The Labour Party is a social-democratic political party in the Netherlands.

The politics of the Netherlands take place within the framework of a parliamentary representative democracy. A constitutional monarchy, the country is organised as a decentralised unitary state. The Netherlands can be described as a consociational state. Dutch politics and governance are characterised by a common striving for broad consensus on important issues, within both of the political community and society as a whole.
The Christian Union is a Christian-democratic political party in the Netherlands. The CU is a centrist party, maintaining more progressive stances on economic, immigration and environmental issues while holding more socially conservative positions on issues such as abortion and euthanasia. The party describes itself as "social Christian".

The Christian Democratic Appeal is a Christian-democratic and socially conservative political party in the Netherlands. It was originally formed in 1977 from a confederation of the Catholic People's Party, the Anti-Revolutionary Party and the Christian Historical Union; it has participated in all but three cabinets since it became a unitary party.

The second Kok cabinet, also called the second Purple cabinet was the executive branch of the Dutch government from 3 August 1998 until 22 July 2002. The cabinet was a continuation of the previous first Kok cabinet and was formed by the social-democratic Labour Party (PvdA), the conservative-liberal People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) and the social-liberal Democrats 66 after the election of 1998. The cabinet was a centrist grand coalition and had a substantial majority in the House of Representatives with Labour Leader Wim Kok serving as Prime Minister. Prominent Liberal politician Annemarie Jorritsma the Minister of Transport and Water Management in the previous cabinet served as Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Economic Affairs, former Progressive-Liberal Leader Els Borst continued as Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport and served as Deputy Prime Minister.
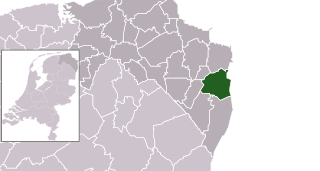
Bellingwedde was a municipality with a population of data missing in the province Groningen in the northeast of the Netherlands. Bellingwedde was established in 1968, when the municipalities of Bellingwolde and Wedde had merged. It contained the villages Bellingwolde, Blijham, Oudeschans, Veelerveen, Vriescheloo, and Wedde. After almost 50 year, Bellingwedde was disestablished in 2018, when the municipalities of Bellingwedde and Vlagtwedde had merged into Westerwolde.
GroenLinks is a green political party in the Netherlands.

The Socialist Party is a democratic socialist and social democratic political party in the Netherlands. Founded in 1971 as the Communist Party of the Netherlands/Marxist–Leninist, the party has since moderated itself from Marxism–Leninism and Maoism towards democratic socialism and social democracy. The SP has also been described as left-wing populist, far-left and Eurosceptic, and is an advocate of Dutch republicanism.

The Pacifist Socialist Party was a democratic socialist Dutch political party. The PSP played a small role in Dutch politics. It is one of the predecessors of GroenLinks.

Adrianus Petrus Wilhelmus "Ad" Melkert is a Dutch politician and diplomat of the Labour Party (PvdA) who has served as a Member of the Council of State since 20 January 2016.

The Communist Party of the Netherlands was a Dutch communist party. The party was founded in 1909 as the Social-Democratic Party (SDP) and merged with the Pacifist Socialist Party, the Political Party of Radicals and the Evangelical People's Party in 1991, forming the centre-left GreenLeft. Members opposed to the merger founded the New Communist Party of the Netherlands.
The Government of Amsterdam consists of several territorial and functional forms of local and regional government. The principal form of government is the municipality of Amsterdam, Netherlands. The municipality's territory covers the city of Amsterdam as well as a number of small towns. The city of Amsterdam is also part of several functional forms of regional government. These include the Waterschap of Amstel, Gooi en Vecht, which is responsible for water management, and the Stadsregio of Amsterdam, which has responsibilities in the areas of spatial planning and public transport.

The Party for the Animals is a political party in the Netherlands. Among its main goals are animal rights and animal welfare.

The Political Party of Radicals was a Christian-radical, progressive Christian and green political party in the Netherlands. The PPR played a relatively small role in Dutch politics and merged with other left-wing parties to form GreenLeft in 1991.

Municipal elections were held in the Netherlands on 7 March 2006. About 11.8 million people could vote in 419 municipalities. Due to local redistricting, 15 municipalities have already held elections in January 2006 and 24 municipalities will hold elections in November 2006. In some cities, such as Amsterdam, there were two elections, for the municipality and for the 'stadsdeelraden'.

Beerta is a village and former municipality with a population of 2,205 in the municipality of Oldambt in the province of Groningen in the Netherlands. In the 20th century, Beerta was a communist stronghold. In 1933, the municipal council was dismissed by the government, and was ruled by a government commissioner until 1935. Between 1982 and 1990, Beerta was the only municipality with a communist mayor.

Nieuwe Pekela is a village in the Dutch province of Groningen. It is located in the municipality of Pekela, about 7 km southeast of Veendam. The village started as a peat colony, and was named after the river Pekel A. During the 19th century, the village was active in the maritime trade, and contains a museum dedicated to the maritime history. In December 1969, the first women strike of the Netherlands occurred in Nieuwe Pekela.
This article gives an overview of socialism in the Netherlands, including communism and social democracy. It is limited to communist, socialist, social democratic, and democratic socialist parties with substantial support, mainly proved by having had a representation in parliament. The sign ⇒ means a reference to another party in that scheme.

Marten "Martin" Zijlstra was a Dutch politician. He started his political career as member of the States of Groningen, serving between 1974 and 1978. Starting in 1977 he served as Mayor of Termunten for thirteen years. He was a member of the House of Representatives of the Netherlands between 1989 and 2002 for the Labour Party and focused on interior affairs and defence policy. After his time as Representative he served two stints as acting mayor in Oldambt and Schiermonnikoog.