reviewed journals and an invited speaker at scientific meetings including Woods Hole and Cold Spring Harbor courses as well as at professional mycology societies.

Kaustuv Sanyal is an Indian molecular biologist, mycologist and a professor at the Molecular Biology and Genetics Unit of the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR). He is known for his molecular and genetic studies of pathogenic yeasts such as Candida and Cryptococcus). An alumnus of Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya and Madurai Kamaraj University from where he earned a BSc in agriculture and MSc in biotechnology respectively, Sanyal did his doctoral studies at Bose Institute to secure a PhD in Yeast genetics. He moved to the University of California, Santa Barbara, USA to work in the laboratory of John Carbon on the discovery of centromeres in Candida albicans. He joined JNCASR in 2005. He is a member of the Faculty of 1000 in the disciplines of Microbial Evolution and Genomics and has delivered invited speeches which include the Gordon Research Conference, EMBO conferences on comparative genomics and kinetochores. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences, in 2012. He has also been awarded with the prestigious Tata Innovation Fellowship in 2017. The National Academy of Sciences, India elected him as a fellow in 2014. He is also an elected fellow of Indian Academy of Sciences (2017), and the Indian National Science Academy (2018). In 2019, he has been elected to Fellowship in the American Academy of Microbiology (AAM), the honorific leadership group within the American Society for Microbiology.
Dafna Bar-Sagi is a cell biologist and cancer researcher at New York University School of Medicine. She is the Saul J. Farber Professor in the department of biochemistry and molecular pharmacology and the department of medicine and senior vice president and vice dean for science at NYU Langone Health. Bar-Sagi has been a member of scientific advisory boards, including the National Cancer Institute, Starr Cancer Consortium, and Pancreatic Cancer Action Network.
Alexander "Sandy" D. Johnson is an American biochemist and Professor and Vice Chair of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of California, San Francisco. He is a member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences.

David G. Drubin is an American biologist, academic, and researcher. He is a Distinguished Professor of Cell and Developmental Biology at the University of California, Berkeley where he holds the Ernette Comby Chair in Microbiology.

Jeffrey Marvin Becker is an American microbiologist who is a retired faculty member from the University of Tennessee. Becker was the Director of the Graduate Program in Cellular, Molecular, and Developmental Biology from 1979 to 1998, founding director of the UT-ORNL Graduate Program in Genome Science and Technology from 1997 to 2005 and Head of department for the Department of Microbiology from 2003 to 2016. Since 2016, he has been the Chancellor's Professor Emeritus. His primary research interests focus on the structure and function of peptides and their receptors/membrane transport in medical mycology.















